Q1. The drawing shows an electron micrograph of parts of epithelial
advertisement

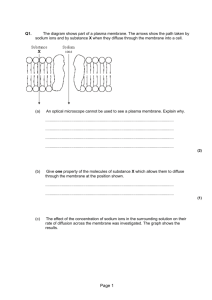
Q1. The drawing shows an electron micrograph of parts of epithelial cells from the small intestine. (a) (i) Name the structures labelled A. ............................................................................................................. (1) (ii) Explain how these structures help in the absorption of substances from the small intestine. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. (1) (b) (i) The scale bar on this drawing represents a length of 0.1μm. Calculate the magnification of the drawing. Show your working. Magnification ............................................. (2) Page 1 (ii) Explain why an electron microscope shows more detail of cell structure than a light microscope. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. (2) (c) The length of mitochondria can vary from 1.5 μm to 10 μm but their width_ never exceeds 1μm. Explain the advantage of the width_ of mitochondria being no more than 1μm. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 7 marks) Q2. (a) (i) The diagram shows the fluid-mosaic model of a cell surface membrane. Name the molecules labelled A and B. A ......................................................................................................... B ......................................................................................................... (1) (ii) How does the bilayer formed by substance A affect entry and exit of substances into and out of a cell? ............................................................................................................. Page 2 ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. (2) (b) A dialysis machine contains artificial membranes which enable urea to be removed from the blood of a person with kidney failure. The diagram shows a dialysis machine. (i) By what process does urea pass from the blood into the dialysis fluid? ............................................................................................................. (1) (ii) Suggest two reasons for keeping the fluid in the dialysis machine at 40 °C rather than room temperature. 1 .................................................................................................……. ............................................................................................................. 2 ........................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................. (2) (iii) The blood and the dialysis fluid flow in opposite directions in the dialysis machine. Explain the advantage of this. Page 3 ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. (2) (iv) Blood flows through the dialysis machine at a rate of 200 cm3 per minute. Calculate the total volume which passes through the machine in 5 hours. Give your answer in dm3 and show your working. Answer .................................... dm3 (2) (Total 10 marks) Q3. (a) Cells of multicellular organisms may undergo differentiation. What is meant by differentiation? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The drawing shows part of a plant cell as seen with an electron microscope. Page 4 (i) Give two features shown in the drawing which are evidence that this cell is eukaryotic. 1 .......................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................. 2 .......................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................. (2) (ii) Calculate the actual width_ of the cell from Y to Z. Give your answer in micrometres (µm) and show your working. Answer ..................................... µm (2) (iii) Give one way in which a typical animal cell differs from the cell shown in the drawing. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. (1) (Total 6 marks) Page 5 M1. (a) (i) microvilli; (reject brush border) 1 (ii) increased surface area (for diffusion); 1 (b) (i) principle of (15 –17 tolerance) ; 160000; (correct answer award 2 marks) 2 (ii) electron microscope has a greater resolving power / objects closer together can be distinguished; electron (beams) have a shorter wavelength; 2 (c) short diffusion pathway /short pathway to the centre / large SA:V ratio for faster, more diffusion; 1 [7] M2. (a) (i) A = phospholipid B = protein; (both correct) 1 (ii) allows movement of lipid soluble/non-polar molecules/named e.g. water/gases; Page 6 prevents movement of water soluble/polar molecules/named e.g. ions / amino acids; idea of selection / membrane partially/differentially permeable/ large molecules do not move through, small molecules do; (accept semi-permeable) 2 max (b) (i) diffusion (reject facilitated) 1 (ii) higher rate of exchange/diffusion; prevents cooling of the blood / prevents increase in viscosity; 2 (iii) concentration gradient maintained / equilibrium never achieved; blood always meets fluid with lower concentration of urea; diffusion/exchange along the whole length of surface; 2 max (iv) 0.2 × 60 = 12 dm3 h-1; (principle: volume per hour) 12 × 5 = 60 dm3; (correct answer 2 marks) 2 [10] M3. (a) cells become specialised/change to carry out a particular function; 1 (b) (i) named organelle e.g. nucleus/nuclear envelope; vacuole; chloroplast; RER; mitochondrion; no membrane bound organelles; (only award if no organelles named) (reject ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall) ref to large(r) size 2 max (ii) Page 7 20.4 – 21.8 (correct answer 2 marks) 2 (iii) no cell wall (permanent) / (large) vacuole / chloroplasts / smaller; (accept microvilli) 1 max [6] Page 8 E1. (a) Only the weakest candidates failed to score here. Some candidates gave villi or failed to gain the mark by giving the examiner the choice of microvilli /villi. (b) Many candidates failed to measure the scale bar and most did not know that there are 1000µm in a mm. Answers were often out by a factor of 10. Most candidates gained the resolution mark but then failed to relate this to the shorter wavelength of the electrons’ beam. Some answers linked detail only to increased magnification. (c) This part was not well answered, only the better candidates recognising the link between width_ and short diffusion pathway. Many referred to SA:V ratio but then failed to relate this to diffusion. A common error was to assume the mitochondria would be able to move around the cell more easily, and weaker candidates often opted for the simple idea that more would fit into a cell. E2. (a) The molecules in the membrane were well identified with many candidates qualifying the type of protein present. There was some confusion in (ii) over the distinction between the movement of water-soluble molecules and water itself with some candidates failing to appreciate that water can move across the membrane in the same way as other very small molecules such as oxygen. A small number of candidates still referred to the membrane as semi-permeable and should be encouraged to follow the Institute of Biology recommended terminology of partially permeable whenever possible. (b) This question produced a wide spread of marks. Most candidates identified the process of diffusion and went on to recognise an increase in rate related to temperature but very few referred to the cooling effect on the blood. Only more able candidates were able to apply the principles of countercurrent flow to the novel situation and gain both marks in part (iii). Many candidates correctly related volume to time in the calculation but were then unable to express this in the correct units, indicating problems with cm³ and dm³. Page 9 E3. (a) Most candidates were aware of cells carrying out different functions, but many did not express the idea of change and therefore failed to gain the mark. Weaker candidates confused differentiation with differential centrifugation. (b) Cell structure was generally well understood, although some candidates assumed that cell walls are a feature of eukaryotic cells and are absent from prokaryotes. The calculation was attempted by the majority of candidates, most of whom measured the scale bar and gained at least one mark. Page 10