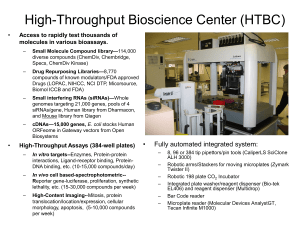
a HORIZONS-AMI biomarker substudy.
advertisement

Online Resource 1 D-dimer levels predict ischemic and hemorrhagic outcomes after acute myocardial infarction: a HORIZONS-AMI biomarker substudy. Wouter J Kikkert, MD; Bimmer E Claessen, MD, PhD; Gregg W Stone, MD; Roxana Mehran, MD; Bernhard Witzenbichler, MD; Bruce R Brodie, MD; Jochen Wöhrle, MD; Adam Witkowski, MD; Giulio Guagliumi, MD; Krzysztof Zmudka, MD; José PS Henriques, MD, PhD; Jan GP Tijssen, PhD; Elias A Sanidas, MD; Vasiliki Chantziara, MD; Ke Xu, PhD; George D Dangas, MD, PhD. Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, NY (BEC, GWS, RM, EAS, VC, DH, SL, KX, GD); Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY (GWS, EAS, VC, DH); Mount Sinai Medical Center, New York, NY (RM, GDD); Academic Medical Center – University of Amsterdam, the Netherlands (WJK, BEC, JPSH, JGPT); Ospedali Reuniti di Bergamo, Italy (GG); Charité Universitatsmedizin Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany (BW); University of Ulm , Germany (JW); LeBauer CV Research Foundation, Greensboro, NC (BB); National Institute of Cardiology, Warsaw, Poland (AW); Szpital Jana Pawla II, Krakow, Poland (KZ) Correspondence to: george.dangas@mssm.edu List of the biomarkers that were measured in the HORIZONS-AMI (Harmonizing Outcomes With Revascularization and Stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction) biomarker substudy Cytokines Interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), interleukin-18 (IL-18), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-1ra (IL-1ra), interleukin-12 (IL-12), cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), chemokine ligand 23 (CCL-23). Matrix metalloproteinases Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), pregnancy-associated protein A (PAPP-A) Growth factors Placental growth factor (PLGF) Vasodilators Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), b-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), pro-atrial natriuretic peptide (proANP), adinopponectin, angiotensinogen Adhesion molecules Endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule (ESAM), inter-cellular adhesion molecule (ICAM), vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM). Markers of myocardial injury Heart-type fatty acid binding protein (hFABP), myeloperoxidase (MPO) Thrombotic biomarkers D-dimer, von Willebrand factor (vWF) Renal function markers Cystatin-C Acute phase proteins C-reactive protein (CRP) Detailed description of biomarker assays Luminex multiplexed bead-based immunoassays were performed on human plasma (or serum) samples in microtiter plates. The primary antibody for each assay was conjugated to modified paramagnetic Luminex beads obtained from Radix Biosolutions. Either the secondary antibodies (sandwich assays) or the antigens (competitive assays) were biotinylated. Fluorescent signals were generated using Streptavidin-R-Phycoerythrin (SA-RPE: Prozyme PJ31S). All assays were heterogeneous and required multiple washes; washes were performed in 96-well plates placed on a 96-well magnetic ring stand (Ambion) in order to keep the paramagnetic beads from being removed. All liquid handling steps were performed with a Beckman Biomek FX. An 8-point calibration curve was made gravimetrically by spiking each antigen into the calibration matrix. For sandwich assays, this matrix was plasma (or serum) from healthy donors; one of the eight points included free antibody to neutralize any endogenous antigen that was present. For competitive assays, this matrix was CD8 buffer (10 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mmol/L NaCl, 1 mmol/L MgCl2, 0.1 mmol/L ZnCl2, 10 mL/L polyvinyl alcohol (MW 9000–10 000), 10 g/L bovine serum albumin, and 1 g/L NaN3). Samples were stored in 384-well microtiter plates keep at -70 C. A source plate was made by thawing the sample plate at 37 C, and then adding replicates of the 8-point calibration curve. The assays were performed at room temperature. The bead-based primary antibody solution was added to a 384-well assay plate (10ul/well) and then samples were added from the source plate (10ul/well), mixed, and incubated one hour. Competitive assays were run in different assay plates than the sandwich assays, and the biotinylated antigen was added to the samples before transfer to the assay plate. Each 384-well plate was split into four 96-well plates for subsequent processing. The plates were washed as described above; the sandwich assays were incubated with biotinylated secondary antibodies and washed again. The assay mixtures were labeled with SA-RPE, washed, and read using a Luminex LX200 reader; the median signal for each assay for was used for data reduction of each sample. The antigen concentrations were calculated using a standard curve determined by fitting a five parameter logistic function to the signals obtained for the 8-point calibration curves. Microtiter immunoassays utilizing human plasma samples were performed in 384-well microtiter plates using Perkin-Elmer Minitrak for all liquid handling steps. Assays were variations of antibody sandwich assays or competitive assays using biotinylated antigen. All assays were heterogeneous and required multiple plate washes. Plates were washed three times with Borate Buffered Saline containing 0.02% Tween 20 (BBS-Tween). Samples were removed from –70o C, thawed at 37o C then processed at room temperature. Test samples (10 µL/well) were added to the 384-well plate. In addition to test samples, each plate contains a calibration curve consisting of multiple analyte concentrations and control samples. Calibration curves were prepared gravimetrically in plasma from healthy donors. For sandwich assays, one concentration in each set of calibrators included neutralizing antibody for correction of endogenous antigen present in the plasma pool. In situations where the sample must be diluted to fit within the calibration curve, the calibrators are prepared in a CD8 assay buffer (10 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mmol/L NaCl, 1 mmol/L MgCl2, 0.1 mmol/L ZnCl2, 10 mL/L polyvinyl alcohol (MW 9000–10 000), 10 g/L bovine serum albumin, and 1 g/L NaN3), which is also used for sample dilution. The plates were read by a fluorometer (Molecular Devices Spectramax 2). Calibration curves were eight points tested at multiple locations on the assay plate. The calibration curve was calculated using a five-parameter logistic fit and sample concentration was determined.