Definitions
advertisement

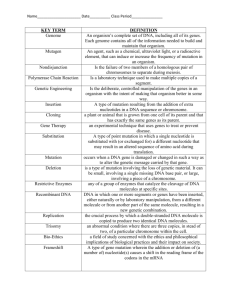
2.5. Genetics Definitions Term Species Heredity Gene Expression Gene DNA RNA DNA profiling Coding dna Non-coding dna Genetic screening Transcription Translation Pyrimidine Bases Purine Bases mRNA tRNA rRNA Gamete Fertilisation Allele Locus Homozygous Heterozygous Genotype Phenotype Progeny Dominance . Definition Organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. The passing on of traits from parent to offspring by means of genes The process of using the information on the gene to make a protein A unit of DNA which codes for the production of a specific protein Deoxyribonucleic Acid – a double stranded nucleic acid Ribonucleic Acid – a single stranded nucleic acid Examining DNA / for a pattern or band / to compare …………………………………………………………. A method of making a unique pattern of bands from the DNA of a person, [which can then be used to distinguish that persons DNA from other DNA] That part of the chromosome which carries the infomation to make a protein That part of the chromosome which does not carry the infomation to make a protein Testing (people) for the presence of a (specific) gene or To establish presence or absence of gene(s) The process of producing mRNA using DNA as a template. The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template Adenine and Guanine are the two pyrimidine bases. They are single ring molecules Cytosine and Thymine are the two purine bases. They are double ring molecules Messenger RNA takes the complementary DNA strand out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA - As the mRNA moves through, tRNA molecules carrying the appropriate amino acid bind to the RNA codon to which they are matched, and the sequence of amino acids is put together. Ribosomal RNA – found in the ribosome and allow protein synthesis to occur A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Is the position of a gene on a chromosome Has identical alleles [for a trait] Has different alleles [for a trait] The genetic make-up of an individual Physical appearance of an organism The offspring that are produced One allele masks the expression of the other. Recessive Allele whose expression is masked by dominant allele Incomplete Dominance Autosomes Variation Neither allele masks the expression of the other. Mutation Mutagen Gene mutation Chromosome mutation Genetic engineering Restriction Enzymes DNA Ligase Evolution Change in the genetic make up An agent that causes a mutation Changes that occur in a single gene Large changes that occur in the structure or number of one or more chromosomes Natural Selection Palaeontology Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment Linkage Sex Linkage Non nuclear inheritance . Non sex chromosomes Difference between members of species or population Manipulation or alteration of genes Enzymes that cut DNA An enzyme that sticks DNA together (Inheritable) change within a population (or species) / in response to change in the environment / by natural selection/over time Is the process by which those organisms with genetically controlled characteristics that allow them to be well adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation The study of fossils Inherited factors are controlled by pairs of factors. These factors separate from each other at gamete formation with only one member of the pair being found on the gamete When gametes are formed either of a pair of factors is equally likely to combine with another pair of factors Genes that are located on the same chromosome The characteristic is controlled by a gene on an X chromosome Extra nuclear genes that are present in mitochondria and chloroplasts and can reproduce by themselves and pass on their genes to resulting organelles. 2.5. Genetics Define the following terms in the space provided: Term Species Heredity Gene Expression Gene DNA RNA DNA profiling Coding dna Non-coding dna Genetic screening Transcription Translation Pyrimidine Bases Purine Bases mRNA tRNA rRNA Gamete Fertilisation Allele . Definition Locus Homozygous Heterozygous Genotype Phenotype Progeny Dominance Recessive Incomplete Dominance Autosomes Variation Mutation Mutagen Gene mutation Chromosome mutation Genetic engineering Restriction Enzymes DNA Ligase Evolution Natural Selection Palaeontology Law of Segregation Law of Independent . Assortment Linkage Sex Linkage Non nuclear inheritance 2.5. Genetics State the term which may apply to the following definitions Term Definition Organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. The passing on of traits from parent to offspring by means of genes The process of using the information on the gene to make a protein A unit of DNA which codes for the production of a specific protein Deoxyribonucleic Acid – a double stranded nucleic acid Ribonucleic Acid – a single stranded nucleic acid Examining DNA / for a pattern or band / to compare …………………………………………………………. A method of making a unique pattern of bands from the DNA of a person, [which can then be used to distinguish that persons DNA from other DNA] That part of the chromosome which carries the infomation to make a protein That part of the chromosome which does not carry the infomation to make a protein Testing (people) for the presence of a (specific) gene or To establish presence or absence of gene(s) The process of producing mRNA using DNA as a template. The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template Adenine and Guanine are the two pyrimidine bases. They are single ring molecules Cytosine and Thymine are the two purine bases. They are double ring molecules Messenger RNA takes the complementary DNA strand out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA - As the mRNA moves through, tRNA molecules carrying the appropriate amino acid bind to the RNA codon to which they are matched, and the sequence of amino acids is put together. Ribosomal RNA – found in the ribosome and allow protein . synthesis to occur A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Is the position of a gene on a chromosome Has identical alleles [for a trait] Has different alleles [for a trait] The genetic make-up of an individual Physical appearance of an organism The offspring that are produced One allele masks the expression of the other. Allele whose expression is masked by dominant allele Neither allele masks the expression of the other. Non sex chromosomes Difference between members of species or population Change in the genetic make up An agent that causes a mutation Changes that occur in a single gene Large changes that occur in the structure or number of one or more chromosomes Manipulation or alteration of genes Enzymes that cut DNA An enzyme that sticks DNA together (Inheritable) change within a population (or species) / in response to change in the environment / by natural selection/over time Is the process by which those organisms with genetically controlled characteristics that allow them to be well adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation The study of fossils Inherited factors are controlled by pairs of factors. These factors separate from each other at gamete formation with only one member of the pair being found on the gamete When gametes are formed either of a pair of factors is equally likely to combine with another pair of factors Genes that are located on the same chromosome The characteristic is controlled by a gene on an X chromosome Extra nuclear genes that are present in mitochondria and chloroplasts and can reproduce by themselves and pass on their genes to resulting organelles. .