Chapter 8 Clicker A
advertisement

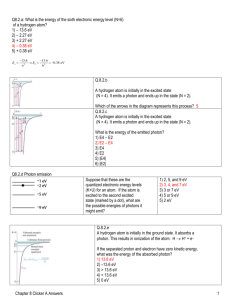
Q8.2.a: What is the energy of the sixth electronic energy level (N=6) of a hydrogen atom? 1) – 13.6 eV 2) – 2.27 eV 3) + 2.27 eV 4) – 0.38 eV 5) + 0.38 eV Q.8.2.b A hydrogen atom is initially in the excited state (N = 4). It emits a photon and ends up in the state (N = 2). Which of the arrows in the diagram represents this process? Q.8.2.c A hydrogen atom is initially in the excited state (N = 4). It emits a photon and ends up in the state (N = 2). What is the energy of the emitted photon? 1) E4 – E2 2) E2 – E4 3) E4 4) E2 5) |E4| 6) |E2| Q8.2.d Photon emission Suppose that these are the quantized electronic energy levels (K+U) for an atom. If the atom is excited to the second excited state (marked by a dot), what are the possible energies of photons it might emit? 1) 2, 5, and 9 eV 2) 3, 4, and 7 eV 3) 3 or 7 eV 4) 5 or 9 eV 5) 2 eV Q.8.2.e A hydrogen atom is initially in the ground state. It absorbs a photon. This results in ionization of the atom: H H+ + e– If the separated proton and electron have zero kinetic energy, what was the energy of the absorbed photon? 1) 13.6 eV 2) –13.6 eV 3) > 13.6 eV 4) < 13.6 eV 5) 0 eV Q8.2.f Photon absorption Imagine an atom which only has two electronic energy levels. The ground state energy is –3.0 eV and the excited state has an energy of –1.1 eV. 1) The detector will detect photons of all energies – none are missing. I irradiate a sample containing many atoms with 2) 1.1 eV visible light which contains photons of all energies 3) 3.0 eV and 1.1 eV from 1.8 eV up to 3.1 eV. 4) 3.0 eV 5) 1.9 eV What are the energies of the photons that are absorbed, and therefore are not detected in the outgoing light beam? Q8.2.g Electron excitation of a gas Suppose that these are the quantized energy levels (K+U) for an atom. Initially the atom is in its ground state (symbolized by a dot). An electron with kinetic energy 6 eV collides with the atom and excites it. What is the remaining kinetic energy of the electron? 1) 9 eV 2) 6 eV 3) 5 eV 4) 3 eV 5) 2 eV Q8.3.a Photon absorption, cold sample Light consisting of photons with a range of energies from 1 to 7.5 eV passes through this collection of objects. A collection of these atoms is kept very cold, so that all are in the ground state. What photon energies will be absorbed from the incoming light beam, and therefore will not be detected in the outgoing beam (“dark lines”)? 1) 2 eV, 5 eV, 9 eV 2) 3 eV, 4 eV 3) 0.5 eV, 3 eV, 4 eV 4) 4 eV, 7 eV 5) 3 eV, 4 eV, 7 eV 6) None of the above Q8.3.b Photon absorption, cold sample Light consisting of photons with a range of energies from 1 to 3 eV passes through this collection of objects. A collection of these atoms is kept very cold, so that all are in the ground state. What photon energies will be absorbed from the incoming light beam, and therefore will not be detected in the outgoing beam (“dark lines”)? 1) 2 eV, 5 eV, 9 eV 2) 3 eV, 4 eV 3) 0.5 eV, 3 eV, 4 eV 4) 4 eV, 7 eV 5) 3 eV, 4 eV, 7 eV 6) None of the above