Chapter 13 Vocabulary and Learning Targets for students
advertisement

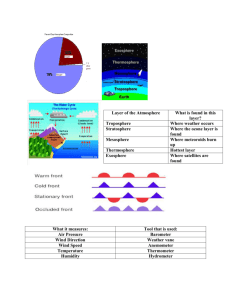
Chapter 13: The Atmosphere Learning Target Lesson 1 I can describe the composition of the atmosphere . . . Vocabulary Word weather Definition Facts or Examples condition of Earth's _____________at a particular _______ and ___________. atmosphere the envelope of ___________ that surrounds the____________. Earth's atmosphere consists of__________, ________ , ___________dioxide, water ___________, and other gases, as well as____________ of liquids and solids. water vapor water in the form of a ________(not the same as steam) The amount of water vapor in the air __________ greatly from place to place. __________in one part of the atmosphere __________ other parts of the atmosphere. The atmosphere is like a ____________because it has ________ and these parts ____________. air has mass, density and_____________ Air is made up of atoms and _____________ that have_______. I can state how the atmosphere is a system . . . Lesson 2 I can identify some properties of air . . . density the amount of_______ in a given ____________ of air. density = mass / volume Symbol/Picture I can describe how barometers can be used to measure air pressure . . . air pressure the result of the __________ of a ______________ of air pushing on an area barometer an _____________ that is used to measure air___________. mercury barometer aneroid barometer I can explain how altitude affects air pressure and density . . . altitude as the air pressure increases, it pushes _______ on the surface of the mercury in the dish. This causes the mercury in the tube to ____________ . an airtight metal __________ that is ____________ to changes in air pressure __________ or distance above______ level Air pressure is measured in inches of ___________ and millibars. As the air pressure drops, the mercury in the ________ falls and the mercury in the _______ rises. When air pressure increases, the thin walls of the chamber are pushed _____. When the pressure drops, the walls bulge _______. As the shape of the chamber changes, the _________ on the dial moves. Air pressure ___________ as altitude increases. As air pressure decreases so does____________. Lesson 3 I can identify the four main layers of the atmosphere and their characteristics . . . I can explain the characteristics of the atmosphere's layers . . . Scientists divide Earth's atmosphere into 4 main __________. troposphere the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere where you ______. Tropo means ____________ stratosphere the second layer of the atmosphere. Strato means ________ or spread out mesosphere the layer above the stratosphere. Meso means__________. thermosphere the _____________ layer, extends from 80 km into space ionosphere ________ part of the thermosphere (80-400 km) 1. Troposphere 2._____________ 3. _____________ 4. Thermosphere Earth's ______________ occurs here. It is between 9-16 km thick. It contains most of the____________ . As altitude increases, temperature_____________. Contains the _________ layer which protects us from ________________ radiation. As altitude increases, temperature___________. ____________ Earth's surface from being hit by ___________. Between 50-80 km above Earth's surface Temperature up to ____________ o C but not much __________ because gas molecules __________ so far apart. Ions are charged particles. This is where the northern and southern lights (auroras) are formed. exosphere ___________ layer, from This is where GPS and TV 400 to thousands of km satellites orbit and spacecrafts go. Lesson 4 I can state in which form energy travels from the sun to Earth . . . electromagnetic ________travels to Earth waves as electromagnetic waves and can move through the _________ of space. Most of the energy from the sun travels to Earth in the form of _________ light and __________ radiation. A smaller amount arrives as ____________radiation. radiation ___________ transfer of energy by _____________________ waves visible light all the colors you see in a ____________ROYGBIV Red and orange have ___________ wavelengths; blue and violet have ___________ wavelengths. infrared radiation wavelengths are ____________ than wavelengths for red light It is invisible to humans but it can be felt as __________. ultraviolet radiation I can explain what happens to sun's energy in the atmosphere and at Earth's surface . . . some sunlight is absorbed or reflected by the ____________ before it can reach the surface. scattering Greenhouse effect Lesson 5 I can describe how temperature is measured . . . an invisible form of energy with wavelengths that are ___________ than wavelengths for violet light temperature thermal energy UV radiation can cause__________ . The rest passes through the atmosphere to the ___________ 50% of the energy that reaches the surface is __________ by land and water and changed into ___________. a process where dustsize particles and gases in the atmosphere __________ light in all ___________. The sky looks blue because gas molecules ___________ short blue __________ more than long red wavelengths. the energy from the ___________ radiation heats the gases in the air. These __________ hold heat in Earth's atmosphere. It is a ___________ process, and keeps Earth at a _____________ temperature. Scientists have evidence that human activities may ____________ the greenhouse effect. the __________amount of energy of __________ of each particle in a substance. the __________ energy of motion in the ________ of a substance. The ___________ the particles are moving, the _________ energy they have and the higher the temperature. The tea in the ______ has more thermal energy than the tea in the _____ because it has more ________ thermometer an instrument that measures temperature When the air