Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
advertisement

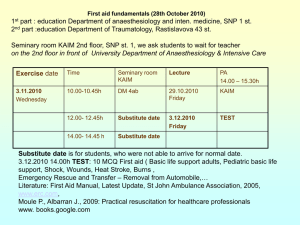
HECMA PROGRAM Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Basic and Survival Chain Prepared by: Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 2011-2012 Early HELP and call 999 EarLy Early Advanced CPR AED Care DESIGNED AND EDITED BY : NAHED YAGHI 27/09/2011 Ch 2 / lesson 5 Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Basic and Survival Chain Early HELP call 999 EarLy Early Advanced CPR AED Care Schools must be prepared for student and staff becoming injured or ill during the school day .every school and district needs to have specific plans for dealing with these situations. Life-threatening emergencies can happen in any school, at any time. These can be the result of pre-existing health Problems, sudden cardiac arrest, allergic reactions, heatstroke, trauma, among other causes. There, the priority in treating any collapsed persons is to establish an open air way and maintain breathing and circulation. The procedure set out in this lesson can maintain a person’s breathing and circulation until emergency aid arrives ,with an unconscious persons ,your priorities are to maintain an open air way, breath for person ( to get oxygen into the body ),and maintain blood circulation ( to get oxygen rich blood to the tissue ) In addition, a machine called a defibrillator can deliver a controlled electrical shock to restore a normal heartbeat. Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 2 Objective: Review survival elements. Explain the importance chest compression. Define the importance of opening the air way passage and breathing. What is an AED? Key Terms:Victim: A person, who has been attacked, injured or killed as the result of a crime, a disease, an accident, etc. Survival: The state of continuing to alive or exist, after despite difficulty or danger. Tilt: to move, or make something move, into a position with one side or end higher than the other Rhythm: strong regular repeated pattern of sounds or movements. Pulse: a rhythmical throbbing of the arteries as blood is propelled through them, typically as felt in the wrists or neck… Recoil: rebound or spring back. Child: young human being below the age of puberty. Infant: human being less than one year old. Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 3 The following factors increase the chances of survival if all elements are complete: EARLY HELP NLKLHL CALL 999 EARLY EARLY ADVANCED CPR AED CARE AE CA LL 99 9 Help is called quickly. Blood circulation is maintained by rescue breathing and chest compression (together known as cardiopulmonary resuscitation or CPR). Use an AED The victim reaches hospital quickly for specialized treatment and advanced care. The 2010 AHA guidelines for CPR recommended a change in the BLS sequences of steps from A-B-C (Airway, Breathing, Chest Compression) to C-A-B (Chest Compression, Airway, Breathing ) for adult ,children and infants . By changing the Sequence to C-A-B, chest compressions will be initiated sooner and the delay in Breathing should be minimal. General Assessment: If the victim is unconscious, the first aider should immediately call an ambulance - you will need professional help regardless of whether they are breathing or not. Waiting would endanger the victim's life unnecessarily. Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 4 Brachial pulse Carotid pulse Kneel beside the victim’s head; look for the chest movement or any signs of circulation such as breathing, coughing or movement ,if no signs , check for carotid pulse for an adult and child victim, and brachial pulse for infant. (The whole process should take less 10 seconds). C: Circulation How to maintain circulation? Vital Organs If the heart stops beating, blood does not circulate through the body .as a result vital organs (Brain, Heart and Lungs), become starved of oxygen .brain cells are enable to survive for more than few minutes without a supply of oxygen. Some circulation can be maintained artificially by chest compression .these compression act as mechanical aid to the heart to get blood flowing around the body .pushing vertically down on the lower half of the breast bone squeeze the heart against the back bone ,expelling blood from heart’s chambers and forcing it into the tissue .As pressure is released ,the chest rises ,and replacement Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 5 blood is “sucked” in to refill the heart ;this blood is then forced out of the heart by the next compression . To ensure that the blood is adequately supplied with oxygen should do effective chest compression with or without rescue breath. A: Airway Important of an open airway Head tilt –chin lift An unconscious victim airway may become narrowed or blocked .this is due to muscular control being lost .allowing the tongue to fall back and block the airway .when this happen the victim’s breathing become difficult and noisy or breathing may become completely impossible .Lifting the chain and tilting the head back lifts the tongue from the entrance to the air passage, allowing the victim to breath. Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 6 B: Breathing Breathing for a victim:- The air we exhale contains about 16 per cent oxygen (5 per cent less than in the air we inhaled) in addition to a small amount of carbon dioxide. Exhaled breath therefore contains enough oxygen to supply another person with oxygen –and keep him alive – when it forced into the victim’s lung during rescue breathing. By giving rescue breaths, you can force air into the victim’s air passage. This air reaches the air sac (alveoli) in the lungs, and oxygen is then transferred to the tiny blood vessels within the lungs .when you remove your mouth from the victim’s mouth, the chest falls and air containing waste product is exhaled. Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 7 Restoring heart rhythm AED (automated external defibrillator) are accurate and easy use after little training, giving CPR right away and using an AED within few minutes will increase the chances of saving the life of someone with sudden cardiac arrest. An AED may give an electrical shock to the heart, this can stop the abnormal heart rhythm and allow a normal heart rhythm to return. References: - Comprehensive school health education, 7Th edition by Linda Meeks, Philip Heit & Randy page. - First aid manual, 8 editions by St. John ambulance, St. Andrew’s ambulance association and the British Red Cross. - Mini dictionary for nurses, 5th edition, Editor Elizabeth A. Martin. Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 20/09/2011 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 8 HECMA PROGRAM CPR Basic and Survival Chain Chapter 2/lesson 6 Students Name:-……………………….. Class: - ………………………….. Work sheet: Survival Elements Time: 5 minutes Student instruction: Write the key elements of survival in the blank boxes according what you learned in the lesson? 1 Prepared By: - Khalil Taha 2 20/09/2011 3 4 Edited and Designed by: Nahed Yaghi 27/09/2011 Page 9