Renal Partners
advertisement

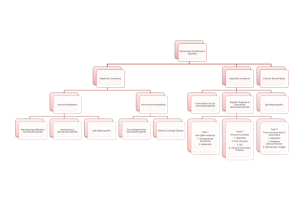
Renal Partners Anti-GBM (non-collagen domain of Type IV collagen) Nephrotic Syndrome Nephritic Syndrome Azotemia Chronic renal failure Slit Diaphragm Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis Lab Post-streptococcal glomuerulonephritis Morphology IgA nephropathy (Berger Disease) Morphology Reccurence Allografts Henoch-Schlonlein Purpura Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Cinical Presentation Goodpasture Syndrome (CP) Goodpasture Syndrome Morphology Crescent Gloumerular Nephritis Wegener Glomerulonephritis (CP) Goodpasture disease -Thickening of the basement membrane -Proteinuria >3g/24 hrs (“frothy urine”) -Hematuria -RBC cast -Hypertension -Azotemia Elevated BUN and creatinine Hyalinzation and sclerosis -Composed of nephrin and podocin -Nephrin molecules are joined by disulfide bridges -Anti-streptolysin O titers -Low complement -LM: mesgial cell proliferation -IF: lumpy-bumpy; coarse granular depositis of IgG and C3 -EM: subepithelial electron dense humps -LM and IF: diffuse mesangial IgA -IgA nephropathy -Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis Type I -Increase in serum IgA -IgA deposit kidney and skin -Skin: Palpable red rash -Kidney: Hematuria -GI: abdominal pain -Purpura from vasculitis (no bleeding disorder) -Hematuria -Hemoptysis -LM: necrosis crescents -IF: Linear peripheral IgG deposits in glomerular BM and alveolar septae -Leakage of fibrin in Bowman’s space -Rapidly progressive glomerular nephritis -Sinusitis -Pneumonitis -Glomerulonephritis Renal Partners 1 Polyarteritis Nodosa Lab Wegener Glomerulonephritis Morphology Polyarteritis Nodosa Lab HUS SLE Secondary Nephritic Syndrome Morphology Scleroderma Secondary Nephritic Syndrome Nephritic Syndrome Nephrotic Syndrome Lipid Nephrosis Lipid Nephrosis Morphology Minimal change disease -Previous HepB infection -eosinphilia -pANCA -LM: cresents -Renal -Skin -GI -Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia -E. coli 0157:H7 -Hematuria -Uncooked hamburger -Schistocytes -IF: IgG and C3 in mesangium and tubules -IF: Full house fluorescence -EM: subendothelial and mesangial deposits -Anti-Scl70 -HTN -Raynaud’s -Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis -IgA Nephropathy -Henoch-Schonlein Purpura -Goodpasture Syndrome -Cresent glomerulonephritis -Wegener Granulomatosis -Polyarteritis Nodosa -HUS -Secondary to SLE and Scleroderma -Lipid Nephrosis -Minimal Change disease -Focal-Segmental Glomerulosclerosis -Membranous glomerulonephritis -Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis -Secondary Diabetes and Amyloides -Children -Recurrent nephrotic syndrome -Selective proteinuria (albumin) -T-cells derived factors caused podocyte damage and effacement -EM: Podocyte fusion -Hodgkins lymphoma Renal Partners 2 -Nephrotic syndrome Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis -No response to steroids -Mixed nephritic/nephrotic syndrome Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis -LM: Juxtamedullary glomeruli focal Morphology sclerosis which spreads superficially as the disease progresses Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis -C1q deposits (FSGS) Types -Collapsing with HIV Collapsing (FSGS) -Collpase of the entire glomerulus -Podocyte hyperplasia associated with HIV drugs Membranous Glomerulonephritis -HepB Predisposing Factors -Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma Membranous Glomerulonephritis -LM: thickened BM Morphology -IF: Fine granular peripheral IgG and C3 -EM: 4 stages Membranous Glomerulonephritis EM 1. Epimembranous deposits four stages 2. Intramembranous deposits and spikes 3. Intramembranous deposits 4. Radioluscents areas Membranoproliferative -Type 1: Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis Types -Type 2: Dense deposit disease Membranoproliferative -Hypertension, hematuria, hearing