04 Alg II Unit 1 PARCC info
advertisement
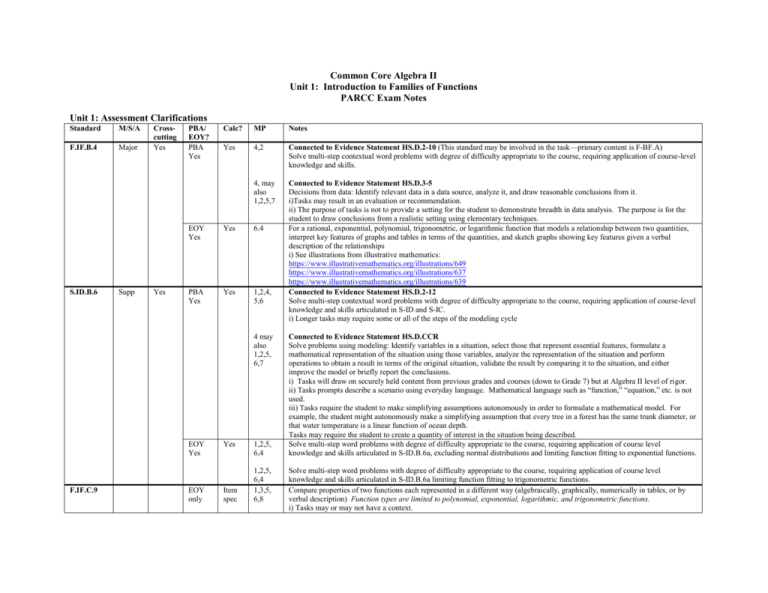
Common Core Algebra II Unit 1: Introduction to Families of Functions PARCC Exam Notes Unit 1: Assessment Clarifications Standard M/S/A F.IF.B.4 Major S.ID.B.6 Supp Crosscutting Yes Yes PBA/ EOY? PBA Yes Calc? MP Notes Yes 4,2 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.2-10 (This standard may be involved in the task—primary content is F-BF.A) Solve multi-step contextual word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course-level knowledge and skills. 4, may also 1,2,5,7 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.3-5 Decisions from data: Identify relevant data in a data source, analyze it, and draw reasonable conclusions from it. i)Tasks may result in an evaluation or recommendation. ii) The purpose of tasks is not to provide a setting for the student to demonstrate breadth in data analysis. The purpose is for the student to draw conclusions from a realistic setting using elementary techniques. For a rational, exponential, polynomial, trigonometric, or logarithmic function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationships i) See illustrations from illustrative mathematics: https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/649 https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/637 https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/639 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.2-12 Solve multi-step contextual word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course-level knowledge and skills articulated in S-ID and S-IC. i) Longer tasks may require some or all of the steps of the modeling cycle EOY Yes Yes 6.4 PBA Yes Yes 1,2,4, 5,6 4 may also 1,2,5, 6,7 EOY Yes F.IF.C.9 EOY only Yes Item spec 1,2,5, 6,4 1,2,5, 6,4 1,3,5, 6,8 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.CCR Solve problems using modeling: Identify variables in a situation, select those that represent essential features, formulate a mathematical representation of the situation using those variables, analyze the representation of the situation and perform operations to obtain a result in terms of the original situation, validate the result by comparing it to the situation, and either improve the model or briefly report the conclusions. i) Tasks will draw on securely held content from previous grades and courses (down to Grade 7) but at Algebra II level of rigor. ii) Tasks prompts describe a scenario using everyday language. Mathematical language such as “function,” “equation,” etc. is not used. iii) Tasks require the student to make simplifying assumptions autonomously in order to formulate a mathematical model. For example, the student might autonomously make a simplifying assumption that every tree in a forest has the same trunk diameter, or that water temperature is a linear function of ocean depth. Tasks may require the student to create a quantity of interest in the situation being described. Solve multi-step word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course level knowledge and skills articulated in S-ID.B.6a, excluding normal distributions and limiting function fitting to exponential functions. Solve multi-step word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course level knowledge and skills articulated in S-ID.B.6a limiting function fitting to trigonometric functions. Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal description) Function types are limited to polynomial, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric functions. i) Tasks may or may not have a context. Overarching Standards: Standard M/S/A N.Q.A.2 Supp A.SSE.A.2 Major Crosscutting Yes Yes PBA/ EOY? PBA only PBA Yes Calc? MP Notes Yes 4,2 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.2-7 Solve multi-step contextual word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course-level knowledge and skills. i) A-CED is the primary content; other standards may be involved in tasks as well. 4, may also 1,2,5,7 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.3-6 Full models: Identify variables in a situation, select those that represent essential features, formulate a mathematical representation of the situation using those variables, analyze the representation and perform operations to obtain a result, interpret the result by comparing it to the situation, and either improve the model or briefly report the conclusions. i) See CCSS, p. 72-73 for more info ii) Task prompts describe a scenario using everyday language. iii) Tasks require students to make simplifying assumptions autonomously in order to formulate a mathematical model. iv) Tasks may require the student to create a quantity of interest in the situation being described (N-Q.A.2) v)Tasks may involve choosing a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations of measurement or limitations of data when reporting quantities (N-Q.3 from Alg I) 4, may also 1,2,5, 6,7 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.CCR Solve problems using modeling: Identify variables in a situation, select those that represent essential features, formulate a mathematical representation of the situation using those variables, analyze the representation of the situation and perform operations to obtain a result in terms of the original situation, validate the