Chapter 6 Objectives
advertisement

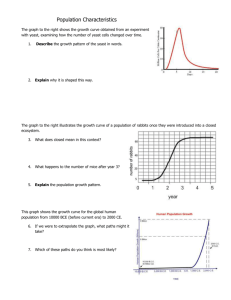
Chapter 6: Population Biology 6.1 Dynamics of Population Growth 1. Explain the relationship between the number of organisms in a population and the abiotic factors of the environment. 2. Explain how exponential growth occurs in a natural population. 3. Explain the relationship between a population and it’s carrying capacity. 4. Describe how species respond to limits differently using r- and K-selected species reproductive strategies 6.2 Complicating the Story: r=BIDE 1. Explain what influences the rate of population growth. 6.3 Factors that Regulate Population Growth 1. Explain how population growth is density independent of abiotic factors and natural disasters. 2. Explain how population growth is density dependent of biotic factors such as predator-prey relationships, stress, crowding, and territoriality. 6.4 Conservation Biology 1. Explain the role of island biogeography in population size, growth, and stability. Essential Knowledge The stability of populations, communities, and ecosystems is affected by interactions with biotic and abiotic factors Biological systems are affected by disruptions such as invasive species, human impact, natural disasters, water limitations, salination to their dynamic homoeostasis. Organisms exchange information with each other in response to internal changes and external cues, which can change behavior (i.e., flight or fight response, predator warnings, protection of young, plant-plant interactions due to herbivory, avoidance response). Living systems have a variety of signal behaviors or cues that produce changes in the behavior of other organisms and can result in differential reproductive success (i.e., herbivory responses, territorial marking in mammals, coloration on flowers). Animals use visual, audible, tactile, electrical and chemical signals to indicate dominance, find food, establish territory and ensure reproductive success (i.e., bee dances, bird songs, territorial marking in mammals, pack behavior in animals, her, flock, and schooling behavior in animals, predator warning). Vocabulary Biotic potential Boom & bust life cycle Carrying capacity (K) Conservation genetics Critical number Density dependent Density independent Doubling time Emigration Exponential growth Fecundity Founder effect Generalist species Genetic drift Genetic drift Hardy-Weinberg Immigration Island biogeography J-curve K-selected species Logistic growth Metapopulation Population r-selected species Rule of 70 S-curve Sigmoid Specialist species Survivorship curves Territoriality