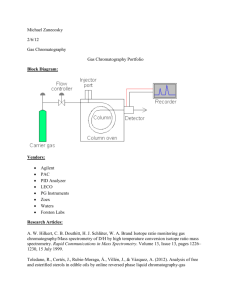
Chromatography Lab
advertisement

Kidnapped! Background: When I arrived at school today, Mr. Koeval was distraught. He told me that his Barbie head had been kidnapped! The kidnapper left a ransom note demanding money for the return of the Barbie head. The SRO has five suspects, and he has asked the chemistry department to help him figure out who kidnapped Mr. Koeval’s Barbie head. I have the pens that were found in each of the suspects’ backpacks, and we need to figure out who wrote the ransom note. General Information: Chromatography is a broad range of physical methods used to separate and to analyze complex mixtures. Chromatography is one of the most useful laboratory methods in chemistry. It is used in thousands of different ways in the chemical and biochemical world. One of the most important is the purification of compounds of all types. Your Task: You will be using paper chromatography to separate the dyes in marker ink using water and ethanol. You will compare your chromatographs to the chromatographs from the ransom note ink to determine who kidnapped Mr. Koeval’s Barbie head. In the Lab: 1. Prepare a data table to record the marker numbers, type of marker, and what components of the dye you observe separating 2. Obtain a piece of chromatography paper. Draw a line close about 1cm from the bottom of the paper in pencil. Make a small dot with each of the five markers on this line. They should be evenly spaced apart from each other to keep them separated. This should look like the picture below. Be sure to record where you put each color on the paper. 3. Pour a small amount of water into the beaker. Make sure the bottom of the beaker is completely covered. The level of the liquid must be lower in the beaker than the dots from the markers on the chromatography paper once it is inserted into the beaker. 4. Carefully place your paper into the liquid so that only the area of paper below the dots is in contact with the water. Do not allow the paper to slip down into the liquid. If the pencil line ever slides into the liquid, you must redo the chromatograph. 5. When the level of the water has advanced through most of the paper, Remove the paper from the developing solution. Hold the paper and observe the colors carefully. 6. Repeat the experiment using ethanol as the developing solvent. Since ethanol evaporates relatively easily, some changes will need to be made. In step 3, after pouring in the ethanol, cover the beaker with a watch glass and swirl the beaker around. Then to place the paper in the beaker, lift the watch glass, insert the paper as before, and then place the watch glass back on the top of the beaker. 7. Keep the chromatographs if you like. Since you are using waste ethanol, if your ethanol is not contaminated with marker, pour the ethanol back in the container. Otherwise pour it down the drain with water. 8. Compare your chromatograph to the ones Mrs. Atkins made using the ink from the ransom note. Record the specific evidence that tells you that which pen was used and determine who kidnapped the Barbie head. Lab Report: Please include the following items: A) Purpose B) Analysis Questions 1) Who was the kidnapper? Give specific evidence from the lab to demonstrate that you chose the correct suspect 2) Why did you use pencil and not pen when marking on the chromatography paper? 3) Why must the marker spots on the paper remain above the level of the liquid in the beaker? 4) Why are Sharpies called permanent markers? If you wanted to clean some Sharpie out of a favorite shirt, what could you use and why? 5) Were there any markers where one dye traveled farther than another dye in the same marker in water? If so, explain what happened to the dye from the marker as it traveled up the paper. What does this tell you about the differences between the interactions of the two dyes with the water? 6) Using at least two specific examples from the markers we used in the lab, explain how colors can be created using a mixture of dyes. 7) What real world applications would this technique of chromatography have? You must name at least two applications and you cannot simply use finding out what color dyes are in something, separating dyes, or removing spots from something. C) Conclusions D) Original Data Sheet