File - Mr. Shanks` Class
advertisement
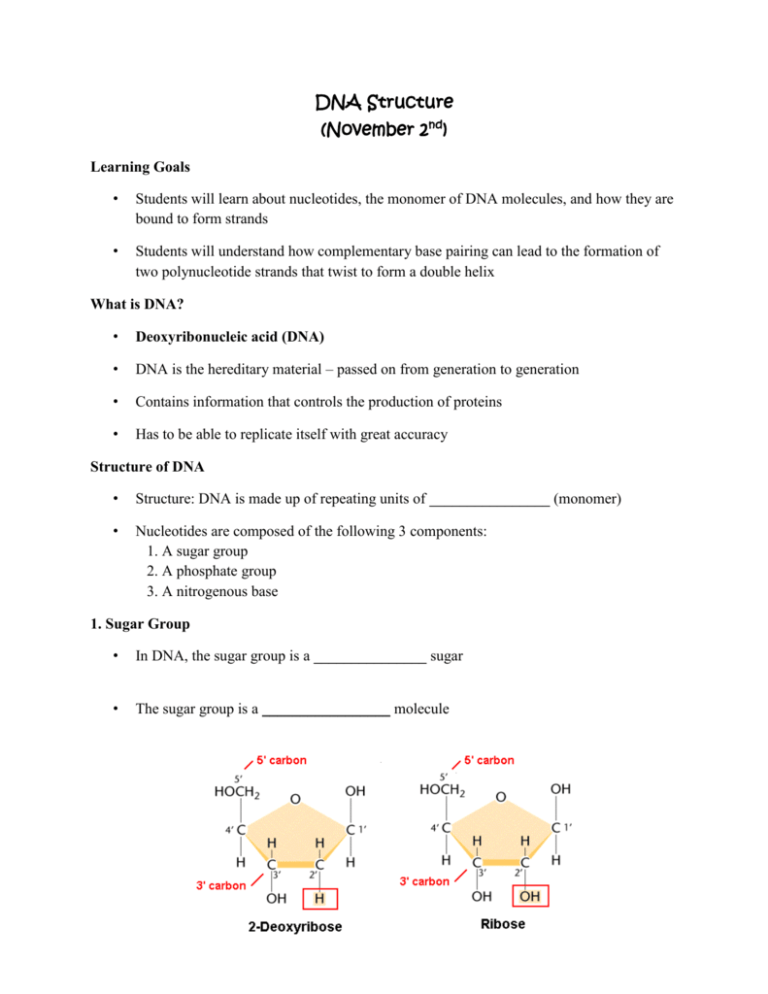
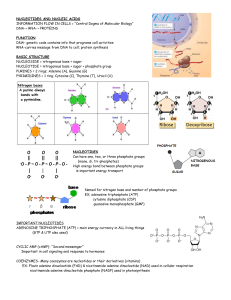
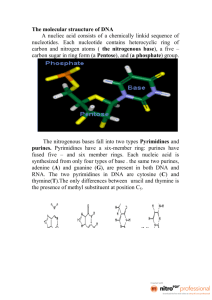
DNA Structure (November 2nd) Learning Goals • Students will learn about nucleotides, the monomer of DNA molecules, and how they are bound to form strands • Students will understand how complementary base pairing can lead to the formation of two polynucleotide strands that twist to form a double helix What is DNA? • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) • DNA is the hereditary material – passed on from generation to generation • Contains information that controls the production of proteins • Has to be able to replicate itself with great accuracy Structure of DNA • Structure: DNA is made up of repeating units of ________________ (monomer) • Nucleotides are composed of the following 3 components: 1. A sugar group 2. A phosphate group 3. A nitrogenous base 1. Sugar Group • In DNA, the sugar group is a _______________ sugar • The sugar group is a _________________ molecule 2. Phosphate Group • The deoxyribose sugar binds with phosphate at both its 3’ and 5’ (three prime and five prime) carbons 3. Nitrogenous Base • A nitrogenous base attaches to the deoxyribose sugar group • There are two different forms of nitrogenous bases: 1. _____________________ 2. _________________ Thymine and Cytosine are pyrimidines Have a ______________ Adenine and Guanine are purines Have ____________________ Drawing of a nucleotide: Nucleoside vs. Nucleotide • A sugar + a nitrogenous base = nucleoside • A sugar + a nitrogen base + phosphate = nucleotide • Phosphorylating a nucleoside makes a nucleotides Primary Structure • Each nucleotide is attached to the next by a ____________________ _____________ • The phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3’ carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5’ carbon atom of the next Think: Phospho (phosphate) + diester (two esters) • This bonding creates a polynucleotide (multiple nucleotides) strand Sugar Phosphate Backbone • Each polynucleotide strand has a backbone of alternating phosphate groups and sugars called the ______________ ___________________ __________________ Binding of two strands • Complementary base pairing: nitrogenous bases on opposite strands pair through hydrogen bond formation such that Adenine pairs with Thymine Cytosine pairs with Guanine • A-T held by _____ hydrogen bonds • C-G held by _____ hydrogen bonds Question: Which pair do you think is stronger? Answer: _______________________________________ Chargaff’s Rule • The amount of adenine is __________ to the amount of thymine AND • The amount of cytosine is equal to the amount of guanine • Question: are purines binding to one another and pyrimidines binding to one another? • Answer:_________________________________________________ Antiparallel • Antiparallel: The two strands run in _______________ directions • Each strand will have a 5’ end and a 3’ end • The 5’ end of one strand lies across from the 3’ end of the complementary strand • The 5’ and 3’ come from the numbering of the carbons on the deoxyribose sugar Antiparallel – Analogy • This is similar to how sports teams face in a different direction when they shake hands at the end of a game • Let’s say the goalie is always at the front of the line (5’) • And the coach is always at the back of the line (3’) Drawing of two antiparallel strands: Secondary Structure – Double Helix • The two bound polynucleotide strands twist around each other to form a double helix • Resources in case you’d like a visual (also on page 213 in textbook): http://www.johnkyrk.com/ -On left hand side click “Structure” under DNA -You can move through the pictures using the arrows in the bottom left corner http://www.dnatube.com/video/3447/DNA-double-helix Questions! 1. 2. 3. 4. How many bonds between A-T? C-G? What kinds of bonds are these? What is a nucleotide and what is a nitrogenous base? Are the two polynucleotide strands that twist around each other identical?