Meiosis - mutations 4-1
advertisement

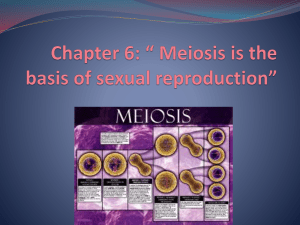
I. Meiosis A. Cell division that results in gametes w/ half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell B. 2 phase process: after interphase, cell enters Meiosis I (PMAT and cytokinesis) and then goes through Meiosis II (PMAT and cytokinesis 1 cell (2n) ---meiosis I---> 2 cells (2n) ---meiosis II---> 4 cells (n)/gametes C. In sexual reproduction, total chromosome number in the fertilized egg cell (zygote) is doubled (2n, diploid); the chromosome number is cut in half in meiosis (n, haploid); these two processes keep the number of chromosomes balanced throughout continuing generations D. II. Chromosomes A. DNA in long strands, combined with proteins and enzymes, make up chromatin ("colored string") B. In interphase and leading into prophase, chromatin shortens and condenses to form chromosomes ("colored bodies") C. One set of chromosomes is received from each parent 1. these chromosomes pair up according to size and location of the centromere to form homologous pairs of chromosomes 2. homologous chromosomes contain matching bands of genes in the same locations 3. the last pair of chromosomes determine gender: XX is female, XY is male 4. too many or too few chromosomes results from nondisjunction III. Nondisjunction and karyotypes A. Nondisjunction - failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly 1. In meiosis 1, one chromosome from each homologous chromosome pair moves to each pole of the cell 2. In nondisjunction, both chromosomes of a homologous pair move to the same pole 3. 2 kinds of gametes result: one gamete has an extra chromosome, one gamete is missing a chromosome a. after fertilization, the zygote will have an extra chromosome if the gamete with the extra chromosome fuses with a normal gamete; called "trisomy". b. organisms with an extra chromosome often survive; organisms lacking one or more chromosomes usually do not; called "monosomy". B. C. Karyotypes 1. metaphase chromosomes, usually from a fetus, are photographed, enlarged, and arranged in pairs according to length and location of the centromere 2. results in a chart of human chromosome pairs used to identify an abnormal chromosome number in cells a. can identify trisomies: 21(Down's syndrome), 18 (Edward's syn.), 13 (Patau's syn.) b. monosomies: sex chromosomes (XO - Turner's syn.) and autosome #5 (Cri du chat) **autosome - the chromosomes that do not determine gender Mutations 1. change in the sequence in DNA 2. from error in replication, transcription, cell division, or by external agents (i.e. uv rays) 3. Can take place in: a. reproductive cells - (egg or sperm) - passed on to offspring b. body cells - not passed on to offspring c. genes controlling cell division - results in uncontrolled cell division (cancer) 4. Types of mutations DNA sequence: TAC AAA TCG ACC ACT mRNA codons: AUG UUU AGC UGG UGA amino acids: methionine phenylalanine serine tryptophan STOP a. point mutation - change in a single nucleotide in DNA or base pair in mRNA mRNA codons: AUG UUa AGC UGG UGA amino acids: methionine LEUCINE serine tryptophan stop b. frame shift mutation - a single DNA nucleotide is lost or added; mRNA codons are shifted by one base and every codon after that is different DNA sequence: TAC AAT CGA CCA CT... mRNA codons: AUG UUA amino acids: methionine leucine GCU GGU GA... alanine glycine c. deletion - part of a chromosome is left out ABCDE - FGH BCDE - FGH d. insertion - part of a chromatid breaks off and is added to the SISTER chromatid ABCDE - FGH / ABCDE - FGH ABABCDE - FGH / CDE - FGH e. inversion - part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards ABCDE - FGH ABCDE - HGF f. translocation - part of a chromatid breaks off and attaches to a NONSISTER chromatid ABCDE - FGH RSTUV - XYZ ---> RSTABCDE - FGH UV - XYZ