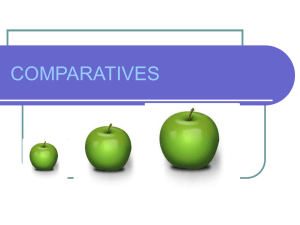
and adjectives to point out a specific object
advertisement

-+ English as a Second Language Curriculum Proficiency Level: Novice Grades: 9-12 UNIT: 3 Title: Community & Landscapes Section Page Number Unit Title and Description with Learning Targets 2-3 Unit Language - Functions and Forms 4-5 Unit Assessment Overview 6 Unit Assessment Checklist 7 Unit Assessment Rubric 8-9 Sample Unit Calendar 10-11 Detailed Unit Calendar 12-15 (INCOMPLETE) Additional Activities 16 (INCOMPLETE) Grammar Cheat Sheet 17-19 Anchor Charts 20-21 1|Page High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ ESOL LEVEL: Novice GRADES: 9-12 UNIT 2: Community and Landscapes Unit duration: Stage 1 Identify Desired Results This unit is all about describing the setting. In this unit students will learn specific nouns for describing Unit different locations in the community and landscapes that will be useful in describing a setting. Adjectives Description are a critical part of this unit as students use landforms to describe setting. Adjectives are a critical part of this unit. Students will to describe setting using nouns and demonstrative adjectives, and adjectives used to limit (ie. a few, some). Students will use the present progressive to describe the actions of people within a setting. Standards Describing Actions: Target Form: Students use the present progressive to demonstrate comprehension of actions by performing or describing an action. Describing Location: Target Form: Students demonstrate commands of prepositions through total physical response. Students use simple sentences with prepositional phrases such as (next to, beside, between, etc.) Asking Informational Questions: Target Form: Students use the present or present progressive tense to ask and answer questions with the verb to be. Students ask and answer simple questions about familiar/concrete subjects. Evaluating: Target Form: Students use adjectives of number (one truck, two buildings), adjective used to limit (few, much, little), and adjectives to point out a specific object (that, this, these, those, every, each) Literary Analysis: Target Form: Students learn to describing setting using a single word - “a castle”. Students use simple sentences (s/v/adj) and (s/v/o) - “The castle is big.” Unit Goals 2|Page I can describe actions. I can describe location and High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum I can specify quantity of objects 4/9/2014 I can use specific nouns to -+ Learning Targets 3|Page I can use the present progressive to describe actions using (to be + verb ing). setting by asking and answering informational questions regarding location. I can use prepositional phrases to describe location. and use adjectives to point out specific objects. I can use exact numbers (+ singular/plural) to show the quantity of objects. I can use specific nouns to identify places in the community. I can use specific nouns to describe locations in the community. I can use the present tense to ask questions. I can use adjectives that express a non specific amount of objects in a place. I can use adjectives that point out a specific object. I can use specific nouns to identify landforms. High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 describe a setting. I can write a descriptive paragraph. I can use simple sentences. I can use weather related verbs to describe a setting. -+ Stage 2 Assessment Evidence: Academic Language (What language will students need to sound like experts?) Key Vocabulary Locations - store, mall, laundromat, aquatic center, hospital, restaurants, bank, fire station, post office, bakery, bus stop, convenience store, apartment, house (home), hotel, gas station, park Actions (verbs) – swim, buy groceries, wash clothes, shop for…, visit the doctor, eat, make a withdrawal/deposit, play, buy gas, send a letter, buy bread, wait for the bus, pick up a pack of gum, visit a friend, rest Language Scaffolding Academic Language Stems: Where does the ___ take place? (setting/story) o The ____ takes place in the _____. o The ____ takes place on a _____ (preposition/prepositional phrase) a/the ___. o The setting is at a ___ (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. What are the characters/they doing? o The ____ is/are ____-ing. o The ___ are ___-ing (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. What is ___ doing? o ___ is ___-ing in the _____. o ___ is ___ing (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ____. Where are you/they/proper nouns going? o I am going to the _____. o ___ are going to the _____. o ___, ___, and ___ are going to the ___ (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. Where is ___? o ____ is ____(prepositional phrase) the _____ (location). o ____ is ____(prepositional phrase) the _____ (location) (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. How many ___ are ___(ing)? o There are ___ (number) ___(people/children/etc) ___-ing at the ____ (location). o There are four children playing at the park. o There are ____ (adjective of limit) _____ (peolpe/children/etc) ____ing at the ___ (location). Things – street, highway, sidewalk, road Defining and Describing – is/are, a couple/a few/some/many/a lot/every/each Describing Location - prepositions: near, far from, next to, by the, a distance from, beside, between, in, on Landscapes - beach, butte, canyon, cave, cliff, coast, desert, dune, hill, island, lagoon, lake, mountain, ocean, pond, field, forest, woods, river, swamp, valley, volcano, waterfall 4|Page High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ 5|Page Are they ___(ing)...? Are they enjoying themselves? o Yes, they are ___-ing… o No, they are not ___-ing... High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ What evidence from formative and summative assessments should you collect to verify student learning? Assessment Tools: Possible Assessments (Student performance based on language productive skills). 