Study Guide Key Solutions Acids Bases Honors
advertisement

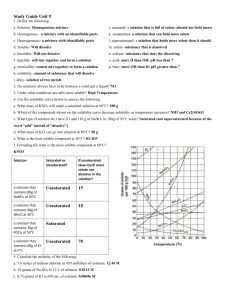
Study Guide Unit 9 1. Define the following: a. Solution- a homogeneous mixture j. saturated- maximum amount of solute is in solution b. Homogenous- uniform mixture k. unsaturated- can hold more solute c. Heterogeneous- non-uniform mixture l. supersaturated- Has more solute dissolved than it should d. Soluble- Able to be dissolved m. solute- Substance being dissolved e. Insoluble- Not able to be dissolved n. solvent- Substance doing the dissolving f. miscible- Soluble o. acid- Substance that donates an H+ ion, has more H+ than OH- g. immiscible- Insoluble p. base- Substance that donates a OH- ion, has more OH- than H+ h. solubility- Amount of solute that can be dissolved at a given temp. i. alloy- Special solution consisting of two metals 2. Do solutions always have to be between a solid and a liquid? No Way Jose!! 3. Under what conditions are salts most soluble? High Temperatures, Pressure doesn’t affect it 4. Use the solubility curve below to answer the following. a. What mass of KNO3 will make a saturated solution at 60°C? about 100 g b. Which of the compounds shown on the solubility curve decrease solubility as temperature increases? NH3 and Ce2(SO4)3 c. What type of solution do I have if I add 110 g of NaNO 3 in 100g of 20°C water? Saturated! I didn’t say 110 g DISSOLVED d. What mass of KCl can go into solution at 80°C? 50 g of KCl e. What is the least soluble compound at 20°C? KClO3 f. Excluding KI, what is the most soluble compound at 80°C? KNO3 Solution Saturated or Unsaturated? If unsaturated: How much more solute can dissolve in the solution? a solution that contains 80g of NaNO3 at 30°C Unsaturated 15 g a solution that contains 40g of NH4Cl at 50°C Unsaturated 10 g a solution that contains 20g of KClO3 at 50°C Saturated a solution that contains 60g of KI at 0°C Unsaturated 70 g 5. Calculate the molarity of the following. a. 5.6 moles of sodium chloride in 450 milliliters of solution. 12.44M b. 19 grams of Na2SO4 in 12 L of solution. 0.011M c. 0.75 grams of KI in 650 mL of solution. 0.0070M Study Guide Unit 9 6. Calculate the grams of solute needed to make the following solutions. a. 5 liters of a 3 M solution of NaCl 876.75 g NaCl b. 100 mL of a 5 M solution of NaOH 20.00 g NaOH c. 300 mL of a 2M solution of C6H12O6 108 g C6H12O6 7. Complete the following dilution calculations a. How much 0.5 M HCl solution can be made by diluting 350 mL of 10 M HCl? 7000 mL or 7 L b. How much water would I need to add to 350 mL of a 4.4 M KCl solution to make a 1.0 M solution? 1190 mL or 1.19 L c. If I have 340 mL of a 0.5 M NaBr solution, what will the concentration be if I add 560 mL of water to it? 0.189 M 8. What type of compound will conduct electricity when dissolved in water? Ionics ONLY!! Also called electrolytes. 9. If I dissolve 40 g of NaCl in water how will it affect the heating curve below? Draw the changes. See notes! It’s in there! 10. Which of the following will conduct electricity when dissolved in water: LiF, Na2SO4, CH4, CH3OH, SO3, MgI2, SrCl2 11. Why is salt added to the roads during winter? To keep them from freezing and causing you to careen into an immovable object. 12. What does the formula of an acid ALWAYS start with? H!!!!! Very important! Can’t stress this enough! 13. What does the formula of a base end in? OH!!!!! 14. What is the pH range of an acid and a base? Acid – 0-6.99 Base-- 7.01-14 15. What are some properties of acids and bases? Acids – Sour taste, react with metals to make Hydrogen gas, pH less than 7. Bases – Bitter taste, Feel slippery, pH greater than 14, React with acids to make salt and water 16. Name the following acids: a. HBr Hydrobromic acid d. H2CO3 Carbonic acid b. HClO3 Chloric acid e. HI hydroiodic acid c. HNO2 Nitrous acid f. HNO3 Nitric acid 17. Write the formula for the following acids: a. Sulfous Acid H2SO3 d. hydrosulfic acid H2S b. Hydrochloric acid HCl e. Chloroic acid HClO3 c. acetic acid HC2H3O2 f. Perchloric acid HClO4 18. What is the pH of a 0.045 M solution of HCl? 1.35 19. What is the pH of a 0.023 M solution of HNO3? 1.64 20. What is the concentration of [H+] in a solution of HClO 3 with a pH of 5.5? 3.16 x 10^ -6 M 21. What is the concentration of [H+] in a solution of HBr with a pH of 3.5? 3.16 x 10^ -4 M 22. What is the pOH of a 0.013 M solution of NaOH? 1.89 23. What is the pOH of a 0.65 M solution of LiOH? 0.19 24. What is the concentration of [OH-] in a solution of Ca(OH)2 with a pH of 8.4? 2.51 x 10^ -6 M 25. What is the concentration of [OH-] in a solution of Mg(OH)2 with a pH of 7.1? 1.26 x 10^ -7 M 26. What is the pH of a 0.067 M solution of KOH? 12.83 27. What is the pH of a 0.089 M solution of LiOH? 12.95 28. What is the pOH of a 0.23 M solution of HI? 13.36 29. Determine the hydrogen ion concentration of 0.780 M aqueous solution of RbOH. 1.28 x 10^ -14 M 30. 160 ml of 2.2 M NaOH are required to titrate 140 ml of HF. What is the M of the HF? 2.51 M HF 31. What volume of 0.40 M NaOH would be required to titrate 17.0 ml of 0.15 M HCl? 6.34 mL 32. 140 ml of 3.1M H2SO4 are required to titrate 50 ml of NaOH to the equivalence point. What is the M of the NaOH? 17.36 M Study Guide Unit 9 33. 85 ml of 2.5M H2SO4 are required to titrate 20 ml of NaOH to the equivalence point. What is the M of the NaOH? 21.25 M







![pH = - log [H + ]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005622524_1-002df1ea50d2a849b15deb604928664e-300x300.png)


