Final Exam Written Review Answers
advertisement

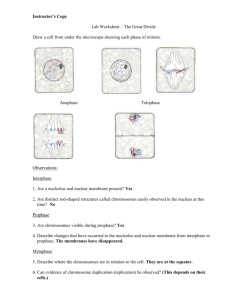
Semester 1 Final WRITTEN REVIEW-answers Name: Complete the following questions to review major topics we’ve covered this semester. You can write some of your answers on your cheat sheet too 1. What are the differences between the following microscopes: TEM, SEM, light microscope (chapter 1) SEM -3D image produced; TEM-2D image produced SEM-scans the surface of a specimen with electron beams TEM-transmits beams of electrons through specimen light microscope: lower magnification and resolution but uses visible light. 2. What is the difference between resolution and magnification? Magnification is simply the number of times an image's size is enlarged. Resolution is a measurement of how well the smallest details of an image can be discerned. 3. List the 7 characteristics of living things. Cells, Movement (response to stimuli), homeostasis, metabolism, Reproduction, growth and development, Genetics and heredity 4. If an atom has 11 protons, 12 neutrons and 11 electrons, what is it’s a)atomic number, b)atomic mass, c) name of element? a)AN = 11, b)AM=23, c)Sodium 5) What is the difference between metals and nonmetals? Where do you find them on the periodic table? On many periodic tables, a jagged black line /stair steps along the right side of the table separates the metals from the nonmetals. The metals are to the left of the line (except for hydrogen, which is a nonmetal), the nonmetals are to the right of the line, and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids. 6) How do you say the ionic compound:K3N? ______________Potassium Nitride___________________ 7) How do you say the covalent compound: N2S3 __________________dinitrogen trisulfide__________________________ 8) What is the difference between acids/bases/neutral? How many times more acidic is a substance that is 3 vs. a substance with a pH of 6? Acids are between 0 and 7, Bases (Alkaline) are between 7 and 14 on pH Scale. Neutral substances are 7 on pH scale. A substance with pH 3 is 1000 times more acidic than a substance with pH 6. 9) What do the following organelles do? Mitochondria, chloroplast, lysosome, Rough ER, smooth ER? Mitochondria: powerhouse of cell, chloroplast: produces glucose through photosynthesis, lysosome: contains enzymes that help to digest old cell parts or foreign material, Rough ER: ribosomes are studded on here and ER provides transportation highway for proteins, Smooth ER: makes hormones and lipids in cells 10) What is the difference between active and passive transport? What are the different categories of each? Active transport requires energy to move items across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient (from low to high). Passive transport moves items across the cell membrane from high to low concentration (with the concentration gradient). Passive Transport types: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion. Active Transport types: Endocytosis, Exocytosis and Protein Pumps (like sodium potassium pumps) 11) What are the main differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) do not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles; reproduce by binary fission. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and organelles; cell reproduction mostly by mitosis and meiosis 12) What are the main differences between plant and animal cells? Animal cells have many different shapes, are usually mobile, contain centrioles and more lysosomes/peroxisomes. Plant cells have more rigid shape, contain cell membrane and central vacuole and chloroplast. Both are eukaryotic cells in Domain Eukarya 13) What is the difference between hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic? When will water move into and out of a cell? Hypertonic environment: more solute/less water when compared to the cell; hypotonic environment: less solute/more water when compared to the cell; isotonic environment: same solute/water as a cell. When placed in hypotonic environment, water moves into the cell from area of high to low concentration, cell swells When placed in hypertonic environment, water moves out of a cell from an area of high to low concentration, cell shrinks When placed in isotonic environment, water moves in and out equally, cell stays same size. 14) What are the differences between the way euglena, amoeba, and paramecium move? How do they feed? How else are they different? euglena: moves with flagella, both autotrophic and heterotrophic (eyespot detects light for photosynthesis) amoeba: moves with pseudopod, heterotrophic (engulfs food with pseudopod) paramecium: moves with cilia, heterotrophic (sweeps food into oral groove with cilia) 15) Describe differences between the structures of: amino acid, nucleic acid, monosaccharide, fatty acid amino acid composed of C,H,O,N, (S) and is the monomer of a protein. A nucleic acid is DNA or RNA. The monomer of a nucleic acid is a nucleotide (C,H,O,N,P) monosaccharide is monomer of carbohydrate (composed of C,H,O); ring shaped; ex. Are glucose and fructose fatty acid is monomer of a lipid (fat). Composed of C,H,O and is in chains. 16)What are the steps of mitosis. Briefly describe what happens in each. Cell Cycle: 1)Interphase: G1: organelles copy, S: DNA copies, G2: cell grows 2) Mitosis: A)Prophase (spindles form, nuclear membrane disappears, chromatin condenses) B)Metaphase (chromosomes line up on equator), C)Anaphase (chromosomes separate at centromere and sister chromatids move to opposite poles, D)Telophase (chromosomes uncoil, spindle fibers disappear, nuclear membrane reforms) 3) Cytokinesis: separation of cytoplasm between daughter cells 17) What are the steps of meiosis? Briefly describe what happens in each. 1)Interphase: G1: organelles copy, S: DNA copies, G2: cell grows 2) Meiosis I: A)Prophase I(spindles form, nuclear membrane disappears, chromatin condenses into chromosomes that pair up in homologous pairs or tetrads, crossing over occurs), B)Metaphase I (homologous pairs line up on equator), C)Anaphase I (tetrads separate and homologs move to opposite poles, D)Telophase I and Cytokinesis(chromosomes begin to uncoil, spindle fibers disappear, nuclear membrane reforms, 2 cells result 3) Meiosis II: A)Prophase II (spindles form, nuclear membrane disappears, chromosomes condense), B)Metaphase II (chromosomes line up on equator), C)Anaphase II (chromosomes separate at centromere and sister chromatids move to opposite poles, D)Telophase II and Cytokinesis(chromosomes uncoil, spindle fibers disappear, nuclear membrane reforms, 4 new haploid cells) 18) What are the products of meiosis? How many? Are they haploid or diploid? 4 haploid daughter cells 19) What kinds of things can you tell from a karyotype? Number of chromosomes (both haploid and diploid), sex (boys are XY, girls are XX), whether diseases or disorders are present (too few or too many chromosomes indicate a disorder) 20)What are the three domains in the classification system? What are the kingdoms? Domains: Eukarya, Bacteria, Archaea Kingdoms: 1. Bacteria, 2. Archaea, 3. Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista (all Eukarya Domain) 21) What are the different parts of the microscope? And what do they do? 21) Please balance the following chemical reaction: +1 -1 2NaCl +2 -2 + MgS +1 -2 Na2S +2 -1 + MgCl2 22) What is the job of enzymes? Proteins / catalysts that speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy. Enzymes usually end in “–ase”. Proteases break down proteins. Lipases break down lipids. Amylases break down starches/carbohydrates. Enzymes join their substrate (what they are breaking down) at the active site. 23) What are the major parts of the digestive system? Name them in order. Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine (Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum), Large intestine (ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon), rectum, anus Accessory organs: liver (makes bile), gall bladder (stores bile), pancreas (make and release digestive enzymes into the duodenum to digest food) 24) What are the major enzymes in the digestive system? What do they do? salivary amylase: released in mouth, breaks down starch in mouth pepsin: released from stomach, breaks down proteins in stomach lipase, trypsin, amylase: enzymes that act on fats, proteins and carbohydrates in small intestine (some released by pancreas) 25) What is the difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic? Organisms that make their own food are autotrophic. Organisms that hunt for their food or get it elsewhere are heterotrophic.