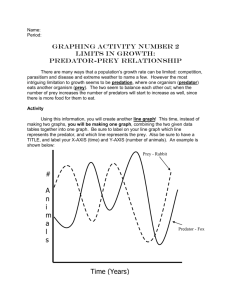
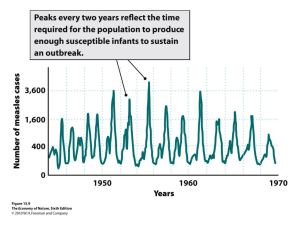
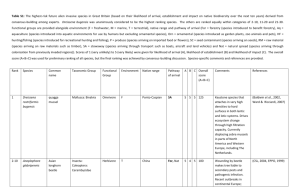
ele12496-sup-0003-AppendixC
advertisement

Appendix C. List of references of studies included in the meta-analysis. List includes studies that evaluated the effect of a toxic prey. 1. Adams, C.E. & Mitchell, J. (1995). The response of a grey heron Ardea cinerea breeding colony to rapid change in prey species. Bird Study, 42, 44-49. 2. Barber, N.A., Marquis, R.J. & Tori, W.P. (2008). Invasive prey impacts the abundance and distribution of native predators. Ecology, 89, 2678-2683. 3. Brown, G.P., Phillips, B.L. & Shine, R. (2011). The ecological impact of invasive cane toads on tropical snakes: Field data do not support laboratory-based predictions. Ecology, 92, 422431. 4. Butler, C.D. & O'Neil, R.J. (2007). Life history characteristics of Orius insidiosus (Say) fed Aphis glycines Matsumura. Biological Control, 40, 333-338. 5. Carrillo, D., Pena, J.E., Hoy, M.A. & Frank, J.H. (2010). Development and reproduction of Amblyseius largoensis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) feeding on pollen, Raoiella indica (Acari: Tenuipalpidae), and other microarthropods inhabiting coconuts in Florida, USA. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 52, 119-129. 6. Cattau, C.E., Martin, J. & Kitchens, W.M. (2010). Effects of an exotic prey species on a native specialist: Example of the snail kite. Biological Conservation, 143, 513-520. 7. Cole, F.R., Medeiros, A.C., Loope, L.L. & Zuehlke, W.W. (1992). Effects of the argentine ant on arthropod fauna of hawaiian high-elevation shrubland. Ecology, 73, 1313-1322. 8. Cottrell, T.E. (2004). Suitability of exotic and native lady beetle eggs (Coleoptera : Coccinellidae) for development of lady beetle larvae. Biological Control, 31, 362-371. 9. Coulas, R.A., Macisaac, H.J. & Dunlop, W. (1998). Selective predation on an introduced zooplankter (Bythotrephes cederstroemi) by lake herring (Coregonus artedii) in Harp Lake, Ontario. Freshwater Biology, 40, 343-355. 10. Crossland, M.R. (2000). Direct and indirect effects of the introduced toad Bufo marinus (Anura : Bufonidae) on populations of native anuran larvae in Australia. Ecography, 23, 283-290. 11. Degerman, E., Nilsson, P.A., Nystrom, P., Nilsson, E. & Olsson, K. (2007). Are fish populations in temperate streams affected by crayfish? - A field survey and prospects. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 78, 231-239. 12. Dijkstra, J.A., Lambert, W.J. & Harris, L.G. (2013). Introduced species provide a novel temporal resource that facilitates native predator population growth. Biological Invasions, 15, 911919. 13. Doody, J.S., Green, B., Rhind, D., Castellano, C.M., Sims, R. & Robinson, T. (2009). Population-level declines in Australian predators caused by an invasive species. Animal Conservation, 12, 46-53. 14. Escudero, L.A. & Ferragut, F. (2005). Life-history of predatory mites Neoseiulus californicus and Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari : Phytoseiidae) on four spider mite species as prey, with special reference to Tetranychus evansi (Acari : Tetranychidae). Biological Control, 32, 378-384. 15. Glenn, S. & Holway, D. (2008). Consumption of introduced prey by native predators: Argentine ants and pit-building ant lions. Biological Invasions, 10, 273-280. 16. Griffiths, A.D. & McKay, J.L. (2007). Cane toads reduce the abundance and site occupancy of Merten's water monitor (Varanus mertensi). Wildlife Research, 34, 609-615. 17. Hagman, M., Phillips, B.L. & Shine, R. (2009). Fatal attraction: adaptations to prey on native frogs imperil snakes after invasion of toxic toads. Proceedings of the Royal Society BBiological Sciences, 276, 2813-2818. 18. Hatherly, I.S., Bale, J.S. & Walters, K.F.A. (2005). Intraguild predation and feeding preferences in three species of phytoseiid mite used for biological control. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 37, 43-55. 19. Hogan, L.S., Marschall, E., Folt, C. & Stein, R.A. (2007). How non-native species in Lake Erie influence trophic transfer of mercury and lead to top predators. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 33, 46-61. 