AVMA core competence 6: Emergency and intensive
advertisement

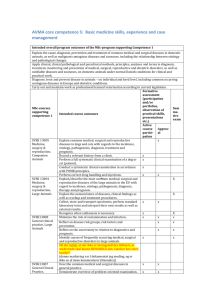
AVMA core competence 6: Emergency and intensive care case management Intended overall program outcomes of the MSc-program supporting Competence 1 Explain the cause, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of common medical and surgical diseases in domestic animals, as well as malignant contagious diseases and zoonoses, including the relationship between etiology and pathological changes. Apply clinical, clinical pathological and paraclinical methods, principles, analyses and terms in diagnosis, treatment, monitoring and prevention of medical, surgical, reproductive and obstetric disorders, as well as notifiable diseases and zoonoses, on domestic animals under normal Danish conditions for clinical and practical work. Diagnose, treat and prevent disease in animals – on individual and herd level, including common occurring contagious diseases in Europe and obstetric conditions. Carry out and maintain work as professional licensed veterinarian according to current legislation. BSc-courses supporting competence 1 Intended course outcomes SVEK 13005 Medicine, surgery & reproduction, Companion Animals SVEK 13004 Medicine, surgery & reproduction, Large Animals Perform a full systematic clinical examination of a dog or cat (patient). SVEK13008 General clinical practice, Large Animals SVEK13001 Veterinary Paraclinics Formative assessment (participation and/or portfolios, observation of practical skills, presentations etc.) Active Approv course al participation x Sum mative exam Draw up a prioritized list of problems and formulate a meaningful diagnostic and therapeutical plan for a patient with a medical, surgical and/or reproductive problem. Recognize when euthanasia is necessary. Participate in emergency work and be able to perform basic first aid. x x Explain functions and main disorders of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets; and the appropriate procedures to evaluate these cells in a blood smear. Interpret common clinical pathological and microbiological test results. Explain the principles of routine diagnostic methods. Prepare a blood smear. Identify healthy and abnormal erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. Perform a leukocyte differential count. Perform urinalysis (sticks, refractometry, sediment analysis). Assess quality of cytological specimens. Identify and classify inflammatory reactions in cytological specimens. Identify and classify neoplastic tissue types and criteria of malignancy in cytological specimens. Perform and interpret antimicrobial susceptibility tests. Perform clear case reports’ (Denne var oversat når jeg fik dokumenterne, men jeg X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X x SVEK13002 Emergency, obstetrics, critical care, clinical anesthesiology MSc-elective courses supporting competence 1 SVEK13013 Advanced companion animals SVEK13020 Equine Clinic SVEK13010 Biomedicine forstår ikke hvad de mener). Choose appropriate samples and methods for laboratory analysis Be able to perform emergency life-saving procedures on large animals including acute wound treatment and acute abdominal treatments, as well as cesarean section in cattle. Be able to perform emergency life-saving procedures in small animals, including pericardiocentesis, thoracocentesis, cardiopulmonary resuscitation and urinary catheterization when there is obstruction. Be able to identify, diagnose and treat the most common emergency cases in relevant animal species, including: severe dehydration, obstetric problems, shock, bleeding, open wounds, respiratory crises, pericardial effusions, obstruction of the urinary tract, eye injuries, burns, tissue trauma, trauma to the limbs and trauma to internal organs. To independently diagnose and treat life threatening conditions. For the most important treatments in specialized companion animal practice, to be able to explain indications, treatment principles, mechanisms of action, technical procedures including anesthesia and surgery and complications and adverse effects. All emergency cases admitted to the hospital are handled by the students in collaboration with a veterinarian. All emergency cases seen in the field practice are handled by the students in collaboration with a veterinarian. Be able to design, execute, evaluate and manage experimental animal research projects. Use theoretical and practical methodology in laboratory experiments employing live animals. x x X X x x x x x x x x x x x x