IPC Fall Semester Review Name Period ______ Teacher Sequence
advertisement
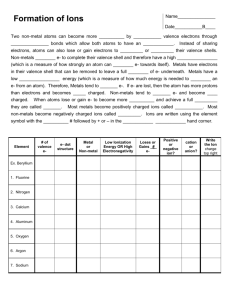
IPC Fall Semester Review Name __________________________________ Period ___________ Teacher _______________ Sequence and define the common steps found in scientific methods in the correct order. 1. State the problem 2. Gather information 3. Form a hypothesis 4. Test the hypothesis 5. Analyze data 6. Draw a conclusion Directions: Choose the term from the word list that best completes each statement. Write the term in the blank at the left of each statement. graph y-axis control vertical line independent 1. A visual display of data or information is a _graph_____. 2. In a line graph, the __vertical____ axis is called the y-axis. 3. In a line graph, the dependent variable is plotted on the __y-axis____. 4. The type of graph that is useful for showing trends or continuous change is a __line____. 5. A variable that changes and affects the measure of another variable is called the __independent____ variable. 6. An experimental setup that does NOT contain the variable being tested is called the ___control__________. Quantity Measured Length Mass Time Temperature Unit Meter Kilogram Second Kelvin Symbol m kg s K Practice with these conversions: 3000 mg = 3 g 198 g = .198 kg 65 L= 65000 mL 8.3 cm = 83 mm 1. Long hair in the laboratory must be A. cut short. B. held away from the experiment with one hand. C. always neatly groomed. D. tied back or kept entirely out of the way with a hair band, hairpins, or other confining device. 2. If you wear contact lenses in the school laboratory, A. take them out before starting the lab. B. you do not have to wear protective goggles. C. advise your science instructor that you wear contact lenses. D. keep the information to yourself. 3. You are heating a substance in a test tube. Always point the open end of the tube A. toward yourself. B. toward your lab partner. C. toward another classmate. D. away from all people E. none of the above 4. The attractive forces in a liquid are a. strong enough to prevent the particles from changing positions. b. too weak to hold the particles in fixed positions. c. stronger than those in a solid and a gas. d. strong enough to provide a definite shape and volume. What is the 5. What is the physical change of a solid to a gas without production of liquid? a. heat of fusion c. sublimation b. condensation d. deposition 6. The energy required to completely change a solid to a liquid is a. heat of fusion b. boiling point c. melting point 7. By which process do gases take the shape of their container? a. evaporation c. adhesion b. expansion d. diffusion 8. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matter a. are in constant motion. c. have different colors. b. have different shapes. d. are always fluid. d. heat of vaporization 9. Particles within a liquid a. do not move. b. vibrate weakly about fixed positions. c. Slide pass each other. d. Rapidly collide with each other. 10. ___D___ good conductors of heat and electricity ___A___ break easy and have no magnetism ___B____ stable and nonreactive ___C___ considered semiconductors; solid at room temp but brittle A. Non metals B. Noble gases C. Metalloids D. Metals 11. A(n) _________ is a mixture that settles upon standing by which produces a sediment. A. solution B. colloid C. suspension D. element 12. A positive Tyndall Effect demonstrated by smoke and fog are examples of a _______________. A. substance B. solution C. colloid D. suspension 13. The law of conservation of mass states that mass cannot be __________________. A. burned B. changed in form C. created or destroyed D. heated or cooled 14. The resistance of a fluid is referred to as _____________. A. pressure B. energy C. viscosity D. buoyancy 15. Examine the figure to the right. Which of the following statements explains why a steel ship will float on saltwater but a bar of steel will sink. A. The density of the ship is greater than water. B. The viscosity of saltwater is less than pure water. C. The buoyancy force on the ship is greater than the weight of the ship. D. The gravitational force is greater than the buoyany force. 16. What is the property of metals which allows them to be hammered into sheets? A. luster B. hardness C. malleability D. ductility 17. If a substance breaks easily, it is said to be ________________. A. reactive B. brittle C. magnetic D. ductile 18. One chemical property that can be measured in a substance is its reactivity with water. What is another chemical property? A. density B. flammability C. malleability D. solubility True 411009 story quiz-2-metals-non 0 0 0 0 0 0 411009 true 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 You have reache First Name Last Name Please enter first OK 734 19. A chemical change __________. A. always can be reversed physically B. results in a new substance C. never will change state D. requires an a acid in order to take place 20. Select from the scientist below to complete the statements: Democritus Bohr Rutherford Thomson Dalton ___Bohr____________ determined that electrons orbit the nucleus like the planets around the sun ___Thomson______________ discovered electrons and developed the plum pudding model ____Rutherford___________ conducted the gold foil experiment and determined that atoms are mostly empty space ____Democritus____________ named the smallest indivisible particle Atomos ____Dalton___________ Stated 5 principles of atomic theory; one being that atoms of the same element have the same properties 21. Complete the table below Subatomic particle Location Charge Relative Mass Proton Nucleus Neutron Nucleus Electron Cloud +1 1 0 1 -1 0 22. 