glomerulonephritis Type I problems Membranoproliferative -LM: lobular pattern proliferation glomerulonephritis Type I Morphology increased mesangial matrix thickening of BM -IF: C3 deposits in a peripheral lobular distribution EM: mesangialization Silver stain: split basement membrane (tram track) Membranoproliferative -LM: lobular pattern proliferation glomerulonephritis Type II Morphology increased mesangial matrix thickening of BM -IF: discontinuous linear deposit of C3 peripheral -EM: Ribbon-like deposits in lamina densa Diabetes Secondary Nephrotic Syndrome -Kimmelsteil-Wilson disease -Microangiopathy leading to BM sclerosis Diabetes Secondary Nephrotic Syndrome -LM: nodular sclerosis; hyalinization of Morphology afferent and efferent arteriles Renal Partners 3 Amyloidosis Secondary Nephrotic Syndome Morphology RBC cast Oval fat body WBC cast Papillary Necrosis (CP) Papillary Necrosis etiology Papillary Necrosis Morphology Acute tubular necrosis types Acute tubular necrosis urinalysis Toxic acute tubular necrosis location Ischemic acute tubular necrosis location Ischemic tubular necrosis morphology Toxic tubular necrosis Interstitial nephritis acute Interstitial nephritis chronic Simple cyst Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) ARPKD mutation Dysplastic Kidney Disease (Potter II) Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) Medullary Cyst (Sponge kidney) Medullary Cyst CP -LM: nodular lesions -IF: positive lambda chains -EM: non-branching fibrils in BM, mesangium, and vessel walls Apple green bifringence with congo red stain -Nephritic syndrome -IgA nephropathy Tubular cells with lipids Indicative of upper (kidney) UTI -Severe flank pain radiating to the groin -Sterile pyuria -Diabetes -Sickle cell disease -Analgesic nephropathy -Necrosis and sloughing of the Papillae -Toxic (Ethylene glycol) -Ischemic Tubular casts Mostly proximal convoluted tubules Segmental proximal and distal Tubulorhexis: rupture of BM Intact BM Type 1 hypersensitivity Rx Analgesic -Benign -Obstruction and impair circulation -oligohydramios -Incompatible with life -Radial cyst thorugh cortex and medulla PKHD1 gene mutation -> receptor for fibrocystin -Presence of mesenchyme (cartilage) in the kidney -Not hereditary -Liver cyst -Berry Aneurysm -Papillary cyst -Hematuria -UTI -Renal stones Renal Partners 4 Adult onset medullary cystic disease Horseshoe kidney Benign recurrent hematuria Alport syndrome morphology Alport Syndrome X-linked mutation Alport Syndrome Familial mutation Alport Syndrome CP Nitrites in urine Urine Examination -RBC -WBC -Tubular cells -Oval bodies -RBC cast -WBC cast -Granular (Broken RBC cast) -Tubular Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma WAGR Syndrome Denys-Drash Syndrome Beckwith-Wiedman Syndrome Sporadic Wilms Extrophy Hunner’s ulcer -Autosomal dominant -Salt loosing polyuria -corticomedullary cyst and shrunken kidneys -Kdney fused at the inferior pole -obstruction -> stasis -> infection Thin capillary loops EM: lamellation of the lamina densa Type IV α5 chain mutation Type IV α3 and α4 chain mutation -Cataracts and lens dislocation -Neurosensory hearing loss Infection -Hematuria -Pyuria -Tubular necrosis -Tubular cells with lipid droplets (Nephrotic Syndrome) -Acute Nephritic Syndrome -Acute pyelonephritis -Acute Nephritic Syndrome -Acute tubular necrosis -von Hippel Lindau gene -Chromosome 3 deletion -Trisomy 1 and 17 -Y chromosome deletion -Mutated MET proto-oncogene -Wilms tumor -Aniridis -Gonadal anomalies -Retardation -Gonadal dysgenesis -Gonadoblastoma -Diffuse mesangial sclerosis -Wilms tumor -Wilms tumor -Organomegaly -Macroglossia -Hemihypertrophy Β-catenin gene mutation Incomplete closure of the anterior abdominal wall and urinary bladder Chronic interstitial cystitis Renal Partners 5 Bladder Squamos Cell Carcinoma Acute bacterial prostatitis Schistosomes -E. coli -Associated with UTI Renal Partners 6