Rocks packet - WordPress.com
advertisement

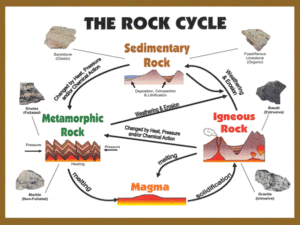
Period:_____ Rocks ummm… Rock!!! You will need this packet for the WHOLE rock unit…please do not lose it! Section 5.1: Classifying Rocks 1. To identify a rock, you have to look at three things: a. Mineral composition: ______________________________________________. b. Color c. Texture is ______________________________________________. This is usually determined by the grains in the rock; the particles of minerals or other rocks. Retrieved from: http://www.cartoonstock.com/newscartoons/cartoonists/rma/lowres/rman3573l.jpg Name:_______________________________________ 2. By identifying the rock, you can determine a rock’s origin, which is________________________________________. 3. There are 3 major groups into which a rock can be classified: a. Igneous rocks form _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________. 1 Name:_______________________________________ Period:_____ b. Sedimentary rocks form _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________. c. Metamorphic rocks form _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________. Retrieved from: http://rlv.zcache.com/pet_rock_cartoon_mousepad-p144131944500712245envq7_400.jpg *~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~* Section 5.2: Igneous Rocks 1. Igneous rocks are classified according to their a. ____________________ b. ____________________ c. ____________________ ____________________. 2. The origin of an igneous rock is determined by _______________________________________________. a. If an igneous rock is extrusive, it formed from _______________________________________. b. If an igneous rock is intrusive, it formed from _______________________________________. 2 Name:_______________________________________ Period:_____ The most abundant intrusive rock in the continental crust is granite. 3. The texture of an igneous rock depends on _________________________________________________. 4. Mineral composition will usually determine the __________ of the rock. Could two igneous rocks have the same mineral composition and have different textures? ______ (Hint: Think back to mineral formation) Why? ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________. *~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~* Section 5.3: Sedimentary Rocks 1. Sedimentary rocks are formed by a series of processes: Retrieved from: http://images.nationalgeographic.com/wpf/medialive/photos/000/008/cache/arizona-rock_824_600x450.jpg When destructive forces (________________________________, _________, or __________) loosen/break off and ___________________________ ______________________________________________. The fragments of rock are referred to as _________________. 3 Name:_______________________________________ Period:_____ Retrieved from: http://memberfiles.freewebs.com/42/50/74975042/photos/Explorationand-Production/Sediment%20Deposition.jpg The sediment is carried until __________________________ _________________________________________________. Retrieved from: http://www.learner.org/courses/essential/earthspace/images/show2_sed_layer_model.jpg Over time, layers of sediment develop and form on top of one another, and ______________________________ ______________________________. You can usually see these layers in sedimentary rock. 4 Name:_______________________________________ Period:_____ Retrieved from: http://regentsearth.com/Tests/Clips/sedimentary.gif Any water that is trapped in the ground with the rocks and in the rocks will slowly _____________________ _____________________, and the minerals will crystallize in the open spaces and _________________________________________________. 2. There are three types of sedimentary rocks: a. Clastic b. Organic c. Chemical Section 5.5: Metamorphic Rocks 1. Metamorphic rocks are classified by __________________ ____________________________. 2. A foliated rock has its grains arranged ________________ ________________________ 3. A nonfoliated rock has its grains arranged _______________________________________________. Retrieved from: http://images.fineartamerica.com/images-medium-large/gneiss-rock-les-palenik.jpg *~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~* 5 Name:_______________________________________ Period:_____ Retrieved from: http://www.cotf.edu/ete/images/modules/msese/earthsysflr/EFCycleP2.gif Section 5.6: The Rock Cycle!! Plate tectonics are a huge help to the rock cycle!!! 1. Plate movements start the rock cycle by __________________________________________. 2. Plate movements also cause __________________________, which contribute to forming sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. 6