result by comparing it to the situation, and either improve the model or briefly report the conclusions. i) Tasks will draw on securely held content from previous grades and courses (down to Grade 7) but at Algebra II level of rigor. ii) Tasks prompts describe a scenario using everyday language. Mathematical language such as “function,” “equation,” etc. is not used. iii) Tasks require the student to make simplifying assumptions autonomously in order to formulate a mathematical model. For example, the student might autonomously make a simplifying assumption that every tree in a forest has the same trunk diameter, or that water temperature is a linear function of ocean depth. Tasks may require the student to create a quantity of interest in the situation being described. Use the structure of polynomial, rational or exponential expressions to identify ways to rewrite it. i) Additional examples: In the equation x2 2x 1 y2 9 , see an opportunity to rewrite the first three terms as (x 1)2 , thus Neutr 7 recognizing the equation of a circle with radius 3 and center (-1, 0). See x2 4 x 3 2 as (x 2 3) 1 x2 3 , thus recognizing an opportunity 1 . x2 3 Use structure of polynomial, rational, or exponential expression to identify ways to rewrite it to write it as 1 EOY Yes Neutr 7 7, 1 i) Additional examples: In the equation x2 2x 1 y2 9 , see an opportunity to rewrite the first three terms as (x 1)2 , thus recognizing the equation of a circle with radius 3 and center (-1, 0). See x2 4 x 3 2 as (x 2 3) 1 x2 3 , thus recognizing an opportunity 1 . x2 3 Rewrite the expression, in a case where two or more requiring steps are required i) An example from the 2009 College and Career Readiness Standards: Factor completely: 6cx 3cy 2dx dy . (A first iteration to write it as 1 A.CED.A.1 F.IF.B.6 Supp Major Yes Yes PBA only Yes PBA Yes EOY Yes 4-2 4,2 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.2-10 (This standard may be involved in the task—primary content is F-BF.A) Solve multi-step contextual word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course-level knowledge and skills. 1,2,5,7 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.3-5 i) Tasks may result in an evaluation or recommendation ii) The purpose of tasks is not to provide a setting for the student to demonstrate breadth in data analysis skills. The purpose is for students to draw conclusions in a realistic setting using elementary techniques. 4, may also 1,2,5, 6,7 Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.CCR Solve problems using modeling: Identify variables in a situation, select those that represent essential features, formulate a mathematical representation of the situation using those variables, analyze the representation of the situation and perform operations to obtain a result in terms of the original situation, validate the result by comparing it to the situation, and either improve the model or briefly report the conclusions. i) Tasks will draw on securely held content from previous grades and courses (down to Grade 7) but at Algebra II level of rigor. ii) Tasks prompts describe a scenario using everyday language. Mathematical language such as “function,” “equation,” etc. is not used. iii) Tasks require the student to make simplifying assumptions autonomously in order to formulate a mathematical model. For example, the student might autonomously make a simplifying assumption that every tree in a forest has the same trunk diameter, or that water temperature is a linear function of ocean depth. Tasks may require the student to create a quantity of interest in the situation being described. Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.2-10 (This standard may be involved in the task—primary content is F-BF.A) Solve multi-step contextual word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course-level knowledge and skills. Calculate and interpret average rate of change of a function (presented symbolically or as a table) over a specified interval with functions limited to polynomial, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric functions. (*Modeling Standard) Tasks have a context 1,2,4, 5,6 Item spec might give 3c(2x y) d(2x y) , which could be recognized as 3c(2x y) d(2x y) on the way to factoring completely as (3c d)(2x y) .) ii) Tasks do not have a context. Connected to Evidence Statement HS.D.2-7 Solve multi-step contextual word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to the course, requiring application of course-level knowledge and skills. i) A-CED is the primary content; other standards may be involved in tasks as well. 1,4,5,7 1,4,5,7 Estimate the rate of change from a graph (*Modeling Standard) i) Tasks have a context. Tasks may involve polynomial, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric functions. PARCC Abbreviation Key: PBA: Performance-Based Assessment EOY: End of Year Assessment M/S/A: Indicates whether this standard is considered Major, Supporting, or Additional Content MP: Standards for Mathematical Practice * Indicates a modeling standard PARCC Sub-Claims: Sub-Claim A: Information on how PARCC will assess major content Sub-Claim B: Information on how PARCC will assess additional and supporting content Sub-Claim C: Information on how PARCC will assess reasoning Sub-Claim D: Information on how PARCC will assess modeling