temperature increases, the temperature of the ________ in the bulb increases and the liquid __________ and rises up the __________. Celsius Scale Freezing point of water = ___o and boiling point is _____o To convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius use the formula: Fahrenheit Scale I can describe how heat is transferred . . . heat convection conduction radiation Freezing point of water is ____ o and boiling point is ______o Thermal energy transferred from a ________ object to a _________ one. The transfer of heat by the _____________ of a _________ (liquids and gases) Transfer of heat between two ____________ that are in direct_____________. Direct transfer of energy by ______________ waves Heat is __________ in three ways convection, conduction and radiation. Ex. air conditioning in your house, boiling noodles Conduction works well in__________ , air and water do not conduct heat ________. Ex. pan touching stove, feet on hot sand Ex. campfire, sun's rays Fahrenheit -32 1.8 Lesson 6 I can explain how scientists describe and explain winds . . . convection currents ___________ movement of warm air and the ___________ movement of cool air. Heat is transferred mostly by convection within the______________ . wind the movement of air _____________ to Earth’s surface move from areas of ______ pressure to __________ pressure caused by __________ heating of the atmosphere I can distinguish between local winds and global winds and identify major global wind belts… anemometer instrument used to measure the __________ of the wind windchill factor the increased ____________ that wind can cause local winds winds that blow over short _____________ form when large scale winds are weak 2 types = sea breezes and land breezes sea breeze during the day, land heats up________, (low pressure), water is ________ , (high pressure) so wind blows from ________ to __________ land breeze global winds Coriolis Effect doldrums during the night, land ________ down faster, (high pressure), water is ____________, (low pressure) so wind blows from _______ to ___________ winds that blow _________ from specific directions over ________ distances the way Earth’s _____________ makes winds __________ ________ area where warm air ___________= little to no wind occur over a large area in Northern Hemisphere global winds turn ___________ in Southern Hemisphere global winds turn counter clockwise a global wind belt occur at the _________ horse latitudes two calming areas of ________ air a global wind belt from equator to _____° North and South latitudes little to no wind threw horses overboard to lighten ships to move in no wind the air stops moving toward the poles and sinks trade winds prevailing westerlies polar easterlies blow from horse latitudes _________ bn the equator Winds blowing from 30 degrees to 0 (equator); sail from Europe to USA blow from west to east, ______ from the horse latitudes Winds blowing from 60 to 30 degrees latitude; most of USA __________ (rain, snow) blow cold air away from the _________ Winds blowing from 90 to 60 degrees latitude; brings USA snow & ________ weather a global wind belt blow from ___to ____ between 30° and 60° N and S blow from ___ to ___ WE LIVE IN THIS global wind belt a global wind belt blow from ___ to ___ Learning Targets Chapter 13 Lesson 1 I can describe the composition of the atmosphere . . . Earth’s atmosphere consists of_____________, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ________________, and other gases, as well as particles of liquids and solids. I can state how the atmosphere is a system . . . Events in one part of the atmosphere ______________ other parts of the atmosphere. Lesson 2 I can identify some properties of air . . . Because air has_____________, it also has other properties, including ______________ and ___________________. I can describe how barometers can be used to measure air pressure . . . Two common kinds of barometers are __________________ barometers and _____________ barometers. I can explain how altitude affects air pressure and density . . . Air pressure ___________________ as altitude _______________. As air pressure______________, do does _________________. Lesson 3 I can identify the four main layers of the atmosphere and their characteristics . . . Scientists divide Earth’s atmosphere into ________________ main layers according to changes in ______________________. I can explain the characteristics of the atmosphere's layers . . . Earth’s weather occurs in the _______________. The stratosphere contains the ________________ layer. The mesosphere protects Earth from ____________________. The ____________________ is the outermost layer of the atmosphere. Lesson 4 I can state in which form energy travels from the sun to Earth . . . The sun’s energy travels to Earth as ______________ light, ______________ radiation and______________ radiation. I can explain what happens to sun's energy in the atmosphere and at Earth's surface . . . Some sunlight is ______________ or reflected by the atmosphere. Some of the energy Earth absorbs is radiated back out as ______________ radiation. Lesson 5 I can describe how temperature is measured . . . Air temperature is usually measured with a______________. I can describe how heat is transferred . . . Heat is transferred in three ways: ______________, ______________and ______________. Heat is transferred mostly by convection within the ______________. Lesson 6 I can explain how scientists describe and explain winds . . . Winds are caused by ______________ in air pressure. I can distinguish between local winds and global winds and identify major global wind belts… The ______________ heating of Earth’s surface within a ______________ area causes local winds. Global winds are caused by the unequal heating of Earth’s surface over a ______________ area.