20. Kajita, Y., Takano, F., Yasuda, H. & Evans, E.W. (2006). Interactions between introduced and native predatory ladybirds (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae): factors influencing the success of species introductions. Ecological Entomology, 31, 58-67. 21. Kamo, T., Tokuoka, Y. & Miyazaki, M. (2010). Influence of aphid-host plant pairs on the survivorship and development of the multicolored Asian ladybird beetle: implications for the management of vegetation in rural landscapes. Ecological Research, 25, 1141-1149. 22. Kelly, D.W. & Dick, J.T.A. (2005). Introduction of the non-indigenous amphipod Gammarus pulex alters population dynamics and diet of juvenile trout Salmo trutta. Freshwater Biology, 50, 127-140. 23. Kestrup, A.M. & Ricciardi, A. (2009). Environmental heterogeneity limits the local dominance of an invasive freshwater crustacean. Biological Invasions, 11, 2095-2105. 24. King, R.B., Ray, J.M. & Stanford, K.M. (2006). Gorging on gobies: beneficial effects of alien prey on a threatened vertebrate. Canadian Journal of Zoology-Revue Canadienne De Zoologie, 84, 108-115. 25. Kohler, G.R., Steiefel, V.L., Wallin, K.F. & Ross, D.W. (2008). Predators associated with the hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) in the Pacific Northwest. Environmental Entomology, 37, 494-504. 26. L'Abee-Lund, J.H., Aass, P. & Saegrov, H. (2002). Long-term variation in piscivory in a brown trout population: effect of changes in available prey organisms. Ecology of Freshwater Fish, 11, 260-269. 27. Letnic, M., Webb, J.K. & Shine, R. (2008). Invasive cane toads (Bufo marinus) cause mass mortality of freshwater crocodiles (Crocodylus johnstoni) in tropical Australia. Biological Conservation, 141, 1773-1782. 28. Llewelyn, J.S., Phillips, B.L. & Shine, R. (2009). Sublethal costs associated with the consumption of toxic prey by snakes. Austral Ecology, 34, 179-184. 29. Lopez, V.F., Kairo, M.T.K. & Irish, J.A. (2004). Biology and prey range of Cryptognatha nodiceps (Coleoptera : Coccinellidae), a potential biological control agent for the coconut scale, Aspidiotus destructor (Hemiptera : Diaspididae). Biocontrol Science and Technology, 14, 475-485. 30. Lynch, B.R. & Rochette, R. (2009). Spatial overlap and interaction between sub-adult American lobsters, Homarus americanus, and the invasive European green crab Carcinus maenas. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 369, 127-135. 31. Madenjian, C.P., Stapanian, M.A., Witzel, L.D., Einhouse, D.W., Pothoven, S.A. & Whitford, H.L. (2011). Evidence for predatory control of the invasive round goby. Biological Invasions, 13, 987-1002. 32. Mallis, R.E. & Rieske, L.K. (2011). Arboreal Spiders in Eastern Hemlock. Environmental Entomology, 40, 1378-1387. 33. McDonald, R.A., O'Hara, K. & Morrish, D.J. (2007). Decline of invasive alien mink (Mustela vison) is concurrent with recovery of native otters (Lutra lutra). Diversity and Distributions, 13, 92-98. 34. Michaud, J.P. & Olsen, L.E. (2004). Suitability of Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri, as prey for ladybeetles. Biocontrol, 49, 417-431. 35. Montserrat, M., Sahun, R.M. & Guzman, C. (2013). Can climate change jeopardize predator control of invasive herbivore species? A case study in avocado agro-ecosystems in Spain. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 59, 27-42. 36. Monzo, C., Juan-Blasco, M., Pekar, S., Molla, O., Castanera, P. & Urbaneja, A. (2013). Preadaptive shift of a native predator (Araneae, Zodariidae) to an abundant invasive ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Biological Invasions, 15, 89-100. 37. Nash, M.A., Thomson, L.J., Horne, P.A. & Hoffmann, A.A. (2008). Notonomus gravis (Chaudoir) (Coleoptera: Carabidae) predation of Deroceras reticulatum Muller (Gastropoda: Agriolimacidae), an example of fortuitous biological control. Biological Control, 47, 328-334. 38. Olsen, P.D. & Marples, T.G. (1992). Alteration of the clutch size of raptors in response to a change in prey availability - evidence from control of a broad-scale rabbit infestation. Wildlife Research, 19, 129-135. 39. Ortega, Y.K., Pearson, D.E. & McKelvey, K.S. (2004). Effects of biological control agents and exotic plant invasion on deer mouse populations. Ecological Applications, 14, 241-253. 