Y5 Grammar & Punctuation NC
advertisement
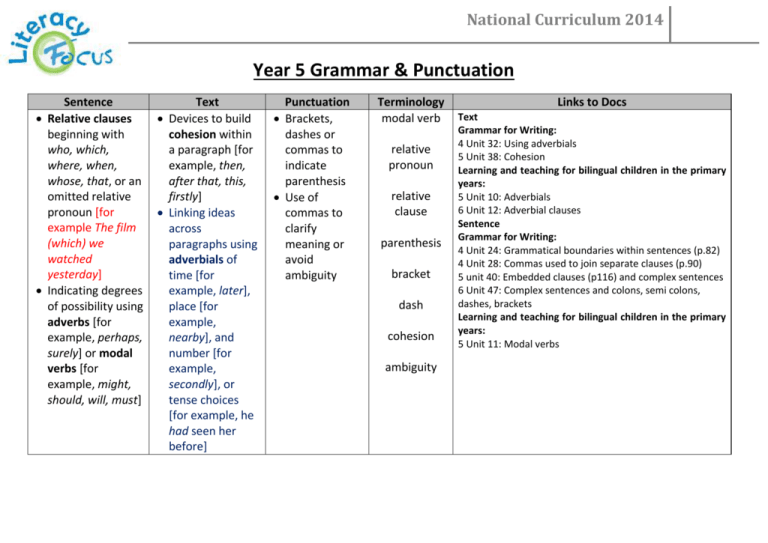
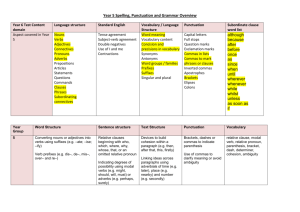
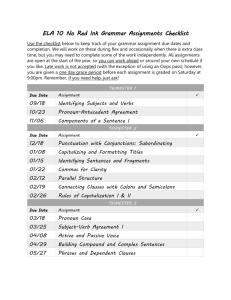
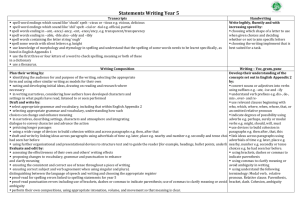
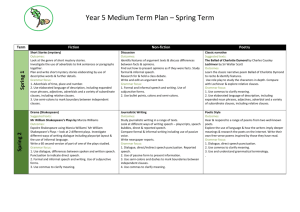
National Curriculum 2014 Year 5 Grammar & Punctuation Sentence Relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that, or an omitted relative pronoun [for example The film (which) we watched yesterday] Indicating degrees of possibility using adverbs [for example, perhaps, surely] or modal verbs [for example, might, should, will, must] Text Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph [for example, then, after that, this, firstly] Linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials of time [for example, later], place [for example, nearby], and number [for example, secondly], or tense choices [for example, he had seen her before] Punctuation Brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis Use of commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity Terminology modal verb relative pronoun relative clause parenthesis bracket dash cohesion ambiguity Links to Docs Text Grammar for Writing: 4 Unit 32: Using adverbials 5 Unit 38: Cohesion Learning and teaching for bilingual children in the primary years: 5 Unit 10: Adverbials 6 Unit 12: Adverbial clauses Sentence Grammar for Writing: 4 Unit 24: Grammatical boundaries within sentences (p.82) 4 Unit 28: Commas used to join separate clauses (p.90) 5 unit 40: Embedded clauses (p116) and complex sentences 6 Unit 47: Complex sentences and colons, semi colons, dashes, brackets Learning and teaching for bilingual children in the primary years: 5 Unit 11: Modal verbs