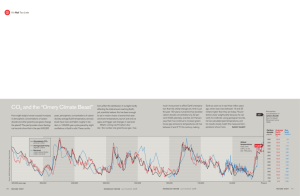
Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide From 2008-2012
advertisement

Name: __________________________________________ Block: ______ Date: ____________ LAB ACTIVITY Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Although carbon dioxide makes up only about 0.03 percent of the total volume of gases in Earth’s atmosphere, its impact on our climate appears to be significant. Scientists have little doubt that Earth was warmer in the past when carbon dioxide levels were higher. Thus, any increase in carbon dioxide levels today would be expected to result in a gradual increase in temperatures throughout the world. Not all carbon dioxid is the result of human activities. Carbon dioxide can be produced naturally. The respiration of animals and the decay of dead plants and animals are two sources. However, neither of these sources is significant when compared with the amount of carbon dioxide released by the burning of fossil fuels as coal, oil, and natural gas. Atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations have been measured for many years. The longest continuous record comes from air samples taken on Mauna Loa, an inactive volcano and the highest peak in Hawaii. LAB SKILLS AND OBJECTIVES Plot several years of carbon dioxide data. Compare and Contrast recent data with older data. MATERIALS Colored pencils Straightedge Calculator Global Surface Temperatures Change graph, Chapter 21, page 476 of your textbook Procedures 11.. Choose a colored pencil and plot the data in the Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide from 2008-2012 data table on the grid provided. Connect the points by drawing straight lines between adjacent points with your straightedge. 22.. Use a calculator to complete the upper data table by calculating the annual average for each of the years from 2008-2012. The annual average is computed by summing the concentrations for all 12 months and dividing by 12. 33.. Use a second colored pencil and a straightedge to plot the annual average on the grid for each of the five years from 2008-2012. Place the straightedge horizontally across the grid at the appropriate concentrations, and then draw a line at the value across the grid boxes that represent the appropriate year. 44.. Use a different color pencil for each data set and straightedge to plot the annual average on the second grid (title annual average concentration from 1959-1963, 1996-2000, and 2008-2012). Place the straightedge horizontally across the grid at the appropriate concentrations, and then draw a line at the value across the grid boxes that represent the appropriate year. Analysis and Conclusions 11.. During which month or months does the minimum value for atmospheric CO2 concentration occur for the years 2008-2012? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 22.. During which month or months does the maximum value for atmospheric CO2 concentration occur for the years 2008-2012? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 33.. Based on your knowledge of the relationship between photosynthesis and CO2, explain why CO2 concentrations cycle throughout the year. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 44.. Based on your knowledge of the relationship between the burning of fossil fuels and CO2, another reason for the cyclic nature of CO2 concentration throughout the year. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 55.. Look at the data table for atmospheric CO2 concentrations for the years 1959-1963. In parts per million, by how much did the annual average increase between 1959 and 1963? What was the largest increase between two years during the period from 1959-1963? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 66.. In parts per million, by how much did the annual average increase between 1996 and 2000? What was the largest increase between two years during the period from 1996-2000? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 77.. In parts per million, by how much did the annual average increase between 2008 and 2012? What was the largest increase between two years during the period from 2008-2012? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 88.. Based on your answers to Questions 5, 6 and 7, how is the trend in CO2 concentrations changing over time? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 99.. Name two ways that the increase in atmosphere CO2 concentrations could be slowed down. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 1100.. Look at the Global Surface Temperature Change graph on page 476 of your textbook. How does the trend in surface temperatures from 1960-2000 compare with the trend in CO2 concentrations? Does this prove that increasing CO2 concentrations are the cause of rising temperatures? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide From 2008-2012 Month JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC Annual Average 2008 385.44 385.73 385.97 387.16 388.50 387.88 386.42 384.15 383.09 382.99 384.13 385.56 Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Concentrations (ppm) 2009 2010 2011 386.94 388.50 391.25 387.42 389.94 392.82 388.77 391.09 392.49 389.44 392.52 393.34 390.19 393.04 394.21 389.45 392.15 393.72 387.78 390.22 392.42 385.92 388.26 390.19 384.79 386.83 389.04 384.39 387.20 388.96 386.00 388.65 390.24 387.13 389.73 391.83 2012 393.12 393.60 394.45 396.18 396.78 395.83 394.30 392.41 391.06 391.01 392.82 394.28 Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide From 1996-2000 Month JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC Annual Average 1996 362.04 363.17 364.17 364.51 365.16 364.93 363.53 361.38 359.60 359.54 360.84 362.18 362.59 Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Concentrations (ppm) 1997 1998 1999 363.04 365.18 368.12 364.09 365.98 368.98 364.47 367.13 369.60 366.25 368.61 370.96 366.69 369.49 370.77 365.59 368.95 370.33 364.34 367.74 369.28 362.20 365.79 366.86 360.31 364.01 364.94 360.71 365.35 365.35 362.44 365.52 366.68 364.33 367.08 368.04 363.71 366.74 368.33 2000 369.25 369.50 370.56 371.82 371.51 371.71 369.85 368.20 366.91 366.99 368.13 369.67 369.51 Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide From 1959-1963 Month JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC Annual Average 1959 315.62 316.38 316.71 317.72 318.29 318.15 316.54 314.80 313.84 313.26 314.80 315.58 315.97 Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Concentrations (ppm) 1960 1961 1962 316.43 316.93 317.94 316.97 317.70 318.56 317.58 318.54 319.68 319.02 319.48 320.63 320.03 320.58 321.01 319.59 319.77 320.55 318.18 318.57 319.58 315.91 316.79 317.40 314.16 314.80 316.26 313.83 315.38 315.42 315.00 316.10 316.69 316.19 317.01 317.69 316.91 317.64 318.45 1963 318.74 319.08 319.86 321.39 322.25 321.47 319.74 317.77 316.21 315.99 317.12 318.31 318.99