Water Systems Unit Outline
advertisement
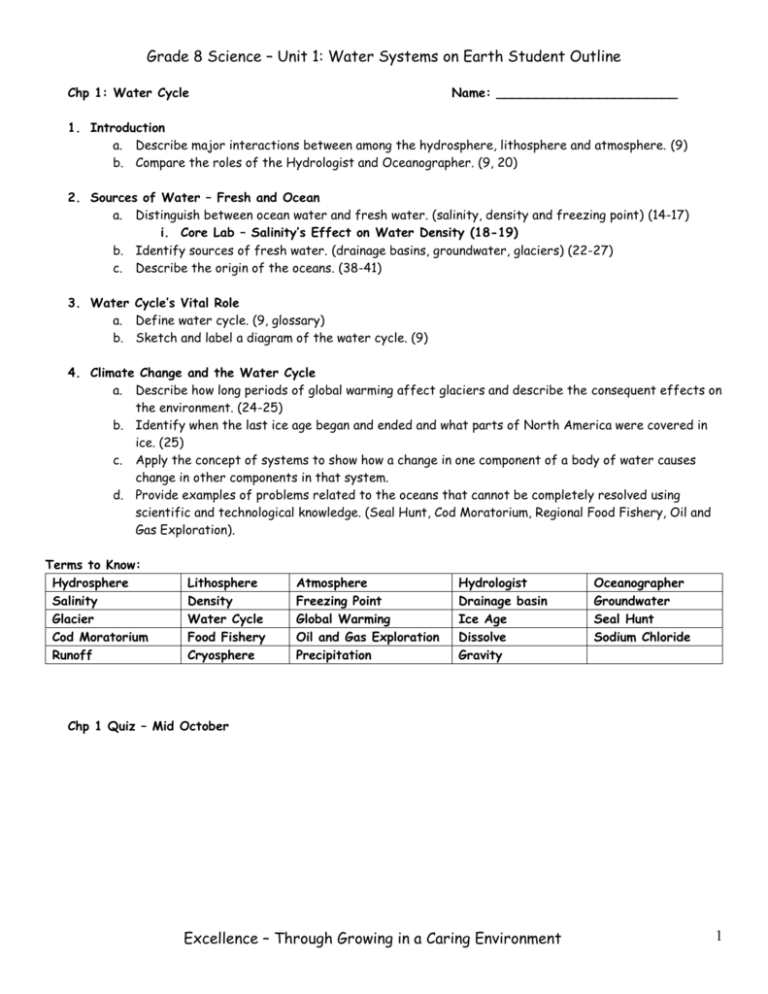
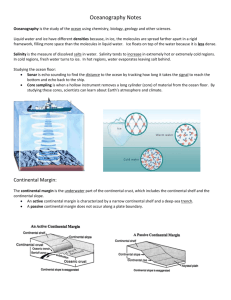
Grade 8 Science – Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Student Outline Chp 1: Water Cycle Name: _______________________ 1. Introduction a. Describe major interactions between among the hydrosphere, lithosphere and atmosphere. (9) b. Compare the roles of the Hydrologist and Oceanographer. (9, 20) 2. Sources of Water – Fresh and Ocean a. Distinguish between ocean water and fresh water. (salinity, density and freezing point) (14-17) i. Core Lab – Salinity’s Effect on Water Density (18-19) b. Identify sources of fresh water. (drainage basins, groundwater, glaciers) (22-27) c. Describe the origin of the oceans. (38-41) 3. Water Cycle’s Vital Role a. Define water cycle. (9, glossary) b. Sketch and label a diagram of the water cycle. (9) 4. Climate Change and the Water Cycle a. Describe how long periods of global warming affect glaciers and describe the consequent effects on the environment. (24-25) b. Identify when the last ice age began and ended and what parts of North America were covered in ice. (25) c. Apply the concept of systems to show how a change in one component of a body of water causes change in other components in that system. d. Provide examples of problems related to the oceans that cannot be completely resolved using scientific and technological knowledge. (Seal Hunt, Cod Moratorium, Regional Food Fishery, Oil and Gas Exploration). Terms to Know: Hydrosphere Salinity Glacier Cod Moratorium Runoff Lithosphere Density Water Cycle Food Fishery Cryosphere Atmosphere Freezing Point Global Warming Oil and Gas Exploration Precipitation Hydrologist Drainage basin Ice Age Dissolve Gravity Oceanographer Groundwater Seal Hunt Sodium Chloride Chp 1 Quiz – Mid October Excellence – Through Growing in a Caring Environment 1 Grade 8 Science – Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Student Outline Chp 2: Oceans Name: _______________________ 5. Ocean Basins a. Describe processes that led to the development of ocean basins and continental drainage systems. (Volcanic action, plate tectonics, erosion and glaciation) (38-41) b. Illustrate a typical continental margin from coastal shoreline to mid-ocean ridge. (Continental shelf, continental slope, abyssal plain and mid-ocean ridge) (41-44) c. Investigate technologies that assist scientists in research of ocean basins. (SONAR, wire line depth probes, satellites, core sampling, underwater photos/video, deep sea submersibles and diving) (4447) i. Core STSE – Undersea Adventure 6. Ocean Currents a. Define ocean current. Ex: Labrador Current and Gulf Stream. (52) b. Identify and explain surface currents. (wind, earth’s rotation – coriolis effect, continental shape) (54-56) c. Identify and explain deep water currents. (Temperature and salinity) (56-57) 7. Ocean a. b. c. Waves Define Wave. (Glossary) Identify features of waves (wavelength, wave height, crest, and trough). (64-65) Distinguish between ocean waves, swells, breakers and tsunamis. (64-66) 8. Ocean Tides a. Define tide, explain and illustrate how the tides are generated by the gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon. (69-71) b. Define tidal range and