C3 - Wednesfield High School
advertisement
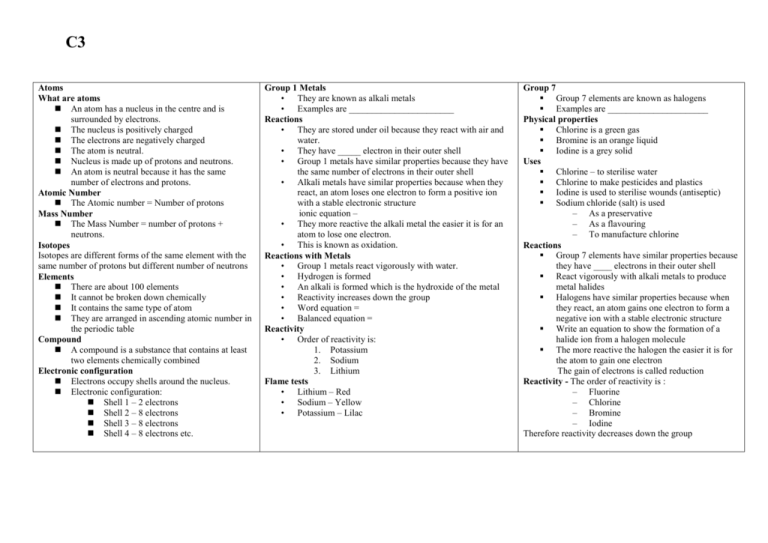
C3 Atoms What are atoms An atom has a nucleus in the centre and is surrounded by electrons. The nucleus is positively charged The electrons are negatively charged The atom is neutral. Nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. An atom is neutral because it has the same number of electrons and protons. Atomic Number The Atomic number = Number of protons Mass Number The Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons. Isotopes Isotopes are different forms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons Elements There are about 100 elements It cannot be broken down chemically It contains the same type of atom They are arranged in ascending atomic number in the periodic table Compound A compound is a substance that contains at least two elements chemically combined Electronic configuration Electrons occupy shells around the nucleus. Electronic configuration: Shell 1 – 2 electrons Shell 2 – 8 electrons Shell 3 – 8 electrons Shell 4 – 8 electrons etc. Group 1 Metals • They are known as alkali metals • Examples are _______________________ Reactions • They are stored under oil because they react with air and water. • They have _____ electron in their outer shell • Group 1 metals have similar properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell • Alkali metals have similar properties because when they react, an atom loses one electron to form a positive ion with a stable electronic structure ionic equation – • They more reactive the alkali metal the easier it is for an atom to lose one electron. • This is known as oxidation. Reactions with Metals • Group 1 metals react vigorously with water. • Hydrogen is formed • An alkali is formed which is the hydroxide of the metal • Reactivity increases down the group • Word equation = • Balanced equation = Reactivity • Order of reactivity is: 1. Potassium 2. Sodium 3. Lithium Flame tests • Lithium – Red • Sodium – Yellow • Potassium – Lilac Group 7 Group 7 elements are known as halogens Examples are ______________________ Physical properties Chlorine is a green gas Bromine is an orange liquid Iodine is a grey solid Uses Chlorine – to sterilise water Chlorine to make pesticides and plastics Iodine is used to sterilise wounds (antiseptic) Sodium chloride (salt) is used – As a preservative – As a flavouring – To manufacture chlorine Reactions Group 7 elements have similar properties because they have ____ electrons in their outer shell React vigorously with alkali metals to produce metal halides Halogens have similar properties because when they react, an atom gains one electron to form a negative ion with a stable electronic structure Write an equation to show the formation of a halide ion from a halogen molecule The more reactive the halogen the easier it is for the atom to gain one electron The gain of electrons is called reduction Reactivity - The order of reactivity is : – Fluorine – Chlorine – Bromine – Iodine Therefore reactivity decreases down the group C3 Electrolysis • The anode is the positive electrode • The cathode is the negative electrode • Anions are negative attached to the anode • Cations are positive ions attached to the cathode • An electrolyte is the liquid which conducts electricity Sulphuric acid solution • Sulphuric acid solution can be broken down by electrolysis into hydrogen and oxygen • Hydrogen (+ve) is made at the cathode (negative electrode) • Oxygen (-ve) is made at the anode (positive electrode) Test for gases • Test for hydrogen = burns with a ‘pop’ when lit using a lighted splint • Test for oxygen = relights a glowing splint Aluminium • Aluminium is extracted from its minerals using electricity • Electrolysis is the decomposition of a liquid using electricity • Bauxite is a mineral containing aluminium. It is molten aluminium oxide. • Oxygen is formed at the graphite anode • Anodes are gradually worn away by oxidation • Aluminium is formed at the graphite cathode • Process has a high electrical energy requirement • Cryolite is used to lower the melting point of the aluminium oxide • Aluminium is expensive because its extraction uses large amounts of electricity Metals • Iron is used to make steel and to make cars and bridges because it is strong • Copper is used to make brass and to make electrical wiring because it is a good electrical conductor. Physical properties of metals • Lustrous, hard and high density • High tensile strength • High melting & boiling point due to strong metallic bonds • Good conductors of heat and electricity • Particles in a metal are held together by metallic bonds Properties • Properties needed by a metal for a particular given use e.g. Saucepan bases need to be good conductors of heat Crystals • Metals have a structure which contains crystals • Particles in solid metals are close together and in a regular arrangement • At low temperatures some metals can be superconductors. Metallic bonding • This can be described as strong electrostatic attraction between a sea of delocalised electrons and close packed positive metal ions • This explains why metals have high melting and boiling points – because of the strong attraction between the delocalised electrons and the positive metal ions needs to be overcome. Electricity • When metals conduct electricity electrons move • These are delocalised electrons Superconductors • Materials that conduct electricity - little or no resistance • They can be powerful electromagnets • However they only work at very low temperatures Transition Elements Examples Copper = Cu Iron = Fe All transition elements are metals and have typical metallic properties Colours • Compounds of transition elements are often coloured – Copper compounds are blue – Iron II compounds are light green – Iron III compounds are orange/brown Catalysts • Transition elements and their compounds are often catalysts – Iron in the Haber process – Nickel in the manufacture of margarine – A catalyst _______ up the rate of a reaction. But it does not get used up. Thermal Decomposition • This is a reaction in which a substance is broken down into at least two other substances by heat. • It usually results in a colour change Precipitation • Reaction between solutions that makes an insoluble solid • Sodium hydroxide solution is used to identify the presence of transition metal ions in solution: – Copper ion = blue solid – Iron II ion = green solid – Iron III ion = orange solid These are all solid precipitates C3