Chapter 3 – Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
advertisement

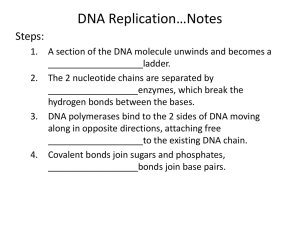
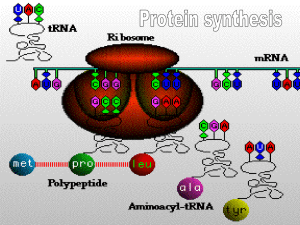
Nucleic Acids and protein synthesis Higher Human Biology Lesson Aims • To examine the structure of DNA • To compare the structure of DNA and RNA • To discuss the differences and similarities between mRNA and tRNA • To examine the role of the nucleus and nucleolus during RNA synthesis • To study the synthesis of proteins • It was Francis Crick and James Watson who unraveled the DNA molecule. DNA Molecule • In 1966 the Genetic code was discovered. • Scientists are now able to predict characteristics by studying DNA. This leads to genetic engineering, genetic counseling. An international team of scientists began the project to map the human genome. 1990 Gene therapy was used on patients for the first time. 1994 The FDA approved the first genetically engineered food -- FlavrSavr tomatoes engineered for better flavour and shelf life. 1997 Dolly the Sheep - the first adult animal clone. Dolly the sheep, pictured here with her first lamb Bonnie 2000 J. Craig Ventor, along with Francis Collins, jointly announce the sequencing of the entire human genome. The Central Dogma • DNA codes for the production of DNA (replication) and of RNA (transcription). • RNA codes for the production of protein (translation). The Central Dogma • Genetic information is stored in a linear message on nucleic acids. We use a shorthand notation to write a DNA sequence: – 5'-AGTCAATGCAAGTTCCATGCAT.... • A gene determine the sequence of amino acids in proteins. We use a shorthand notation to write a protein sequence: NH2-Met-Gln-Cys-Lys-Phe-Met-His.... (or a one letter code: M Q C K F M H) DNA Structure - Nucleotide DNA Structure – Double Helix Comparison of DNA and RNA DNA RNA Found in nucleus Found in nucleus and cytoplasm Double strands Single strand Bases – A, T, Bases – A, U, G, C G, C Deoxyribose Ribose sugar sugar Transcription Part of chain B sequence. Uncoiled DNA double helix which has split exposing bases • • • • • First stage of protein synthesis Occurs in the nucleus Double helix uncoils Double strands split DNA strand acts as template for formation of mRNA (messenger RNA) Transcription Single strand of DNA coding for Chain B Strand of mRNA copied from DNA • Free RNA nucleotides in the nucleus base pair with DNA nucleotides A-T, T-U, G-C, C-G • Strong bonds form between phosphate group and ribose sugar of neighbouring RNA nucleotides • Catalysed by enzyme RNA polymerase • mRNA moves out of nucleus through nuclear pore Role of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Network of membranes • Found in cytoplasm • Has ribosomes on surface • Proteins produced during translation pass into ER Translation • Second stage of protein synthesis • Occurs on ribosomes in cytoplasm • Code on mRNA is used to make protein chain Translation Comparison of mRNA and tRNA • • • • • mRNA Messenger RNA Made in nucleus during transcription Moves to cytoplasm Codes for protein Base triplets codons • • • • • tRNA Transfer RNA Found in cytoplasm Involved in translation Assembles amino acids into correct order for proteins Anti-codons present Overview Overview Role of Golgi Apparatus • Found in cytoplasm • Flattened sacs which are continually formed • Involved in processing and packaging proteins • Vesicles bud off with processed protein Secretion • Also called exocytosis • Vesicle which has pinched off Golgi apparatus moves towards cell membrane • Membrane of vesicle fuses with cell membrane • Insulin secreted from cell The Facts You Need To Know • page 1-2 • from “chromosomes which remain in ….” • to “the sequence of bases in the DNA…”