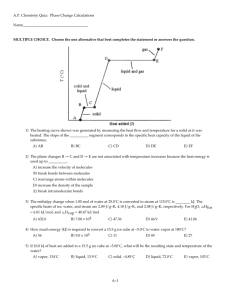
Unit 2 – Water Review Questions 1. Phase/state of water in which

Unit 2 – Water Review Questions
1. Phase/state of water in which the molecules densest. liquid
2. Phase/state of water in which the molecules are least dense. gas/vapor
3. In which 2 phases/states of water are the molecules able to move about freely and randomly? liquid and gas/vapor
4. In which phase/state of water are the molecules vibrating in place in an organized pattern?
solid/ice
5. Term used to describe water because water molecules stick together. cohesion
6. Term used to describe water because a water molecule is able to stick to another material. adhesion
7. Term used to describe water moving upward against gravity through narrow tubes or materials made of fibers with tiny spaces between the fibers. capillary action
8. Term used to describe molecules such as water because they have a negative side and a positive side. polar molecule
9. What is water’s chemical formula? H
2
O
10. What does its chemical formula mean? a water molecule has 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom
11. Term used to describe all the water in the world including water in Earth’s atmosphere, on and under Earth’s surface. hydrosphere
12. Term used to describe water because it dissolves many substances without changing the pH of the substance or undergoing a chemical reaction. universal solvent
13. Term used to describe the “skin” or “film” on the top of water that is caused by the molecules of water holding tight together. surface tension
14. What is the pH of water? 7
15. What is the density of water? 1 g/mL
16. What is the freezing point/temperature of water?
0 o C
17. What is the boiling point/temperature of water? 100 o C
18. The process of liquid water molecules gaining enough energy and rising in the atmosphere as water vapor. evaporation
19. The process of water molecules changing from vapor to liquid to form clouds. condensation
20. The process of water falling from the sky in the form of rain, snow, sleet or hail. precipitation
21. Term used to describe areas on Earth where water gathers. collection
22. Term used for bodies of water such as lakes, rivers, and ponds which are fit to drink. fresh water
23. Term used for bodies of water such as oceans and tidal water which are not fit to drink. salt water
24. Process of water trickling through the layers of Earth and soil. percolation
25. Term used for bodies of water under Earth’s surface. groundwater
26. The process of plants losing water into the atmosphere. transpiration
27. Term used for water that flows along the surface of Earth until it meets a body of water? runoff
28. The process of water changing from solid(ice) to liquid. melting
29. The process of water changing from liquid to solid(ice). freezing
30. Substances such as soap which decrease surface tension. surfactant
31. Sketch the water molecule. Label the Hydrogen atoms, the Oxygen atom, the positive (+) side and the negative (-) side of the molecule.
H
+
H
O
-
32. Sketch water molecules when they are solid, liquid and gas.
solid liquid gas
33. Sketch the Water Cycle. Label the 10 steps.