General Properties of Light
advertisement
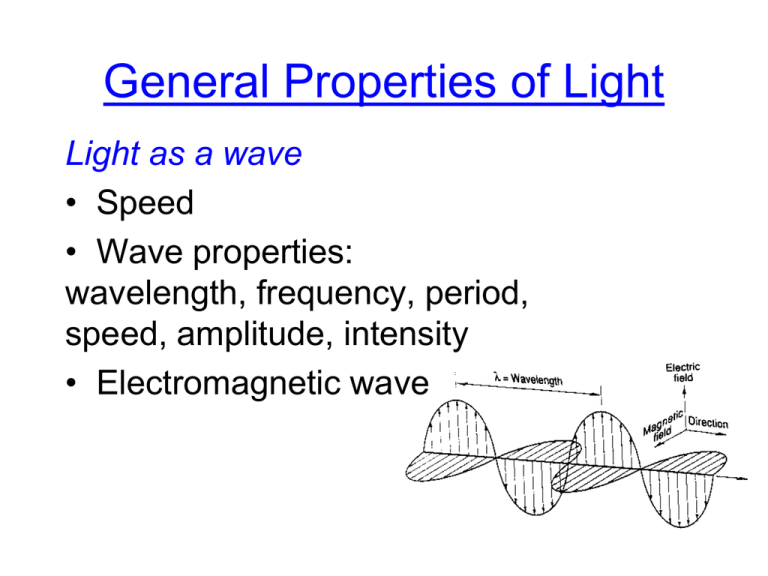
General Properties of Light Light as a wave • Speed • Wave properties: wavelength, frequency, period, speed, amplitude, intensity • Electromagnetic wave EM Spectrum 4 x 10-11 4 x 10-7 3 x 104 Long waves 102 104 4 x 10-3 3 x 10-4 3 Radio waves 106 108 4 x 101 3 x 10-8 Infrared 1010 1012 4 x 105 1014 Ultraviolet 1016 Visible Light Energy (eV) 3 x 10-12 X-rays 1018 Wavelength (m) Gamma rays 1020 1022 Frequency (Hz) • Diffraction – the bending of waves at an aperture or obstacle Double-slit pattern of water/sound waves • Interference – double-slit, speckle Optic axis Ipeak=4Io screen y D d Path difference = d sin Iaverage=2Io • Polarization Light as a particle • • • • Photon Energy packet Photoelectric effect Double slit- revisited photocathode anode A * * * Double Slit Experiment with Electrons Detections come in lumps = quanta Intensity exhibits interference Reducing intensity of the light, so that only one electron arrives at the slits at a time Questions? Why do no electrons (or photons) ever arrive at some locations? Clearly Ptot ( x) P1 ( x) P2 ( x) How can we get interference when only 1 particle at a time is going through the slits? What does that particle interfere with? Suppose we actually check which slit each particle went through and know with certainty – what happens then? How can this be? Resolution comes from QED with Feynman Electron diffraction How is light produced? • Chemical energy - fire • Electrical energy - lightning • Nuclear energy - stars – Incandescent – Electric discharge – continuous vs discrete spectrum – Fluorescence Special Properties of Laser Light • • • • • Monochromatic Intense Pencil beam – collimated Coherent Can be cw or pulsed Prototype Laser • • • • • • Energy levels Absorption, spontaneous emission Stimulated emission Population inversion Metastable state Pump – optical, electron excitation, atomatom collisions, chemical • Resonant cavity – gain, cavity modes, beam Types of Lasers • 3-level vs 4-level • Ruby, first, a 3-level pulsed laser • He-Ne, gas, 4-level • Argon ion, gas • CO2 – molecular gas laser • Neodymium – solid-state Diode laser Dye – liquid laser Laser Applications • Communications • Coding information, fiber optics • Medical uses • Materials processing • Science Laser Tweezers Pout Pin Pin Pout Pright Pleft Pnet • Holography