Protein Synthesis Quiz
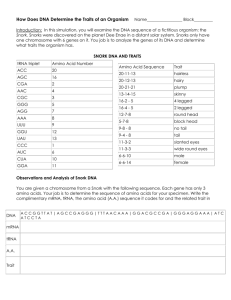
advertisement

Name: ______________________________________ Evaluation Allocation Achievement Category Marks Received Knowledge/Understanding (K/U) /17 Thinking & Inquiry (I) /17 Communication (C) /13 TOTAL: /50 Achievement Level Part A Multiple Choice (10 marks) (K/U) Answer each of the following by circling the letter of your choice. 1. a) b) c) d) e) Which of the following best describes ribonucleic acid (RNA)? composed of a linear backbone of sugar deoxyribose and phosphates with amino acids attached to the sugar residues identical to DNA except that the base uracil is present instead of thymine identical to DNA except that the sugar ribose is present instead of the sugar deoxyribose identical to DNA except that it is always single-stranded, whereas DNA is always found as a double helix containing two strands similar to DNA but it contains ribose in place of deoxyribose and uracil instead of thymine 2. Which list correctly shows the order in which the cellular machinery becomes involved in protein synthesis? a) DNA polymerase, mRNA, ribosome, tRNA b) mRNA, RNA polymerase, ribosome, tRNA c) RNA polymerase, mRNA, tRNA, ribosome d) RNA polymerase, mRNA, ribosome, tRNA 3. The anitcodons arginine, serine, and tyrosine are GCA, UCA, and AUA, respectively. If a segment of DNA codes for these amino acids in the sequence listed (arginine, serine, tyrosine), which of the following would be the sequence of nitrogen bases of the strand of the DNA molecule that coded for these amino acids? a) GCATCAATA d) GCAUCAAUA b) CGUAGUUAU e) CGTUCAAUA c) CGATCTAUA 4. A small polypeptide contains 9 amino acids. The corresponding mature mRNA would consist of how many ribonucleotides? a) 9 b) 3 c) 1 d) 27 e) None of the above 5. Base-pair substitutions involving the third base of a codon may not result in an error in the polypeptide. Whcat is partly responsible for this avoidance of error? a) Base-pair substitutions are corrected before transcription. b) Base-pair substitutions are restricted to introns, and these regions are later deleted from the mRNA. c) Most tRNAs bind tightly to a codon with only the first two bases of the anticodon d) A signal-recognition particle corrects coding errors before the mRNA reaches the ribosome. e) Transcribed errors attract spliceosomes which then stimulate splicing and correction. 6. Transcription begins at a) the start codon of the mRNA b) the start codon of the tRNA c) a sequence on the DNA that is close to the promoter d) the start codon on the DNA e) the first exon region 7. A mutation occurs to the gene coding for the repressor protein in the lac operon. This results in the protein losing its ability to attach to DNA. If this is the case, which of the following would be true? a) No transcription of the lac Z, lac Y, and lac Z genes will be possible. b) The organism would not be able to digest lactose under any conditions. c) The organism would waste a lot of energy creating enzymes in the absence of lactose. d) Transcription would proceed, yet translation would not be possible. e) The entering of lactose into the cell would allow the genes to be transcribed and translated. 8. “Charging” a tRNA involves a) having it bind with the ribosomes and mRNA b) attaching an amino acid to its 3’ end c) maximum hydrogen bonding occurring between its anticodon and the corresponding codon on the mRNA d) the reaction of its attached amino acid with another tRNA’s attached amino acid e) the tRNA entering at the A site of the ribosome 9. The enzyme responsible for opening the DNA in transcription is a) helicase b) DNA polymerase c) RNA polymerase d) Ligase 10. Mistakes in protein synthesis are more common than in DNA replication because a) mRNA codons are lousy with how they match up with tRNA anticodons b) RNA polymerase lacks exonuclease activity c) RNA polymerase isn’t as specific when it brings in complementary base pairs d) tRNAs often bind the incorrect amino acid e) Ribosomes work too quickly, and as a result mistakes are bound to occur. Part B Modified True/False (7 marks) (K/U) Identify the statements as being true (T) or false (F). If the statement is false, correct the italicized word/phrase to make the statement true in the blank provided. 1. The genetic change responsible for sickle cell anemia would be considered a nonsense mutation. _________________________ 2. The mRNA transcript of a gene is made up of the same bases, in the same proportion, as the strand of DNA complementary to the template strand, except the uracil will be replaced by the thymine. __________________________________________________ 3. Ribosomes move along the mRNA in the 3’ 5’ direction. ___________________ 4. In translation, the role of rRNA is to bring amino acids to the site of protein synthesis. _______________________________________ 5. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the cytoplasm and translation in the nucleus. _______________________________________ 6. Introns are sequences along a gene region that will go on to code for amino acids comprising a polypeptide. _______________________________________ 7. During elongation of translation, incoming tRNAs usually bind to the ribosome at the A site. ____________________________________ Part B Completion (13 marks) (C) Fill in the appropriate term/phrase to complete each of the following statements. 6. The sequence of ____________________ in DNA determines the sequence of ____________________ in the polypeptide for which the DNA codes. 7. After transcription, the first-formed mRNA is modified in eukaryotic cells. A ____________________ is added at the 5' end and a _____________________ made up of many ____________________ nucleotides is added at the 3' end. 8. The DNA of the ____________________ strand of a gene is ___________________ into mRNA, then ____________________ into protein. 9. Translation proceeds along the mRNA until the __________________ is reached. Since no ____________ corresponds to this, a sequence of events is triggered that releases the grown polypeptide and dissembles the ribosomal complex. 10. In bacteria, transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the ________________ of the cell. They are also easier to understand gene regulation since not only do they have only _____ chromosome(s), but they also do not possess ______________ within their genes. Part C Short Answer (17 marks) (T/I) Complete the following in the space provided or on a separate piece of paper. 10. The genetic code is often termed to be 'redundant’. What is the meaning of this term, and elaborate on the importance of this characteristic as it applies to protein synthesis? (3 marks) 11. The following is a segment from a mRNA isolated from a prokaryotic cell: 5’ GGC CAG AAA CAA GAA UGA 3’ a) Write out the DNA template and coding strand that would correspond to this sequence. Include direction of strands. (2 marks) b) Translate the mRNA into a polypeptide using the table of codons in your text. (2 marks) c) Using one of the codons from above, show the anticodon that could correspond to this. Identify the direction on both triplets. Is it possible for this anticodon to bind to other codons? Explain. (3 marks) 12. It is common to find intervening sequences in a gene region that do not code for any amino acids in the polypeptide produced. What are these “interrupting” sequences called and how have they become important in refuting the “one gene-one polypeptide” hypothesis. (3 marks) 13. Researchers learned about the lac operon due to observations made as a result of mutations affecting lactose metabolism. a) If a mutation occurred affecting the operator site such that a component could not bind, what effect on the transcription of structural genes would one observe in the presence and absence of lactose. Clearly state your response to both scenarios. What would be the disadvantage to the organism? (2 marks) b) A bacterium contains a mutation in the lacZ gene, such that beta-galactosidase cannot be made. It also contains a mutation that prevents it from producing lacI, the repressor protein. Comment on the impact of these mutations on the bacterium in an environment with surrounding lactose. (2 marks)