SYLLABUS COURSE TITLE Inorganic chemistry Faculty/Institute
advertisement
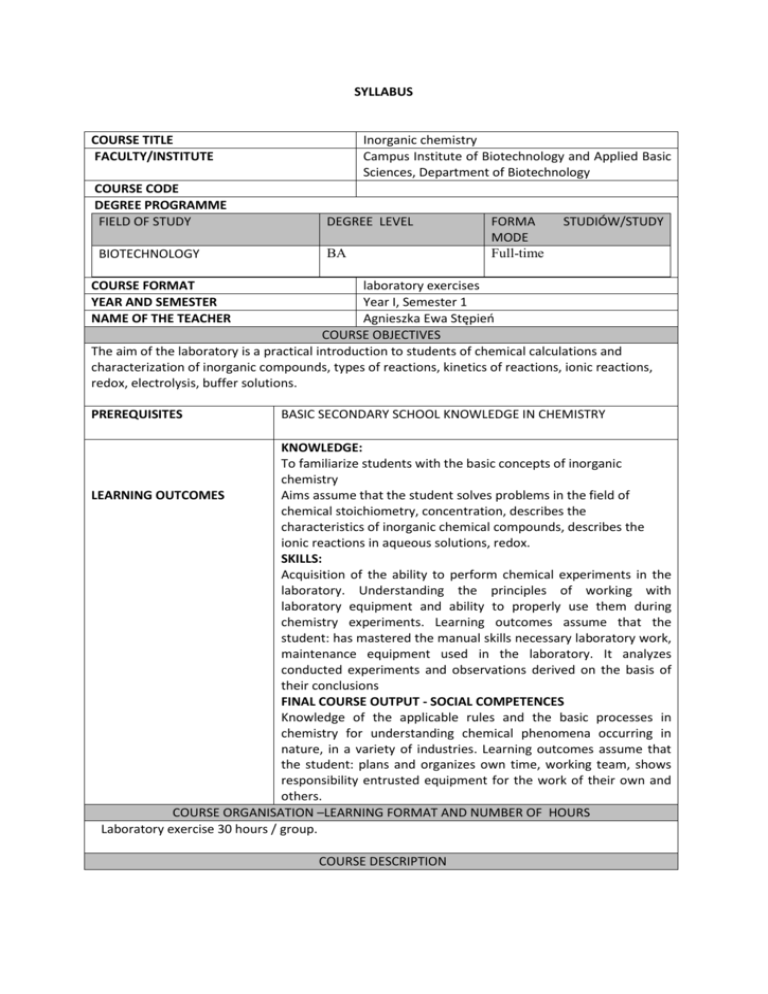
SYLLABUS COURSE TITLE FACULTY/INSTITUTE Inorganic chemistry Campus Institute of Biotechnology and Applied Basic Sciences, Department of Biotechnology COURSE CODE DEGREE PROGRAMME FIELD OF STUDY DEGREE LEVEL BIOTECHNOLOGY BA FORMA MODE Full-time STUDIÓW/STUDY COURSE FORMAT YEAR AND SEMESTER NAME OF THE TEACHER laboratory exercises Year I, Semester 1 Agnieszka Ewa Stępień COURSE OBJECTIVES The aim of the laboratory is a practical introduction to students of chemical calculations and characterization of inorganic compounds, types of reactions, kinetics of reactions, ionic reactions, redox, electrolysis, buffer solutions. PREREQUISITES BASIC SECONDARY SCHOOL KNOWLEDGE IN CHEMISTRY KNOWLEDGE: To familiarize students with the basic concepts of inorganic chemistry LEARNING OUTCOMES Aims assume that the student solves problems in the field of chemical stoichiometry, concentration, describes the characteristics of inorganic chemical compounds, describes the ionic reactions in aqueous solutions, redox. SKILLS: Acquisition of the ability to perform chemical experiments in the laboratory. Understanding the principles of working with laboratory equipment and ability to properly use them during chemistry experiments. Learning outcomes assume that the student: has mastered the manual skills necessary laboratory work, maintenance equipment used in the laboratory. It analyzes conducted experiments and observations derived on the basis of their conclusions FINAL COURSE OUTPUT - SOCIAL COMPETENCES Knowledge of the applicable rules and the basic processes in chemistry for understanding chemical phenomena occurring in nature, in a variety of industries. Learning outcomes assume that the student: plans and organizes own time, working team, shows responsibility entrusted equipment for the work of their own and others. COURSE ORGANISATION –LEARNING FORMAT AND NUMBER OF HOURS Laboratory exercise 30 hours / group. COURSE DESCRIPTION Exercise organizational-safety regulations and rules of the chemistry. Basic chemical calculations. Systematics of inorganic compounds. Types of chemical reactions: synthesis, analysis, exchange. The reactivity of the resulting metal in a series of voltage position. Preparation of solutions of the desired concentration. Effects of temperature, catalyst concentration and the rate of chemical reactions. Salt hydrolysis reactions. Constant and the degree of hydrolysis. Properties of selected cations, anions. The processes of oxidation - reduction (redox). Acid-base titration. METHODS OF INSTRUCTION REQUIREMENTS AND ASSESSMENTS GRADING SYSTEM TOTAL STUDENT WORKLOAD NEEDED TO ACHIEVE EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES EXPRESSED IN TIME AND ECTS CREDIT POINTS Laboratory exercises: work in groups Assessment of laboratory: obtaining a positive evaluation of the test involved, presence, performing experiments in the classroom and complex reports 2-5 Exercise 23 hours. Preparing to exercise 45 hours. Participation in consultation 5 hours. Time to write reports 15 hours. LANGUAGE OF INSTRUCTION INTERNSHIP MATERIALS TOTAL HOURS 88 NUMBER OF CREDITS ECTS 4 ENGLISH PRIMARY OR REQUIRED BOOKS/READINGS: 1.Kathleen A. House , James E. House, Descriptive Inorganic Chemistry, Academic Press 2011 2. Pauling L., P. Pauling, Chemistry 3. Julie Fisher, John R.P. Arnold, Chemistry for biologists. Short lectures 4.P. A. Cox, Short lectures. Inorganic Chemistry SUPPLEMENTAL OR OPTIONAL BOOKS/READINGS: 1.McMurry, John E., Fay, Robert C., Chemistry with MasteringChemistry (6th Edition) (MasteringChemistry Series), Prentice Hall 2011 2. F. Albert Cotton, Geoffrey Wilkinson, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated, 1999