KARTA PRZEDMIOTU
advertisement
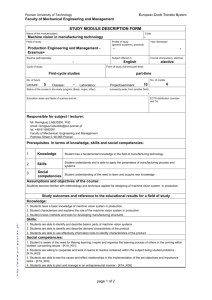
Poznan University of Technology European Credit Transfer System Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Management STUDY MODULE DESCRIPTION FORM Name of the module/subject Code Production Management - Field of study Profile of study (general academic, practical) Production Engineering and Management Erasmus+ Year /Semester - Elective path/specialty - Subject offered in: - Course (compulsory, elective) English Cycle of study: elective Form of study (full-time,part-time) First-cycle studies part-time No. of hours Lecture: No. of credits 5 - Classes: 10 Laboratory: Status of the course in the study program (Basic, major, other) Project/seminars: 6 - (university-wide, from another field) - - Education areas and fields of science and art ECTS distribution (number and %) Responsible for subject / lecturer: Ms. Eng. Justyna TROJANOWSKA email: justyna.trojanowska@put.poznan.pl tel. +48 61 647 5991 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Management Piotrowo Street 3, 60-965 Poznań Prerequisites in terms of knowledge, skills and social competencies: 1 Knowledge Student has a fundamental knowledge in the field of production organization and management 2 Skills Student understands and is able to apply the parameters of manufacturing process and systems for designing of production structures Social competencies Student understanding of the need to learn and acquire new knowledge Assumptions and objectives of the course: 3 Students become familiar with methodology and technique applied for designing of production systems and modern concepts of production management Study outcomes and reference to the educational results for a field of study Knowledge: 1. Students have a basic knowledge of production management, production systems design, lean manufacturing, theory of constraints 2. Student characterizes and explains the role of the production system 3. Student knows methods and tools for developing manufacturing structures Skills: 1. Students are able to identify and describe basics types, forms and varieties of production organizations, group technology, production structure, the role of stock production in productive process and is able to indentify and describe the basic elements of production cycle, manufacturing cycle. 2. Students are able to identify and describe production system, production system surrounding, the basic of production and manufacturing operations and processes which would be in production system. 3. Students are able to use effectively tools and methods of production management Social competencies: page 1 of 2 Poznan University of Technology European Credit Transfer System Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Management 1. Student is aware of the need for lifelong learning; inspire and organize the learning process of others in the coming within studied concerning issues - [K1A_K01] 2. Students are willing to cooperate and work in teams to resolve contained within the subject being studied problems [K1A_K03] 3. Students are able to see the cause-and-effect relationships in the implementation of the set objectives and importance tasks - [K1A_K04] 4. Students are able to plan and manage in an entrepreneurial manner - [K1A_K06] Assessment methods of study outcomes presentations, computer game, project, oral exam Course description The production process and its surroundings. Basic concepts of the production process. Elements of the production process. Relations of materials, energy and information of production process. Criteria for the organization and design of production systems. Basic concepts, definitions of production process and manufacturing. Technical and organizational characteristics of basic types of manufacturing process. Production planning. Gantt charts. The production cycle and manufacturing. Stocks of production. Production structures. Types, forms and varieties of production organization. Lean Manufacturing. Theory of Constraints. New trends in the field of operations management. Basic bibliography: 1. Arora K.C., Comprehensive Production and Operations Management, Laxmi Publikations, New Delhi, 2004 2. Rother M., Shook, J., Learning to See: Value Stream Mapping to Add Value and Eliminate MUDA. Brookline, MA: Lean Enterprise Institute, 2003 3. Goldratt E.M., Cox J, The Goal. Excellence In Manufacturing, North River Press, New York, 1984. Additional bibliography: 1. Liker, J. K., The Toyota way: 14 management principles from the world's greatest manufacturer, New York: McGraw-Hill Professional, 2004 2. Goldratt E.M., Cox J., The Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement, The North River Press Publishing Corporation, 2008 3. Woeppel M., The manufacturer's guide to implementing the theory of constraints, St. Lucie Press, Boca Raton, Florida 2001 Result of average student's workload Time (working hours) Activity 1. Participation in lectures 5 2. Participation in laboratories and projects 10 3. Literature studies 10 4. Preparation for exam 5 Student’s workload Source of workload hours Total workload 30 page 2 of 2 ECTS 6