Chapter 04
advertisement

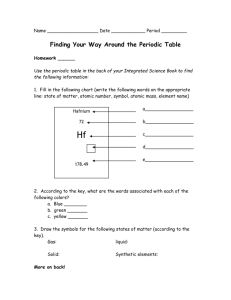
Chapter 04– Learning Objectives and Study Questions What are the three subatomic particles? You should be able to describe their symbols, their charges, and their relative masses. You also need to know where they are located in the atom. Relatively, how big is the nucleus compared to the size of the atom? You should be able to write atomic symbols. o What is mass number? How is it calculated? Where is it written in the atomic symbol? o What is atomic number? How and where do you look it up? Where is it written in the atomic symbol? o What is charge? How is it calculated? Where is it written in the atomic symbol? What is the difference between atomic symbols and the way information is presented in the boxes on the periodic table? You should be able to use an atomic symbol to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons indicated by the symbol. You should also be able to use the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons to determine the corresponding atomic symbol. What are ions? Isotopes? You should be able to recognize if two atomic symbols are ions or isotopes of each other. What is the difference between mass number and atomic mass? What does the symbol amu stand for? You should be able to calculate the average weight/mass of an element if I give you % abundance and isotopic mass information. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing……? What are groups/families on the periodic table? What are periods on the periodic table? You should be able to identify the following areas on the periodic table: o metals o nonmetals o transition metals o lanthanides and actinides (inner transition elements) o metalloids o alkali metals o alkaline earth metals o halogens o noble gases You should be able to identify elements based on their positions in the periodic table You should know the basic properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. What is found in the space outside the nucleus of an atom? What is the significance of Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment?