Lesson Plan - Building Structures
advertisement

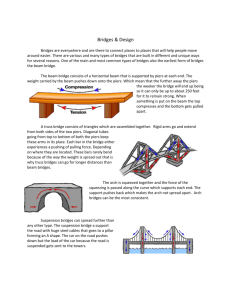
Teacher: Grade/ Subject: Grade 3 Science Unit: Building with a variety of materials Topic: covered Bridges Date: Length of Lesson: GLO: 3-1 investigate the nature of things, demonstrating purposeful action that leads to observations and inferences. 3-7 – Construct structures, using a variety of materials and designs, and compare the effectiveness of the various materials and designs for their intended purposes. Specific SLE 1 – Using a variety of materials and techniques, design, construct and test structures that are intended Learning to: support objects. Outcomes: SLE 5 – understand an intended purpose and use of structure to be built, and explain how knowing the intended purpose and use helps guide decisions regarding materials and design. Learning Students will learn about covered bridges. Objectives: Students will consider the purpose of covered bridges. Students will engage in building a covered bridge that can fit a small car. Materials Popsicle sticks, paper, tape. – covered bridge Handout - Bridges Notebook Review Cable Bridges – suspension and cable stay. Bring up first slide on notebook presentation What type of bridge is this? – trick question because they don’t know it yet! Does it look like some of our bridges combined? Which ones? They might say that it is like a beam bridge This is called a covered bridge! We are very lucky because Canada gets to brag that WE have the longest covered bridge in the world. In heartland New Brunswick. What do you notice about the inside of a covered bridge? – trusses, wood, has a roof. Lots of these bridges were built a long time ago when people started using horse carts. Their horses would have to cross a river with that big heavy load, so they couldn’t just trot through the river, they had to get it all across at once, so they started building these bridges. But why would they cover it? Have a class discussion. Real Reasons: - Helps keep the road dry and saves it from getting wrecked in bad weather. - Helped in the olden days so that the horses didn’t get freaked out by the water underneath. - People used to sneak into the bridges to kiss each other. - Keeps the bridge under better conditions so that it doesn’t have to be repaired as often. What are the parts of a covered bridge? - Beam. – nice and strong, might be like our accordion beam we saw earlier - Piers – if it is a long bridge it might need support in the middle - Reaches to both ends of the land = abutments. - Roof – pointed so snow can slide off - Walls. – usually reinforced with trusses Okay, we haven’t actually built anything for a while in this class, so today we are going to attempt to build a covered bridge! It needs to be the length of one ruler. It needs to have a beam made out of popscicle sticks. It needs to have walls on either side It needs to have a roof that holds itself up. It needs to fit THIS blue car! – instead of testing weight it needs to fit the car! What are some strategies that we might use? Strong beam, how to make the roof stand up – popscicle sticks and paper. Go over the materials – everyone should have the same just to make it fair. Go through the notebook file, explain the rules, Fill out paper as you go. On the right is an example of what students might make – I made one to show as an example so that they could compare in the end! NAME: ________________ Building a Covered Bridge Draw a picture of your bridge here: My Bridge: Has a strong beam Has a pointed OR curved roof The walls and roof stand on their own Spanned the gap of a whole ruler Fit the toy car through it. YES NO