Name_____________________ Date__________ Class
advertisement
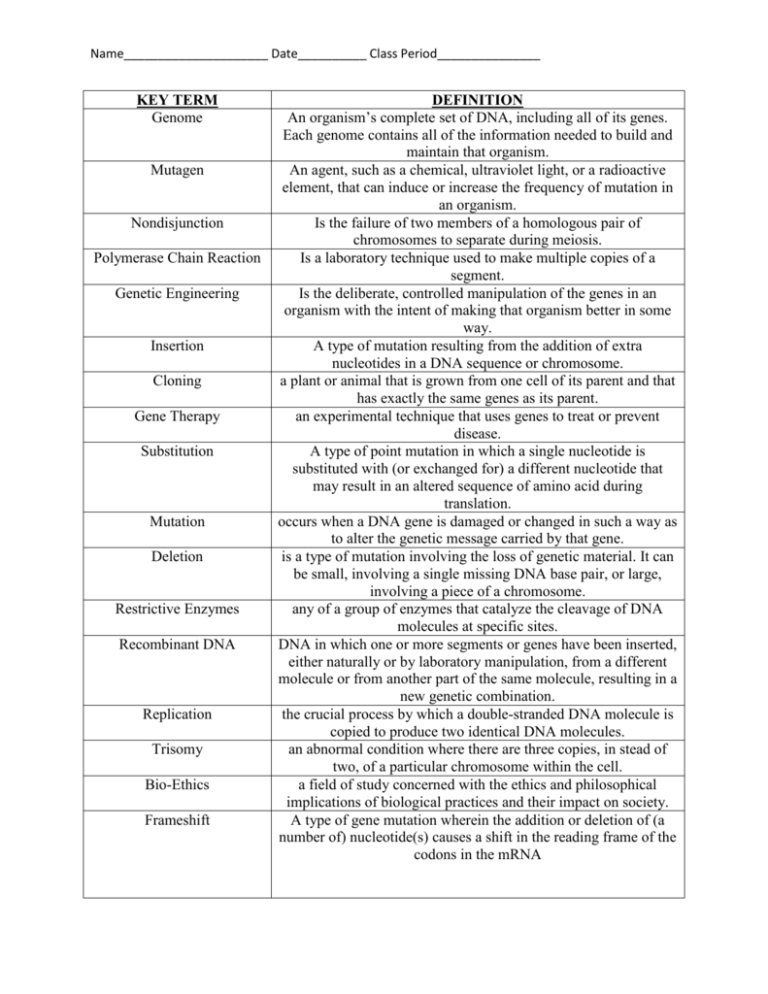
Name_____________________ Date__________ Class Period_______________ KEY TERM Genome Mutagen Nondisjunction Polymerase Chain Reaction Genetic Engineering Insertion Cloning Gene Therapy Substitution Mutation Deletion Restrictive Enzymes Recombinant DNA Replication Trisomy Bio-Ethics Frameshift DEFINITION An organism’s complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. An agent, such as a chemical, ultraviolet light, or a radioactive element, that can induce or increase the frequency of mutation in an organism. Is the failure of two members of a homologous pair of chromosomes to separate during meiosis. Is a laboratory technique used to make multiple copies of a segment. Is the deliberate, controlled manipulation of the genes in an organism with the intent of making that organism better in some way. A type of mutation resulting from the addition of extra nucleotides in a DNA sequence or chromosome. a plant or animal that is grown from one cell of its parent and that has exactly the same genes as its parent. an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease. A type of point mutation in which a single nucleotide is substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation. occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic material. It can be small, involving a single missing DNA base pair, or large, involving a piece of a chromosome. any of a group of enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of DNA molecules at specific sites. DNA in which one or more segments or genes have been inserted, either naturally or by laboratory manipulation, from a different molecule or from another part of the same molecule, resulting in a new genetic combination. the crucial process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. an abnormal condition where there are three copies, in stead of two, of a particular chromosome within the cell. a field of study concerned with the ethics and philosophical implications of biological practices and their impact on society. A type of gene mutation wherein the addition or deletion of (a number of) nucleotide(s) causes a shift in the reading frame of the codons in the mRNA Name_____________________ Date__________ Class Period_______________ Genetically modified Organisms Gel Electrophoresis DNA Fingerprinting Transgenic organisms Karyotype organism whose genome has been engineered in the laboratory in order to favor the expression of desired physiological traits or the production of desired biological products a technique for separating protein molecules of varying sizes in a mixture by moving them through a block of gel, by means of an electric field, with smaller molecules moving faster and therefore farther than larger ones A laboratory technique used especially for identification (as for forensic purposes) by extracting and identifying the base-pair pattern of an individual's DNA an organism that has had genes (one or more DNA sequences) from another species put into its genome having been introduced by artificial means such as recombinant DNA techniques. Chromosomes which have been stained, photographed, and grouped by size and banding patterns