LESSON PLANS—HONORS Ecological Relationships Objective
advertisement

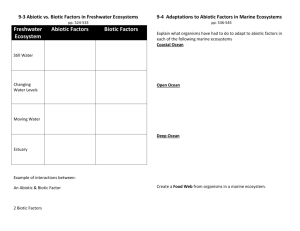
LESSON PLANS—HONORS Ecological Relationships Objective: ACOS 13a To describe the interdependence of biotic/abiotic factors in an ecosystem ACT QUALITY CORE: Explain how organisms cooperate and complete in ecosystems and how interrelationships/interdependencies of organisms may generate ecosystems that are stable for thousands of years Describe examples of competition, symbiosis, predation ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How do biotic and abiotic factors influence an ecosystem and what interactions occur between different organisms? LEARNING TARGET: I can analyze data to determine rainfall effect on primary productivity. BEFORE (Strategy: Interpretation of Data) A. Using the graph on page 84, determine what happens to primary productivity when rainfall increases. What factors other than water might affect primary productivity? (Rainfall increases, productivity increases; sunlight, types and amounts of nutrients in soil, number of herbivores) LEARNING TARGET: I can identify the causes of climate and the 3 main climate zones. DURING (Strategy: Graphic Organizer—Wagon Wheel) B. Using the 4 subtopics in chapter 4-1, create a 4 spoke wagon wheel to summarize the main ideas about climate. Climate 1. Average year-after-year conditions of precipitation and temperature. 2. Greenhouse effect is natural situation in which heat is retained by carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor. 3. Solar radiation hits the Earth at different degrees latitude which creates the different climate zones. 4. Unequal heating of land surfaces and water drives wind and water currents which transport heat throughout the biosphere. LEARNING TARGET: I can identify the symbiotic relationships in ecosystems. AFTER (Strategy : Pre-read) C. Create graphic organizer while reading pp. 92-97 defining and giving examples for each symbiotic relationship. (plant-plant; plant-animal; animalanimal) Relationship Define Examples Mutualism both benefit lichen; yucca plant-moth; gazelle-ostrich Commensalism + 0 orchid-tree; bird-tree; shark-remora Parasitism + mistletoe-spruce; aphids—roses; tick-deer EQ: Abiotic factors such as precipitation and temperature affect the climate of a region. Climate regions have particular biotic factors that are characteristic of the region. Within these regions, there are symbiotic relationships that enable organisms to be more successful. An example is the orchid which lives high in the canopy of trees in the rainforest to allow it access to more sunlight and moisture. HOMEWORK Study for chapter 3 test