Laser - College of Science
advertisement

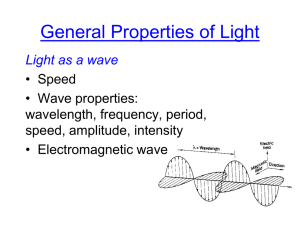
University of Salahaddin-Erbil College of Science Physics Department course book of laser physics Bsc. 4td Year Applied Physics (communication Branch). Instructor: Eman A. Saied E-Mall: emanabdulmaged@ yahoo.com Meeting days, times and places: Monday Academia year :2014-2015 A.D 11:30 –1:30 am. , Hall : Ph4 Course Disruption :Laser is a annually intermediate subject that provide a systematic study of the properties and behaviour of laser and its interactions with matter. The course designed for 4rd year applied(communication branch) Physics /College of science /Salahaddin University. The content of course intended to provide a foundation of laser and its applications. Objective :In this course we will discuss many aspects of laser physics. Starting with an overview of how lasers work, we’ll work through the origin of gain in different media, rate equations for continuous-wave and pulsed lasers, Gaussian beams, resonators, laser types. We’ll also discuss more advanced topics such as laser stabilization, getting lasers to make short pulses (Q-switching and mode-locking), laser amplifiers, non-linear optic, and Fibre optic . Prerequisite:Optics, atomic and molecule and two Semesters of Calculus. Text Book: Principles of laser, by O.sevilto and D.Hanna (5th edition )2009,springer. Reference Books: These books are available in the college’s library and department store of books Introduction to laser technology, by B.hitiz ,J.Ewing,J.Hech, (3rd edition)2001new yourk . Introduction to optics, 3rd ,F.L .Pedrotti, L.S Pedrotti and L.M. Pedrotti(2007). Grading: Exams and assignments require analytical work and not just memorization of topics or articles. Questions on above instruments may be in the form of : multiple choice fill in the blank short answers problems 10% Lecture Participation with in class assigned quizzes , report, Homework Guided Practice 30% -15 for two semester tests 60% Final Exam Syllabus :Chapter one : Introductory concepts :1.1 historically back ground . 1.2 The laser Idea 1.3 properties of laser beam 1.4 laser types. (3 lecture) Chapter two: Introduction to principle of lasers :2.1 Absorption and emission of radiation 2.1.2 spontaneous emission 2.1.3 stimulated emission 2.2 Boltzmann distribution. 2.3 Einstein coefficients. 2.4 population inversion. (3 lecture) Chapter three :- laser theory :3.1 Active medium 3.1.1 Three level system. 3.1.2 Four level system. 3.2 pumping source, types of pumping source. 3.3 Resonators. 3.3.1 plane parallel (fabry-perrot) resonator. 3.3.2 Stable resonator. 3.3.3.Unstable resonator. (7 lecture) Chapter four : Continues and transited laser behaviour. 4.1 Q. switching. 4.2 types of q-switches. 4.3 Mechanical Q-switches. (3 lecture) Chapter five : Laser types:5.1 solid state laser . 5.2 liquid laser. 5.3 Gas laser . (2 lecture) Chapter six: semiconductor laser:6.1 Semiconductor Physics 6.2 Modern Diode Lasers 6.2.1 Wavelength of Diode Lasers 6.2.2 Vertical Cavity, Surface-Emitting Lasers. (4lecture) Chapter seven : laser applications:7.1 laser applications:7.1.1 laser application in Communication. 7.1.2 laser application in industry. 7.1.3 laser application in medicine. (2 lecture) Chapter eight :- non linear optic Chapter eight :- Fibre Optics (2 lecture) ( 4 lecture) Note:- This syllabus may be subject to changes, i.e. we may take either longer or shorter time to finish a topic, if any changes happened you will be notified well in advance.