dense continental
advertisement

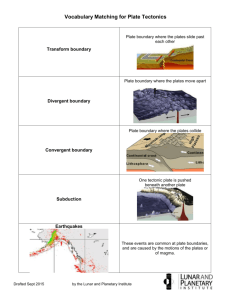
Name__________________________________Date________________________ Plate Tectonics 1. What happens when an oceanic plate converges with a continental plate? The less dense oceanic plate slides under the denser continental A) plate. The denser oceanic plate slides on top of the less dense continental B) plate. The less dense oceanic plate slides past the denser continental C) plate. The denser oceanic plate slides under the less dense continental D) plate. 2. A divergent boundary is a boundary between two plates that __________. A) B) C) slide along each other move away from each other move toward each other 4. What clue supported the continental drift theory? A) Similar rock structures have been found on different continents. Fossils of animals have been found on continents separated by B) oceans. C) D) a puzzle-like fit of all the continents all answers are correct 5. What is the plate tectonic theory? the belief that continents have moved slowly apart to their current A) locations on Earth the belief that Earth is broken into sections that fit together into one B) sphere the belief that hot, less dense material is forced up through Earth's C) crust through mid-ocean ridges the belief that Earth's crust and upper mantle is broken into sections Name__________________________________Date________________________ Plate Tectonics 6. What are strike-slip faults? Need a Hint? a boundary where rocks move in the same directions at the same A) rate a boundary where rocks on the same side of the fault move in the B) same direction, but at different rates a boundary where rocks on opposite sides of the fault move in C) opposite or the same directions at different rates D) a boundary where rocks in the fault never move 7. Why was the discovery of no rocks older than 2 billion years old on the ocean floor so important? Need a Hint? This evidence proved that new seafloor features are constantly A) being added due to reversals of Earth's magnetic field. This evidence proved that the rocks on the seafloor were older than B) rocks on continents. This evidence proved that new seafloor features are constantly C) being added due to seafloor spreading. This evidence proved that new seafloor features are constantly D) being added due to continental drift. 8. How do scientists explain the formation of underwater mountain ranges? Need a Hint? A) B) C) continental drift convection currents seafloor spreading strike-slip faults D) Name__________________________________Date________________________ Plate Tectonics 9. How do scientists use sound waves to figure out the shape of the ocean floor? Need a Hint? The longer it takes a sound wave to return to the ship, the more A) shallow the water is. The longer it takes a sound wave to return to the ship, the colder the B) water is. The less time it takes a sound wave to return to the ship, the deeper C) the water is. The longer it takes a sound wave to return to the ship, the deeper D) the water is. 10. How can crust disappear at the edge of a boundary? Need a Hint? A) B) C) D) because new crust is being added to the other edge of the boundary The other edge of the boundary is being pulled into Earth's core. Gravity is pulling it down. It is too dense and is sinking into Earth. 12. Who first proposed the theory of continental drift? Need a Hint? A) B) C) Galileo Galilee Alfred Wegener Albert Einstein Harry Hess D) Name__________________________________Date________________________ Plate Tectonics 13. What do scientists believe is the force behind the plate tectonics theory? Need a Hint? A) B) C) the movement of the planets convection currents the Sun's gravity gravity slab pull D) 14. What is a transform boundary? Need a Hint? A) B) C) D) A transform boundary is when two plates slide past one another. A transform boundary is when two plates collide. A transform boundary is when two plates move toward each other. A transform boundary is when two plates pull away from each other. 15. What is the lithosphere? Need a Hint? A) B) C) D) the upper part of the mantle the plates that make up the crust and the upper part of the mantle large, flat stones sitting on top of malleable magma the plates that make up the crust