Topic XXII – RNA and Protein Synthesis - Science - Miami
advertisement

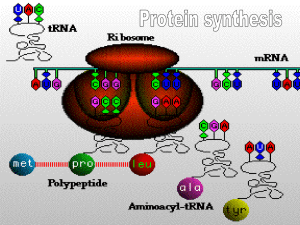
MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I Course Code: 200031001 TOPIC XXII: MOLECULAR GENETICS - RNA and Protein Synthesis Pacing Date Traditional 5 days Block ESSENTIAL CONTENT A. RNA Synthesis: Transcription (16.3, 16.5) 1. Role in the cell 2. Comparing RNA and DNA 3. Functions of RNA (types) 4. Codons (mRNA; Start and Stop) B. Protein Synthesis: Translation (16.5) 1. Ribosomes (rRNA; “P” and “A” sites) 2. Amino Acids (tRNA; Anticodon) 3. Codon table 4. Translation 5. Gene Expression C. Types of Mutations: (16.4) 1. Types a. Point b. Frameshift c. Chromosomal 2. Effects a. Harmful (16.8) b. Beneficial c. Variation d. Neutral Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks OBJECTIVES Summarize the process of transcription. Identify the different types of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) and explain the structure and function of each. ** Demonstrate how specific code sequences are translated into traits through protein synthesis. Trace the information flow from DNA to a protein. Students will explain the basic processes of transcription and/or translation, and their roles in the expression of genes. Describe how amino acids are coded. Identify that certain chromosomal mutations can lead to human disorders such as sickle-cell disease. List possible mutagens and distinguish between chemical and physical mutagens. Differentiate the cellular processes of DNA replication, transcription, and/or translation (ALD) Students will explain how gene and chromosomal mutations may or may not result in a phenotypic change. Relate that mutation and genetic recombination increase genetic variation. (ALD) 2.5 days 03-31-16 to 04-07-16 03-31-16 to 04-07-16 INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS Core Text Book: Ch.13 Vocabulary: DNA, RNA, Transcription, Messenger RNA, Ribosomal RNA, Transfer RNA, Translation Codon, Anticodon, Ribosome, Amino Acid, Polypeptide, Protein, Nucleotide, Helix, Base pairing, Hydrogen bonding, Peptide Bond, RNA splicing, RNA polymerase Technology: 1. HHMI: Translation (Basic Detail) 2. Interactive Art: Transcription and Translation 3. Art Review: Point Mutations 4. Data Analysis: Complicated Operon 5. NOVA: RNAi 6. DNA tube: Detailed Explanation of mRNA Translation 7. NOVA: Cracking the Code of Life 8. Bozeman Podcast: Mutations 9. HippoCampus Biology: The Transcription of DNA to RNA: Overview 10. HippoCampus Biology: Genes Encode Proteins 11. HippoCampus Biology: RNA Structure and Function HippoCampus Biology: The Initiation of Transcription 12. HippoCampus Biology: Elongation, Termination and Processing 13. HippoCampus Biology: The Transcription of DNA to RNA: Summary 14. HippoCampus Biology: Translation, Protein Synthesis: Overview 15. HippoCampus Biology: Decoding RNA 16. HippoCampus Biology: The Components of Translation 17. HippoCampus Biology: The Mechanism of Translation 18. HippoCampus Biology: Translation, Protein Synthesis: Summary 19. Edgenuity 20. Extended Learning Modules Page 1 of 5 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I SC.912.L.16.5 Standard: SC.912.L.16.3 Course Code: 200031001 RNA and Protein Synthesis Video How a Specific Sequence in a DNA Molecule is Replicated to Create an Identical Copy of Itself Video Mutation DNA Mutations Genetic Disease Image DNA sequence; nature of mutation Base pairing errors; generation of mutations Base substitution mutation Insertion and deletion mutations Standard: SC.912.L.16.4 Standard: SC.912.L.16.5 Video Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks The Central Dogma: RNA and Transcription The Central Dogma: Translation and the Code What Is RNA? RNA Polymerase and Transcription Simulating the Process of Transcription With Models Exceptions to the Rules of Transcription The Cell Cycle: Replication The Cell Cycle and DNA Introduction: DNA Replication The mRNA Template What is the Role of RNA? How Does RNA Know Where to Start Coding From a DNA Molecule? Introduction: Translation and Protein Synthesis Degenerate Code System The Process of Protein Synthesis Translating the Message into Protein Closing Remarks: Transcription of DNA to Messenger RNA Gene Expression DNA and RNA Review of the Processes of Transcription and Translation of mRNA The Standard Deviants School Biology: RNA: Introduction Translation Page 2 of 5 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I Course Code: 200031001 Standard: SC.912.L.16.5 Image Cell with ribosomes highlighted Standard: SC.912.L.16.8 Video DNA and the Genetics of Cancer Defining Cancer Standard: SC.912.L.16.9 Video Gene Expression Overview Amino Acid and the Language of Life The Role of Genes Mendel's Laws of Inheritance Inheritance Patterns Heredity: How Our Parents' Genes Affect Us Basic Facts About Cancer Obesity Diabetes Video Standard: HE.912.C.1.7 Audio Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks Hunting Down the Genes Involved in Disease DNA and the Genetics of Cancer Genetic Disease Families and Genetic Disease Genetic Case Study: Addison's Disease Cystic Fibrosis Risk Factors for Heart Disease DNA Screening High & Low Risks for Cancer High & Low Risks for Cardiovascular Disease High & Low Risks for Diabetes Is Tone Deafness Hereditary? Can Your Grandfather's Diet Shorten Your Life? Page 3 of 5 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I Course Code: 200031001 Video Image Science Behind the News: Influenza & Flu Vaccines Georgia Tech Chemist Designs Molecules That May Stop or Slow Effects of Alzheimer's NIH Discovers Key to Sickle Cell Cure California Funds Stem Cell Research and Pushes for Quick Results For Mixed Race Patients, Few Bone Marrow Donors Animals, Injected with Human Genes, Are Possible Source of Transplantable Organs Stem Cells Provide Hope for Heart Failure Patients New Research May Help People Increase Their Lifespans Pick Your Poison: Cobra Venom Shows Therapeutic Promise Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks Page 4 of 5 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Learning Goals BIOLOGY I Course Code: 200031001 SC.912.L16.3: Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. ( Cognitive Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning) SC.912.L16.5: Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation and how they result in the expression of genes. ( Cognitive Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning ) SCALE LEARNING PROGRESSION I am able to distinguish among the cellular processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Using a given DNA nucleotide sequence, trace the pathway from replication to transcription and translation. Identify the corresponding protein sequence that will form based on the original DNA nucleotide sequence and what could occur if the original DNA sequence was changed in any way. Score/Step 5.0 I am able to differentiate the cellular processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Create a diagram demonstrating the processes of DNA replication, transcription and translation. Include descriptions of each process and how they differ from one another. I am able to differentiate the cellular processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Given a diagram of the processes of DNA replication, transcription and translation, identify the correct sequence of each process. I am able to choose the correct cellular process of DNA replication. Given a diagram of the components of DNA replication, identify the correct sequence of replication. I am able to understand that every organism has hereditary information stored in DNA that get passed on from one generation to another. Score/Step 4.0 Score/Step 3.0 Target (Learning Goal) Score/Step 2.0 Score/Step 1.0 SAMPLE PROGRESS MONITORING AND ASSESSMENT ACTIVITIES Division of Academics – Department of Science Third Nine Weeks Page 5 of 5