Molecular Polarity Notes
advertisement

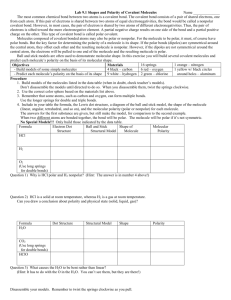
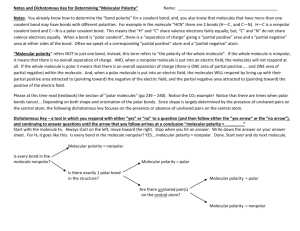
Polarity Polarity: Separation of charge by a distance. Molecular Polarity: Net imbalance of charge in a molecule (separation of + and – charge by a distance.) Molecule will have a partial + side and a partial – side. 1. If molecule has only 2 atoms: The polarity of the molecule is the same as the bond polarity. 2. If molecule has more that 2 atoms, molecular polarity is determined by: A. Bond Polarity Molecule must have at least 1 polar bond to be a polar molecule. Otherwise, it is nonpolar. (ex- Cl2) If there is at least 1 polar bond , must also consider the molecular shape. B. Molecular Shape 1. If Shape is symmetrical (all e- groups around central atom have the same electronegativity) then bond polarities cancel out, and molecule is NON Polar. Examples: Ex: HCl has a polar bond, is a polar molecule. Ex: Cl2 has a nonpolar bond, is a nonpolar molecule. 2. If shape is asymmetrical (e- groups around central atom are not all the same (electro negativities do not cancel out) then molecule is polar. Examples: CCl4 – Molecule is nonpolar. Although it has slightly polar bonds, the molecule is symmetrical. CHCl3 – Molecule is polar. Asymmetrical electronegativity differences. NH3 – Molecule is polar. The lone pair makes it asymmetrical. H2O – Molecule is polar. 2 lone pairs make it polar.



![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)