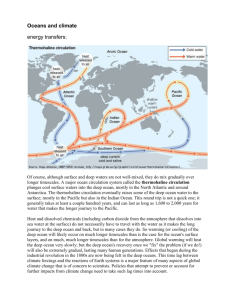
Open Ocean Biome
advertisement
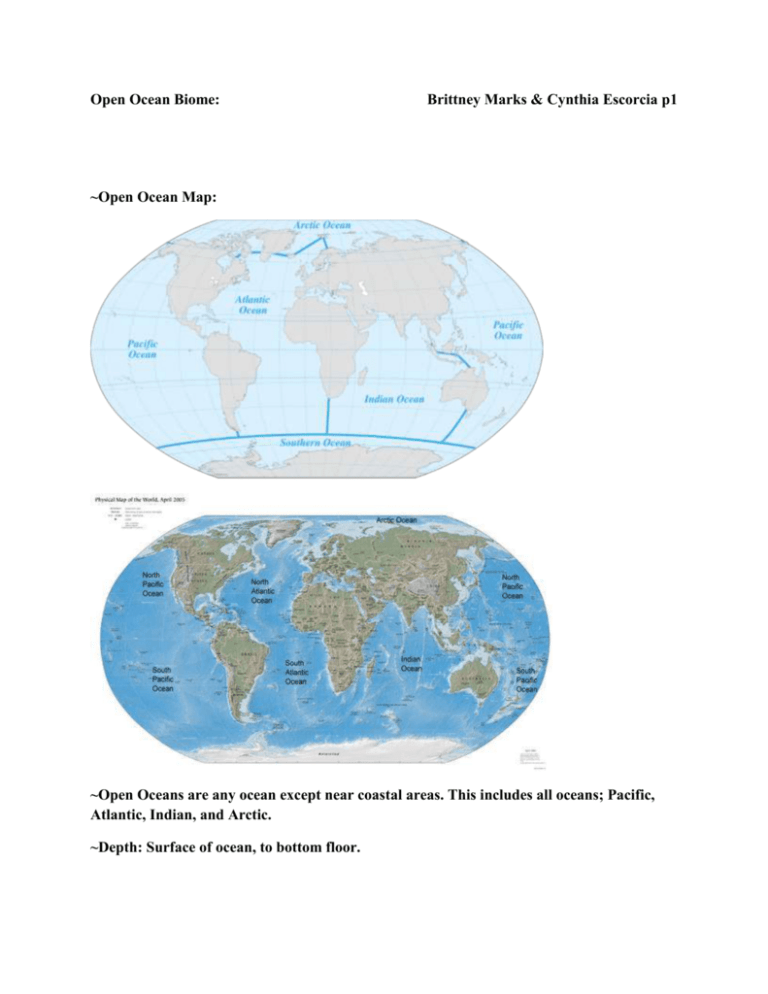
Open Ocean Biome: Brittney Marks & Cynthia Escorcia p1 ~Open Ocean Map: ~Open Oceans are any ocean except near coastal areas. This includes all oceans; Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. ~Depth: Surface of ocean, to bottom floor. ~Salinity: The average ocean salinity is around 35 ppt. The salinity can also vary between 32 and 37 ppt. This is because of ice, rainfall, and runoff. ~Temperature: The average temperature of open oceans usually ranges from 30 through 60 degrees Fahrenheit depending on the location of the ocean. For example, if the water is close to the equator, it will receive more sunlight increasing the temperature. ~Depth: There are three parts: the intertidal zone, which is near the surface, the neritic zone, which is on the continental shelf,and the deep ocean zone. The deep-ocean zone's depth varies from 200-9,000 meters deep. ~Base of food web: seaweed, turtle grass, phytoplankton, and algae. ~Animals found: crabs, sharks, rays, dolphins, whales, squid, seals, salmon, Bluefin tuna. ~Ocean Zones: -Intertidal: the area you see in front of you when you sit on the beach, the shoreline. Interrupted by the constant to and from of the ocean waves. Tidal pull supports sea life – small fish, crabs, and hardy creatures that can sustain the constant pounding of the waves. -Pelagic zone- waters further from land, generally cold. Plants in this zone are surface seaweeds, species like whales and dolphins feed on the plankton in this zone. -Benthic zone- area below pelagic zone. The bottom of the zone consists of sand, slit, and dead organisms. Temperature decreases since no light can reach this zone. Organisms include bacteria, fungi, sponges, sea anemones, worms, sea stars, and fish. Abyssal zone- The deep ocean, water in this region is very cold, highly pressured, high in oxygen but low in nutrients. Species include invertebrates and fish.