distinguish between spring tides and neap tides. (69) 9. Shorelines a. Describe the processes that form shorelines. (shape, slope, type of rock, wave energy) (66-69) b. Define headlands and bays with how they are affected by waves and tides. (67-69) c. Describe the results of erosion and deposition from wave action and tides. (Beaches, shoal, sand bar, sea caves, sea arches and sea stacks.) (66-69) d. Provide examples of various technologies designed to contain damage due to waves and tides. (breakwaters, jetties/wharves and vegetation) (NIT) Terms to Know: Ocean Basin Drainage System Volcanic Action Plate Tectonics Erosion Glaciation Continental Margin Continental Shelf Continental Slope Abyssal Plain Mid Ocean Ridge SONAR Depth Probe Satellite Imaging Core Sampling Submersible Ocean Current Labrador Current Gulf Stream Surface Currents Coriolis Effect Deep Currents Wave Wavelength Wave Height Crest Trough Swell Breaker Tsunami Tide Tidal Range Spring Tide Neap Tide Shoreline Wave Energy Headlands Bays Erosion Deposition Beach Shoal Sand Bar Sea Cave Sea Arch Sea Stack Breakwater Jetty Wharf Chp 2 Quiz – Late October Excellence – Through Growing in a Caring Environment 2 Grade 8 Science – Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Student Outline Chp 3: Climate and Species Distribution Name: _______________________ 10. Oceans, Weather and Climate a. Distinguish between weather and climate. (82) b. Define heat capacity. Note difference between this and Specific Heat Capacity. (83, glossary) c. Describe how the heat capacity of water affects climate. (83) d. Describe how convection affects weather. (85) e. Describe how oceans moderate climate. (frequency of fog, temperature fluctuations) (82) f. Distinguish between the effects of El Nino and La Nina as global climatic influences. (85-86) 11. Species Distributions (6P) a. Describe species found in freshwater environments. (Lakes and ponds, wetlands, rivers and streams, estuaries). (90-93) b. Describe species found in saltwater environments. (Pelagic zone – top 180m, benthic zone > 180m). (9394) c. Identify the effects of abiotic factors on plant and animal distributions in freshwater ecosystems. (temperature, dissolved oxygen, phosphates, pH, turbidity, pollution) i. Core Lab “Water Health Test Lab A” (108-110) *Field Trip to Fluvarium? d. Identify the effects of abiotic factors on plant and animal distributions in marine ecosystems. (upwelling, salinity, ocean currents) (NIT) e. Describe positive/negative effects of marine technologies on ocean species. (Confederation Bridge, Oil Exploration, Fishing Technologies such as drag nets, fish finders, factory freezer trawlers, aquaculture) (104-107) Terms to Know: Weather El Nino Pelagic Zone pH Ocean Currents Fish Finder Phytoplankton Invasive Species Climate La Nina Benthic Zone Turbidity Marine Technology Factory Freezer Trawler Zooplankton Overfishing Heat Capacity Species Abiotic Factors Pollution Confederation Bridge Aquaculture Convection Fog Wetland Estuary Dissolved Oxygen Phosphate Upwelling Salinity Oil Exploration Drag Net Bio-Indicator Species Bioluminescence Plankton Acid precipitation Habitat Biotic Index Urban Development Unit Test – Mid November Excellence – Through Growing in a Caring Environment 3