40. Page, H.M., Dugan, J.E., Schroeder, D.M., Nishimoto, M.M., Love, M.S. & Hoesterey, J.C. (2007). Trophic links and condition of a temperate reef fish: comparisons among offshore oil platform and natural reef habitats. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 344, 245-256. 41. Pearson, D.E. & Fletcher, R.J. (2008). Mitigting exotic impacts: Restoring deer mouse populations elevated by an exotic food subsidy. Ecological Applications, 18, 241-253. 42. Phillips, B.L., Greenlees, M.J., Brown, G.P. & Shine, R. (2010). Predator behaviour and morphology mediates the impact of an invasive species: cane toads and death adders in Australia. Animal Conservation, 13, 53-59. 43. Pons, P., Bas, J.M. & Estany-Tigerstrom, D. (2010). Coping with invasive alien species: the Argentine ant and the insectivorous bird assemblage of Mediterranean oak forests. Biodiversity and Conservation, 19, 1711-1723. 44. Pope, K.L., Garwood, J.M., Welsh, H.H. & Lawler, S.P. (2008). Evidence of indirect impacts of introduced trout on native amphibians via facilitation of a shared predator. Biological Conservation, 141, 1321-1331. 45. Poulin, B., Lefebvre, G. & Crivelli, A.J. (2007). The invasive red swamp crayfish as a predictor of Eurasian bittern density in the Camargue, France. Journal of Zoology, 273, 98-105. 46. Pratt, P.D. & Croft, B.A. (1998). Panonychus citri (Acari : Tetranychidae) on ornamental Skimmia in Oregon, with assessment of predation by native phytoseiid mites. PanPacific Entomologist, 74, 163-168. 47. Ransom, T.S. (2012). Comparison of direct, indirect, and ecosystem engineering effects of an earthworm on the red-backed salamander. Ecology, 93, 2198-2207. 48. Richman, S.E. & Lovvorn, J.R. (2004). Relative foraging value to lesser scaup ducks of native and exotic clams from San Francisco Bay. Ecological Applications, 14, 1217-1231. 49. Rius, M., Pineda, M.C. & Turon, X. (2009). Population dynamics and life cycle of the introduced ascidian Microcosmus squamiger in the Mediterranean Sea. Biological Invasions, 11, 2181-2194. 50. Salas-Araiza, M.D., Jones, R.W., Pena-Velasco, A., Martinez-Jaime, O.A. & Salazar-Solis, E. (2011). Population dynamics of two species of Greenidea (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and their natural enemies on Psidium guajava (Myrtaceae) and Ficus benjamina (Moraceae) in central Mexico. Florida Entomologist, 94, 97-105. 51. Sobhy, I.S., Sarhan, A.A., Shoukry, A.A., El-Kady, G.A., Mandour, N.S. & Reitz, S.R. (2010). Development, consumption rates and reproductive biology of Orius albidipennis reared on various prey. Biocontrol, 55, 753-765. 52. Stapanian, M.A., Edwards, W.H. & Witzel, L.D. (2011). Recent changes in burbot growth in Lake Erie. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 27, 57-64. 53. Steinhart, G.B., Stein, R.A. & Marschall, E.A. (2004). High growth rate of young-of-the-year smallmouth bass in Lake Erie: a result of the round goby invasion? Journal of Great Lakes Research, 30, 381-389. 54. Suarez, A.V. & Case, T.J. (2002). Bottom-up effects on persistence of a specialist predator : Ant invasions and horned lizards. Ecological Applications, 12, 291-298. 55. Tablado, Z., Tella, J.L., Sanchez-Zapata, J.A. & Hiraldo, F. (2010). The Paradox of the LongTerm Positive Effects of a North American Crayfish on a European Community of Predators. Conservation Biology, 24, 1230-1238. 56. Ware, R., Yguel, B. & Majerus, M. (2009). Effects of competition, cannibalism and intra-guild predation on larval development of the European coccinellid Adalia bipunctata and the invasive species Harmonia axyridis. Ecological Entomology, 34, 12-19. 57. Wuellner, M.R., Willis, D.W., Blackwell, B.G. & Lott, J.P. (2011). Empirical assessment of potential interactions between walleye and smallmouth bass. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 27, 1173-1180. 58. Zannou, I.D., Hanna, R., de Moraes, G.J. & Kreiter, S. (2005). Cannibalism and interspecific predation in a phytoseiid predator guild from cassava fields in Africa: evidence from the laboratory. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 37, 27-42.