condensed version - e-Bug
advertisement
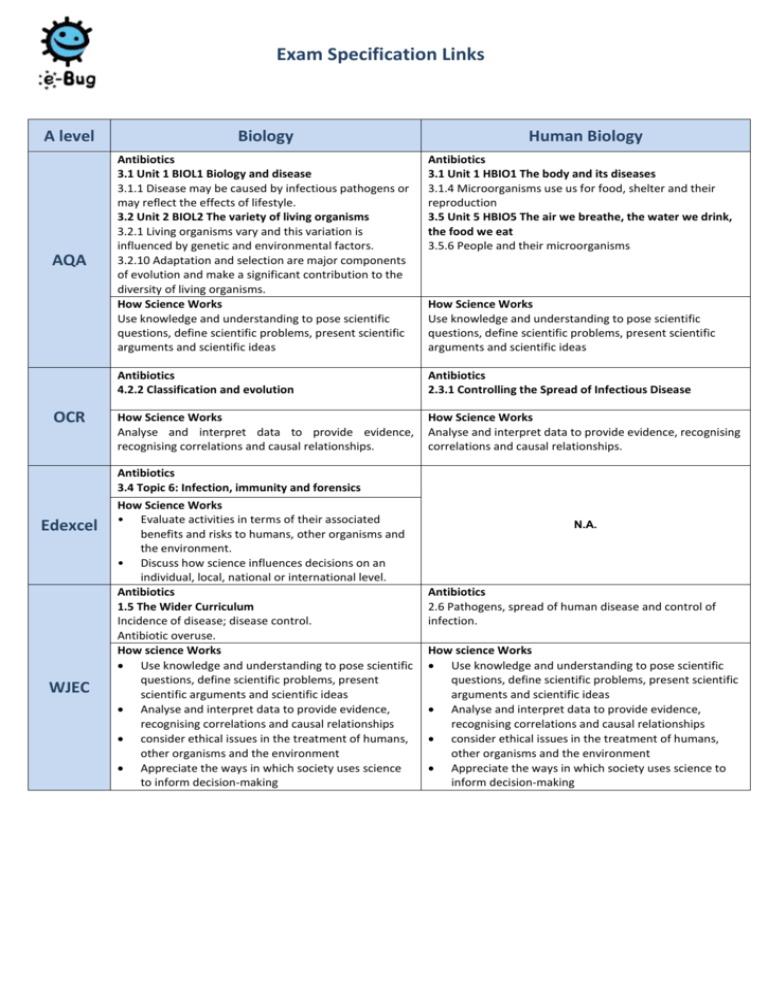
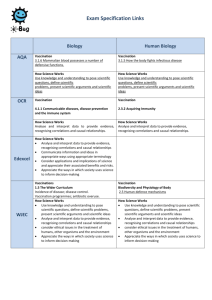
Exam Specification Links A level AQA OCR Biology Human Biology Antibiotics 3.1 Unit 1 BIOL1 Biology and disease 3.1.1 Disease may be caused by infectious pathogens or may reflect the effects of lifestyle. 3.2 Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. 3.2.10 Adaptation and selection are major components of evolution and make a significant contribution to the diversity of living organisms. How Science Works Use knowledge and understanding to pose scientific questions, define scientific problems, present scientific arguments and scientific ideas Antibiotics 3.1 Unit 1 HBIO1 The body and its diseases 3.1.4 Microorganisms use us for food, shelter and their reproduction 3.5 Unit 5 HBIO5 The air we breathe, the water we drink, the food we eat 3.5.6 People and their microorganisms Antibiotics 4.2.2 Classification and evolution Antibiotics 2.3.1 Controlling the Spread of Infectious Disease How Science Works Analyse and interpret data to provide evidence, recognising correlations and causal relationships. How Science Works Analyse and interpret data to provide evidence, recognising correlations and causal relationships. How Science Works Use knowledge and understanding to pose scientific questions, define scientific problems, present scientific arguments and scientific ideas Antibiotics 3.4 Topic 6: Infection, immunity and forensics Edexcel WJEC How Science Works • Evaluate activities in terms of their associated benefits and risks to humans, other organisms and the environment. • Discuss how science influences decisions on an individual, local, national or international level. Antibiotics 1.5 The Wider Curriculum Incidence of disease; disease control. Antibiotic overuse. How science Works Use knowledge and understanding to pose scientific questions, define scientific problems, present scientific arguments and scientific ideas Analyse and interpret data to provide evidence, recognising correlations and causal relationships consider ethical issues in the treatment of humans, other organisms and the environment Appreciate the ways in which society uses science to inform decision-making N.A. Antibiotics 2.6 Pathogens, spread of human disease and control of infection. How science Works Use knowledge and understanding to pose scientific questions, define scientific problems, present scientific arguments and scientific ideas Analyse and interpret data to provide evidence, recognising correlations and causal relationships consider ethical issues in the treatment of humans, other organisms and the environment Appreciate the ways in which society uses science to inform decision-making Other relevant Curriculum links: The e-Bug Young Adult resources also cover a range of other A-levels and applied courses: AQA Science in Society A-level - 3.1.2 Infectious Diseases Now AQA Health and Social Care A-level - 3.10.4 Strategies to Prevent Disease: Immunisation BTEC, for example: Edexcel BTEC Level 4 HNC Diploma in Applied Biology -The Immune Response System -Infectious Diseases -Medical Microbiology Edexcel BTEC Level 3 90-credit Diploma in Health and Social Care -Defence against Disease -Public Health -Infection Prevention and Control -Introduction to Microbiology for Health and Social Care The resources may also be applicable to other examining body specifications, health educators and in a pastoral care setting i.e. Travel Vaccine Information and Antibiotic Advice Skills gained: Research Communication – e.g. within the debate cards and peer education lessons Analytical – exam style questions on student worksheets Written communication Team Work