The atomic mass - Pharos University in Alexandria
advertisement

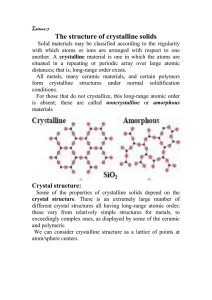
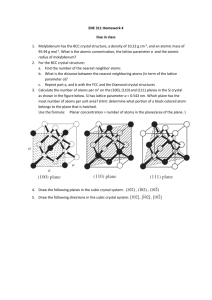
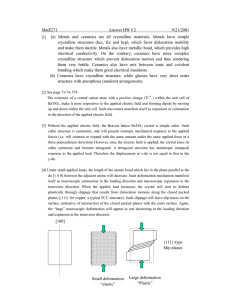
Pharos University Faculty of Engineering Petrochemical Department Lecturer: Dr.Ehssan Nassef Material Science (PE217) Fall (2012-2013) Revision on the definitions from lecture (2) to lecture (11) 1. CERAMICS: CERAMICS are compounds between metallic and nonmetallic elements. 2. COMPOSITES: A number of composite materials have been engineered that consist of more than one material type. 3. ADVANCED MATERIALS: Materials that are utilized in high-technology (or high-tech) applications are sometimes termed advanced materials. 1 4. Atom: Each atom consists of a very small nucleus composed of protons and neutrons, which is encircled by moving electrons. Atomic number (Z): Is the number of protons in the nucleus atomic weight; of an element corresponds to the weighted average of the atomic masses of the atom’s. Crystalline: A crystalline material is one in which the atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances. Crystal structure: Some of the properties of crystalline solids depend on the crystal structure of the material, the manner in which atoms, ions, or molecules are spatially arranged. Lattice: lattice is used in the context of crystal structures; in this sense ‘‘lattice’’ means a three-dimensional array of points coinciding with atom positions (or sphere centers). 2 UNIT CELLS: The atomic order in crystalline solids indicates that small groups of atoms form a repetitive pattern. The coordination number: For metals, each atom has the same number of nearestneighbor or touching atoms, which is the coordination number. The atomic packing factor (APF) Answer the following questions: Define stress –strain relation. State Hooke’s law. Modules of elasticity. Tensile strength ,percent elongation ,Ductility. Hardness and the different tests methods for measuring it. Brittle fracture ductile fracture. Fatigue. Elastic deformation and plastic deformation Substitutional and interstational impurities atoms. 3 Types of ceramics crystal structure. Defects in ceramics: Frenkel Defect:a cation is out of place. Shottky Defect a paired set of cation and anion vacancies. • Polymer: The term polymer denotes a molecule made up by the repetition of smaller molecules, the monomer. Thermo plastic polymers: Thermosetting polymers are network polymers.They become permanently hard during their formation, and do not soften upon heating. 4 STRESS–STRAIN BEHAVIOR of polymers Composite Is considered to be any multiphase material that exhibits a significant proportion of the properties of both constituent phases such that a better combination of properties is realized. 5 Many composite materials are composed of just two phases; one is termed the. Matrix, which is continuous and surrounds the other phase, often called the dispersed phase. Corrosion in metals: is defined as the destructive and unintentional attack of a metal; it is electrochemical and ordinarily begins at the surface. An oxidation reaction: 6 B-In basic or neutral medium: O2+2H2O+4e- 4(OH)- Corrosion in ceramics Corrosion in polymers(Degradation) 7