53 The atomic number for this element is ___53____________ I The atomic mass for this element is ___126______________ 126 Number of protons____53_____; neutrons _____73_____; electrons _____53______ Group Number____17_________; Name of group_____Halogen_________________ Number of valence electrons ____7__________; draw Lewis dot structure Which group of elements would have similar properties to I? F Cl Br sb Te Xe I C P Se 23. Which is an example of an ion? Isotope? An atom loses 2 electrons __ion______ Oxygen-16 and Oxygen-18 ___isotope__________ Number of protons stays the same, but the mass changes _____isotope_________________ An atom gains 1 electron ___ion_______ 24. Select from the following: Metal Non-Metal Metalloid ___Metalloid_________ Elements that lie along the stair-step line ____Non-Metal________ Poor conductors of electricity __Metal__________ Malleable and ductile ____Non-Metal________ Gas at room temperature ____Metalloid________ Semiconductors ___Metal_________ Lustrous ___Non-Metal_________ Brittle 25. Select from the following Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals ___Halogen___________________ Group 17 Transition Metals Noble Gas _____Alkali__________________ 1 valence electron ___Alkali_______________Highly reactive metal ___Transition___________________ Groups 3-12 26. Name the element Halogens _____Alkaline Earth__________________2 valence electrons ____Noble gas_____________ Complete valence shell _______________ I’m in energy level 5 and have 6 valence electrons _______________ I’m in Group 17 and have a mass greater than Cl _______________I’m an alkaline earth metal with 56 neutrons _______________ I’m the lightest noble gas _______________ I have one valence electron but I’m a nonmetal _______________ I’m the heaviest alkali metal 27. The forces that hold different atoms or ions together are __________ a. Electric currents c. physical bonds b. Chemical bonds d. nuclear forces 28. Ionic bonds occur between _____________ and ________________ a. Metals, metals c. metals, nonmetals b. Nonmetals, nonmetals d. ions 29. Covalent bonds occur between ____________ and _________________ a. Metals, metals c. metals, nonmetals b. Nonmetals, nonmetals d. cations, anions 30. A charged atom is call a/an _________________ a. Ion c. formula b. Molecule d. valence electron 31. Atoms joined by covalent bonds ________________ electrons a. Gain c. reject Lose d. share 32. According to the __________________, atoms will form bonds by gaining, losing or sharing valence electrons in order to become more stable a. Octet rule c. Law of Conservation of Mass b. Periodic Law d. Chemistry Guidelines 33. The bonding characteristics of oxygen are most similar to the bonding characteristics of_ a. Hydrogen b. Silicon c. sulfur d. helium 34. Which of these elements is most likely to donate one electron? c. Be d. Si c. K d. He 35. The elements of which of these groups on the periodic table are most resistant to forming compounds? e. Group 1 f. Group 9 c. Group 14 d. Group 18 36. Elements in Group 16 of the periodic table usually g. Form large molecules c. gain electrons when bonding h. Act like metals d. solidify at room temperature 37. Which compound is formed from two oppositely charges ions? i. j. Sugar, C12H22O11 Quartz, SiO2 c. carbon dioxide, CO2 d. salt, NaCl 38. According to the periodic table, which of these elements will form an ion with a -2 charge? k. S l. Mg c. F d. Rb 39. Matching Match the molecule or compound with the type of bond: a) Covalent bond or b) Ionic bond MgBr2 Ionic O2 Covalent NaF Ionic P205 Covalent CO2 Covalent 40. Using subscripts in the chemical formula to make the charges of ions cancel out, which is the correct chemical formula for Cs+1 , O-2? a. CsO2 b. Cs2O c. CsO d. Cs3O 41. Using subscripts in the chemical formula to make the charges of ions cancel out, which is the correct chemical formula for Al+3 , N-3? c. Al3N3 d. AlN c. AlN3 d. Al2N 42. Using subscripts in the chemical formula to make the charges of ions cancel out, which is the correct chemical formula for Li_ , F_ (you must determine the superscripts/oxidation numbers)? e. LiF f. Li2F2 c. LiF3 d. Li2F 43. Using subscripts in the chemical formula to make the charges of ions cancel out, which is the correct chemical formula for Al_ , Cl_ (you must determine the superscripts/oxidation numbers)? g. AlCl h. Al2Cl2 c. AlCl3 d. Al3Cl 44. Matching Match the element with its oxidation number C-D a. +1 Na - A b. -2 S-B c. 0 He - C d. +/- 4 45. A bond in which electrons are shared unequally resulting in a slightly positive and slightly negative end is called a i. j. Nonpolar bond Hydrate bond c. Polar bond d. Metallic bond 46. Metals typically lose electrons and become positively charged ions called k. Anions l. Cations c. positrons d. isotopes