2015 Whitaker Conference Abstract, SW Crowder
advertisement

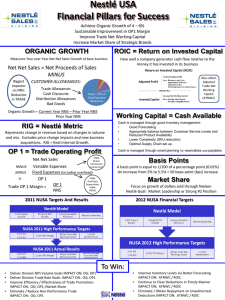
Biophysical interactions of human mesenchymal stem cells and porous silicon nanoneedles SW Crowder1,2, CS Hansel1, C Chiappini1,2, MM Stevens1,2,3 1 Department of Materials, 2Department of Bioengineering, and 3Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Imperial College London, London, UK Abstract: Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) are a promising cell source for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. hMSCs exhibit a particular sensitivity to the biophysical environment with which they interact, and altering the physicochemical properties of synthetic culture substrates has allowed for elucidation of processes that regulate hMSC biology. Recently, the Stevens Group has developed highaspect ratio, porous silicon nanoneedles (nNs) for in vitro and in vivo manipulation of cell behaviour. Interestingly, the nNs penetrate the cell membrane but do not damage the nucleus, instead stimulating nuclear condensation (shrinking); however, the mechanisms by which the needles generate changes in the nucleus have not been explored. In the present study, we have investigated the biophysical interactions between hMSCs and nNs, including changes in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton and expression of key components of the nuclear envelope that occur in response to the presence of nNs. Furthermore, we have measured the pattern of methylated histones in the DNA of hMSCs on nN and are working to correlate these data with functional capacity for differentiation. Our data indicate that the presence of nN affects the organization of the actin cytoskeleton and the morphology of the nucleus, and these effects are thought to be mediated through changing expression patterns of focal adhesion and nuclear envelope genes. This ongoing work employs a novel cell culture platform for investigating and elucidating fundamental processes in stem cell biology, and will be used to enhance the differentiation capacity of hMSCs for tissue engineering applications.