Transcription Translation notes completed
advertisement

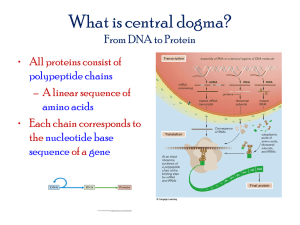
Let’s Review! Where is the DNA stored? In the nucleus What is the membrane around that organelle called? Nuclear envelope What are the openings in that membrane that lead to other parts of the cell called? Nuclear pores What organelle makes proteins? Ribosomes While DNA has the information for all the cell’s activities, it is not directly involved in the day to day operations of the cell. Proteins are responsible for implementing the instructions contained in DNA Each gene along a DNA molecule directs the synthesis of a specific type of messenger RNA molecule (mRNA). The mRNA interacts with the protein-synthesizing machinery to direct the ordering of amino acids in a polypeptide. RNA= ribonucleic acid Ribonucleic acid Ribose= Single stranded Needed for the production of proteins Nitrogenous base uracil instead of thymine Steps from DNA to Proteins 1. DNA is copied or transcribed into a single strand of mRNA (messenger RNA) 2. The mRNA exits the nucleus through a nuclear pore 3. The mRNA then is read by Ribosomal RNA. 4. In the ribosome, the mRNA is read and amino acids attached to tRNA (transfer RNA) are assembled to make proteins. DNA -> RNA -> Protein Genetic code DNA contains a triplet code Every three bases on a DNA strand code for one amino acid Each three-letter unit on mRNA is called a codon Some amino acids can have more than one codon The code is nearly universal to all living organisms All animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, archaea, and viruses use this same genetic code. All these organisms evolved from the same chemical basis, so the same chemical process continued through evolution. Transcription Transcription= process in which DNA’s nucleotide sequence is converted to the form of a singlestranded RNA molecule mRNA= messenger RNA RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template DNA molecule unzips RNA bases pair with the complementary DNA bases RNA has uracil instead of thymine RNA polymerases links the RNA nucleotides together RNA polymerase Enzyme found in the nucleus Separates the two DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases Then moves along one of the DNA strands and links RNA nucleotides together In prokaryotes, the mRNA transcribed from a gene is the direct messenger molecule needed to make a protein In eukaryotes, the mRNA has to be modified before it leaves the nucleus Noncoding nucleotides interrupt the nucleotide sequences Internal noncoding sequences are called introns Researchers are still trying to determine their function The coding regions, or the parts of the gene that will be expressed are called exons Before mRNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons are connected together in a process called RNA splicing Translation tRNA= transfer RNA, translates the three-letter codons of mRNA to the amino acids that make up proteins (an “interpreter”) Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating in the cytoplasm Transports amino acids to the mRNA Have anticodons that are complementary to mRNA codons Recognizes the appropriate codons on the mRNA and bonds to them with Hydrogen bonds (there is a different version of tRNA molecule that matches each codon) Ribosome Coordinates the functioning of mRNA and tRNA Consists of two subunits made up of proteins and rRNA (ribosomal RNA) Small subunit with a binding site for mRNA Large subunit with a binding site for tRNA rRNA= made in nucleolus, and functions to decode the mRNA into amino acids The subunits of the ribosome act as a vise holding the mRNA and tRNA close together The ribosome connects the newly arrived amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain Mutations A. Mutation = permanent alteration in cell’s DNA base sequence B. Almost all cancers begin as a mutation that is passed along at replication. 1. In somatic cells (body cells) 2. Mutation rate is low, but after decades of accumulated mutations, cells can become malignant. C. Heritable mutations occur in germ-line cells (cells that divide to make sperm and eggs). D. Heritable mutations also create genetic diversity.