6|Page Rubric Assessment Checklist Reading Writing Speaking Listening High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 Student Name 7|Page 5 POINT SCALE: Exceeds = 5; Proficient =4; Almost Proficient = 3; Limited = 2; High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum Not Proficient = 1 4/9/2014 I can use adjectives that point out a specific object. I can use adjectives that express a non specific amount of objects in a place. I can use exact numbers (+ singular/plural) to show the quantity of objects. I can use the present tense to ask questions. I can use specific nouns to describe locations in the community. I can use prepositional phrases to describe location. I can use the present progressive to describe actions using (to be+ verb -ing). -+ Unit of Study Assessment Checklist Notes -+ Learning Target Proficient I can use the present progressive to describe actions using (to be + verb ing). I correctly use the verb to be plus the progressive tense in complete sentences to describe actions. I am going to the bank. Developing Emerging I use the verb to be plus an article in complete sentences to describe actions. I use the verb to be in simple phrases to describe actions. I am go to the bank. I is go to bank. Beginning I can use simple phrases to describe actions. I go to bank. I can use prepositional phrases to describe location. I can use a prepositional phrase in a simple sentence. I can use a prepositional phrase to indicate the location of an object. I can combine a motion and occasionally use a prepositional phrase to indicate the location of an event. I can use a motion to indicate the location of an object. I can use specific nouns to describe locations in the community. I can use specific nouns in simple sentences. I can use specific nouns in simple sentences with occasional errors in sentence structure. I can use a single word noun or simple phrase to accurately identify objects. I can identify a noun by pointing at a picture. I can use the present tense to ask questions. I can use specific vocabulary and accurate syntax to ask questions regarding a location. I can use circumlocution, phrases, I can use simple phrases and and gestures with accurate intonation to ask questions syntax to ask questions regarding regarding location. location. I can use intonation with single words to indicate a question. I can use exact numbers (+ singular/plural) to show the quantity of objects. I can use the verb to be, exact numbers, and singular/plural to accurately identify the quantity of objects. There are five boats I can use the verb to be and exact numbers to quantify objects. Singular/plural may be inaccurate. There is five boats I can use single words, write or show with fingers 8|Page High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum I can use exact numbers to quantify objects. Singular/plural may be inaccurate. 4/9/2014 5 boat. -+ I can use adjectives that express a non specific amount of objects in a place. I can use a variety of adjectives to express amounts of objects. There are many people. I can use adjectives that point out a specific object. 9|Page I can accurately use adjectives that point out a specific object. I can use a variety of adjectives to I can use a limited amount of express amounts of objects adjectives to express amount of Singular/plural may be objects. inaccurate. There is many peoples. a little/ a lot I can use numbers to express amount of objects. I can classify adjectives that point out specific objects as near or far. I can point to indicate specific objects. High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum I can classify objects as near and far, singular and plural. 4/9/2014 -+ Stage 3 Plan Learning Experiences and Instruction SAMPLE UNIT CALENDAR Day 1 Day 2 Vocabulary Vocabulary Day 6 Where does the ___ take place? (setting/story) Day 7 What are the characters/they doing? The ____ takes place in the _____. Day 11 How many ___ are ___(ing)? There are ___ (number) ___(people/children/etc) ___-ing at the ____ (location). There are four children playing at the park. Day 3 Vocabulary Day 8 What is ___ doing? The ____ takes place in the _____. Day 9 Where are you/they/proper nouns going? Day 13 Day 14 Prepositions Prepositions High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 There are ___ (number) ___(people/children/etc) ___ing at the ____ (location). Day 15 Where does the ___ take place? (setting/story) Yes, they are ___-ing… No, they are not ___-ing... The ____ takes place in the _____. The ____ takes place on a _____ . Day 10 How many ___ are ___(ing)? I am going to the _____. ___ are going to the _____. There are ____ (adjective of limit) _____ (people/children/etc) ____ing at the ___ (location). 10 | P a g e Are they ___(ing)...? Are they enjoying themselves? Day 5 Where does the ___ take place? (setting/story) ___ is ___-ing in the ____ The ____ is/are ____-ing. Day 12 Day 4 Where does the ___ take place? (setting/story) The ____ takes place on a _____ (preposition/prepositional phrase) a/the ____. The setting is at a ___ (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. -+ Day 16 What are the characters/they doing? Day 17 What is ___ doing? The ___ are ___-ing (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. 11 | P a g e ___ is ___ing (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ____. Day 18 Day 19 Where are you/they/proper nouns going? ___, ___, and ___ are going to the ___ (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum Where is ___? ____ is ____(prepositional phrase) the _____ (location). ____ is ____(prepositional phrase) the _____ (location) (preposition/prepositional phrase) the ___. 