15.3 Gas Exchanges in the Body - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
advertisement

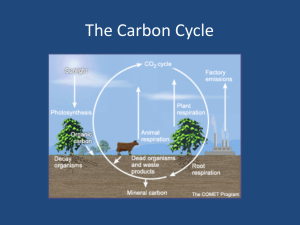
15.3 Gas Exchanges in the Body 1. Overview a. Diffusion is the underlying reason why O2 or CO2 enters or leaves the blood in the lungs and in the tissues. 2. External Respiration a. The exchange of gases between the air in the alveoli and blood in the pulmonary capillaries b. Partial pressure: the pressure each gas exerts i. PO2 = partial pressure of oxygen ii. PCO2 = partial pressure of carbon dioxide c. In the blood of the pulmonary capillaries, PCO2 > PO2 , therefore CO2 diffuses out of the plasma into the lungs and O2 diffuses out of the lungs and into the plasma of the blood. d. CO2 i. Most CO2 is carried by the blood as the bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) ii. As CO2 diffuses out, more HCO3- becomes CO2 through the following reaction: H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 H20 + CO2 Hydrogen ion + bicarbonate ion carbonic acid water and carbon dioxide Carbonic anhydrase (an enzyme) speeds up the breakdown of H2CO3 e. Hyperventilation i. Breathing at a high rate ii. Reaction is pushed too far to the right iii. Blood has fewer hydrogen ions, so pH becomes too high (alkaline) = alkalosis iv. Symptoms: dizziness, uncontrolled muscle contractions v. Buffers bring down pH or coma and/or death may result f. O2 i. blood in the pulmonary capillaries is low in oxygen and alveolar sacs contain a higher partial pressure of oxygen ii. O2 diffuses into the plasma and then into the red blood cells in the lungs iii. Hemoglobin (Hb) carries the oxygen and becomes oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) Hb + O2 HbO2 g. Actual gas use in external respiration i. Inhaled air has about 21% O2, exhaled air still contains 16-17% O2 ii. Explains why artificial respiration can work 3. Internal Respiration a. Refers to the exchange of gases between the blood in systemic capillaries and the tissue fluid b. Brings O2 to cells and removes CO2 from cells c. Needed for ATP production d. Oxygen diffuses out of the blood into the tissues b/c PO2 is higher outside the cells than inside the cells. This is because O2 is continually being used in cellular respiration. e. Carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood from the tissues b/c PCO2 is higher inside the cells than outside the cells. This is because CO2 is being continually produced by cellular respiration. f. The reverse reactions with hemoglobin and carbonic anhydrase occur compared to external respiration Answer p.291 #1-2 15.3 Gas Exchanges in the Body 1. Overview a. ____________________ is the underlying reason why O2 or CO2 enters or _________________ the blood in the _________________ and in the tissues. 2. External Respiration (blood and lungs) a. The ________________ of gases between the air in the _________________ and blood in the _________________ capillaries b. _________________ pressure: the pressure each gas exerts i. PO2 = partial pressure of _________________ ii. PCO2 = partial pressure of _______________ _______________ c. In the blood of the _________________ capillaries, PCO2 > PO2 , therefore _________________ diffuses _________________ of the plasma into the _________________ and O2 diffuses out of the lungs and into the plasma of the blood. d. CO2 i. Most CO2 is carried by the _________________ as the _________________ ion (HCO3-) ii. As CO2 _________________ out, more HCO3- becomes CO2 through the following reaction: + H + HCO3- H2CO3 H20 + CO2 Hydrogen ion + bicarbonate ion carbonic acid water and carbon dioxide Carbonic _________________ (an enzyme) speeds up the breakdown of H2CO3 e. Hyperventilation i. Breathing at a _________________ rate ii. Reaction is pushed too far to the right iii. Blood has _________________ hydrogen ions, so pH becomes too _________________ (alkaline) = _________________ iv. Symptoms: dizziness, uncontrolled muscle _________________ v. Buffers bring _________________ pH or coma and/or death may result f. O2 i. blood in the _________________ capillaries is _________________ in oxygen and alveolar sacs contain a _________________ partial pressure of oxygen ii. O2 _________________ into the plasma and then into the red blood cells in the lungs iii. Hemoglobin (Hb) carries the oxygen and becomes _________________ (HbO2) Hb + O2 HbO2 g. Actual gas use in external respiration i. Inhaled air has about ________% O2, exhaled air still contains _____-_____ O2 ii. Explains why artificial respiration can work 3. Internal Repiration (blood and cells) a. Refers to the exchange of gases between the blood in _________________ capillaries and the _________________ fluid b. Brings O2 to _________________ and _________________ CO2 from cells c. Needed for _________ production d. Oxygen diffuses _________ of the blood into the tissues b/c PO2 is _________________ outside the cells than _________________ the cells. This is because O2 is continually being used in _________________ respiration. e. Carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood from the tissues b/c PCO2 is _________________ inside the cells than _________________ the cells. This is because CO2 is being continually _________________ by cellular respiration. f. The reverse reactions with hemoglobin and carbonic anyhydrase occur compared to external respiration Helpful review: http://quizlet.com/13901560/gas-exchange-flash-cards/ Answer p.291 #1-2