4/9/2014 Day 20 -+ DETAILED UNIT CALENDAR Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday OBJECTIVE LANGUAGE ACTIVITY MATERIALS 12 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 Friday -+ Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday OBJECTIVE LANGUAGE ACTIVITY MATERIALS 13 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 Friday -+ Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday OBJECTIVE LANGUAGE ACTIVITY MATERIALS 14 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 Friday -+ Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday OBJECTIVE LANGUAGE ACTIVITY MATERIALS 15 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 Friday -+ Superior Additional Activities I can use the present progressive to describe actions using (to be + verb -ing). I can use prepositional phrases to describe location. I can use specific nouns to describe locations in the community. I can use the present tense to ask questions. I can use exact numbers (+ singular/plural) to show the quantity of objects. I can use adjectives that express a non specific amount of objects in a place. I can use adjectives that point out a specific object. 16 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ Grammar Teacher Cheat Sheet: Verb to be Present Tense of verb to be I am We are You are You are He/She/It is They are Present Progressive [am/is/are + present participle] Examples: You are watching TV. Are you watching TV? You are not watching TV. Use for right now: Use the Present Continuous with normal verbs to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something is not happening now. Examples: You are learning English now. You are not swimming now. Are you sleeping? I am sitting. Prepositions A preposition links nouns, pronouns and phrases to other words in a sentence. The word or phrase that the preposition introduces is called the object of the preposition. Prepositional phrases Prepositions connect nouns, pronouns, and phrases with other words in a sentence. It gives information about location, direction, space, or time. Prepositions are usually part of a phrase because they often have a noun or pronoun after them. Here are two examples of prepositions in sentences. Examples: to the right of to the left of behind in front of on the corner near far from next to across the street from Adjective 17 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ Adjectives in English are not inflected (the endings do not change). In fact, English adjectives do not change at all, whether they are describing one or many of a noun, or whether they are describing females, males or things. For example: A tall man. / A tall woman. / A tall Tall trees. / Tall boys. / Tall girls. Notice that the adjective - here I am using the adjective tall - does not change in any of the examples. The order of adjectives Adjectives are used in a certain order. Watch how you can build up this adjective set. football boots. Old football boots. Three old football boots. Three old black Spanish football boots Three small old black Spanish football boots These three small old black Spanish football boots So the order is demonstrative, number, size, age, color, nationality and noun adjective.. We have not done participles. when we do these you will see that a participle can be used where the noun adjective is. When we use more than one adjective of a kind, we use commas to separate them. For example: A cold, windy autumn day. Here there are two adjectives of the same kind (cold and windy) and one of a different kind (autumn), because autumn is about time, not weather, so we do not use a comma between windy and autumn. You can put many adjectives before a noun, but English speakers do not usually use more than two or three, especially if they are adjectives of the same kind. Instead we put an extra part (usually a relative clause) afterward. For example: The big, scary house was dark and empty. / She had two black dogs which were noisy, messy and friendly. Adjectives of number and limit Numbers are usually adjectives, because the information they give is how many of the noun. They can be cardinal (like one, two, three), or ordinal (like first, second, third). For example: A thousand pounds. The second example. Sometimes numbers can look like nouns because of ellipsis (ellipsis is when you do not say all of the words in a sentence because the other person knows what the words will be). For example: Jane has one boyfriend, but Mary has two (boyfriends) one and two are both adjectives. Sometimes adjectives of number are not precise. For example: A few days. Many kinds of adjective. In grammar, adjectives of number come before most other kinds of adjective. 18 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ Adjectives used to point out (Demonstrative Adjectives) These are called demonstrative because they show something. The demonstrative adjectives are: this and that (singular), and these and those (plural). This and these mean "the one(s) here"; and that and those mean "the one(s) over there". For example: This apple here is green, that apple there is red. These examples are useful, and those given above are useful too. Demonstrative adjectives come even before adjectives of number. Simple sentences A simple sentence, also called an independent clause, contains a subject and a verb, and it expresses a complete thought. In the following simple sentences, subjects are in yellow, and verbs are in green. A. Some students like to study in the library. B. Juan and Arturo work at the bank. C. Alicia goes to the school and teaches every day. 19 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ ANCHOR CHARTS: 20 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014 -+ 21 | P a g e High School, Novice ESOL, Unit3 By Pedro Marquez with help from Lena Baucum 4/9/2014