Question 3 - REVISION-IB2
advertisement

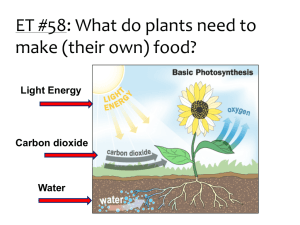
IB Biology Topic 3 Revision Standard Level Topics: 3.1Chemical elements and water 3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins 3.3 Enzymes 3.4 DNA structure 3.5 DNA replication 3.6 Transcription and translation 3.7 Cell respiration 3.8 Photosynthesis 1 1. (a) Define Enzyme (3) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (b) Describe enzyme activity, using the ‘lock-and-key model.’ (6) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (c) Explain two examples of how enzymes are used in biotechnology. (8) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2 2. Explain the signficance of water and its properties to living organisms (9) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. (a) Outline the absorption of light by photosynthetic pigments in plants. [5] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3 (b) Describe the effect of different light intensities on the rate of photosynthesis. [5] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (c) Explain how the rate of photosynthesis can be determined by using direct and indirect methods. [8] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. (a) List three major groups of food macromolecules and the products formed upon complete digestion. [3] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4 5. Which of the following is the most soluble in water? A. Olive oil B. Glycogen C. Glucose D. Cellulose 6. What molecule does the following structure represent? A. Glycerol B. Glucose C. An amino acid D. A fatty acid 7. 5 8. If mRNA has a codon CAU, what would be the corresponding anticodon on the tRNA molecule? A. CAT B. GUA C. CAU D. GTA 9. Which of the following is an organic compound? A. Calcium carbonate B. Carbon dioxide C. Glucose D. Water 10. 11. Which of the following is an organic compound? A. Calcium carbonate B. Carbon dioxide C. Glucose D. Water 6 12. Which of the following is the most soluble in water? A. Olive oil B. Glycogen C. Glucose D. Cellulose 13. 7 14. 15. Which group of three molecules makes up one RNA nucleotide? A. Phosphate, ribose, uracil B. Phosphorus, ribose, adenine C. Uracil, deoxyribose, phosphorus D. Guanosine, deoxyribose, phosphate 16. Many elements are necessary to form biochemicals required by living organisms. For each element below, state the name of one molecule containing the element and state the function of the molecule. (a) Iron: [2] Molecule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ……………………………….. Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . …………………………………………………………….. (b) Phosphorus: [2] Molecule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..................................................... 8 17. There are many abiotic factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis in terrestrial plants. Wheat is an important cereal crop in many parts of the world. Wheat seedlings were grown at three different concentrations of carbon dioxide (in parts per million) and the rate of photosynthesis was measured at various light intensities. (Nov 2002) (a) Describe the relationship between the rate of photosynthesis and light intensity for wheat seedlings grown at a CO2 concentration of 500 ppm.[2] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (b) Outline the effect of CO2 concentration on the rate of photosynthesis of the wheat seedlings. [3] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9 (c) The normal atmospheric concentration of CO2 is 370 ppm. Deduce the effect of doubling the CO2 concentration to 740 ppm on the growth of wheat plants.[2] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Leaf area and chlorophyll levels were measured in sun leaves and shade leaves of Hedera helix (English Ivy) and Prunus laurocerasus (Cherry Laurel). Sun leaves developed under maximal sunlight conditions while shade leaves developed at reduced sunlight levels in the shadow of other leaves. (d) Calculate the percentage increase in the amount of chlorophyll in shade leaves of ivy compared to sun leaves of ivy. [1] (e) Suggest a reason for the differences in chlorophyll concentration and leaf area in sun and shade leaves in these two species. [2] ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 10 18. a. The table below compares the properties of organic componds. If the property is a characteristic featured of the compound, mark the appropriate box or boxes with a tick. (3) Property Glucose Starch Lipids A source of energy A polysaccaride A main food store in some seeds b. When a disaccaride is formed, what is released? (1) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 19. The diagram below shows possible pathways for the breakdown of glucose in various cells. (a) State the names of processes Q and R. Q: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . [1] R: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . [1] 11 (b) Deduce the names of substances A and D. A: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .[1] D: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . [1] c) State the organelle in which process R takes place. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .[1] 20. State the main photosynthetic pigment in plants. [1] ................................................................. (b) State the two materials used to convert carbon dioxide to organic molecules in plants. [2] ................................................................. ................................................................. 12 Revision Packet Unit 2 Answer Key: Question 1 Question 2 good solvent / most substance dissolve in it; many substances dissolved / many reactions take place in cytoplasm; high specific heat capacity / (words to that effect); water heats up and cools down slowly; easier to maintain constant body temperature; water is a habitat for many organisms; temperature of ponds / rivers / sea is (relatively) stable; high latent heat of vaporisation / (words to that effect); water used as a coolant in sweating / transpiration; water is liquid at most temperatures on Earth; can be used as a transport medium as in blood / xylem / phloem; water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other; water molecules are cohesive; xylem transport / transpiration stream based on cohesion; surface tension of water; possible for organisms to live on the surface of water (despite being denser); 13 water is transparent; light passes though the leaf to the chloroplasts / the eye to reach the retina; water is incompressible; used in hydrostatic skeletons / amniotic fluid / turgid plant cells; Question 3 (a) most light absorbed by chlorophyll; light absorbed by carotenoids; light (energy) converted to chemical energy; red light absorbed well / efficiently; blue light absorbed well / efficiently; green light mostly reflected; sketch of absorption spectrum; pigments in chloroplasts / thylakoids / photosystems; electrons excited / raised to higher energy levels; excited electrons enter electron transport chain; coupled to photophosphorylation / ATP production; photolysis of water; [5 max] (b) little / no photosynthesis in low light intensity; rate of photosynthesis increases as light intensity rises; linear increase at moderate light intensities; smaller increases at higher light intensities; light saturation / no further increases at highest light intensities; some other factor becomes limiting (such as uptake); 2 CO graph with axes correctly labelled and linear increase and plateau phases; [5 max] (c) (No details expected.) simple equation for photosynthesis / statement of reactants and products of photosynthesis; measure production of ; 2 O measured by counting bubbles; measuring volume produced; measure uptake of ; 2 CO measured by radioactive ; 2 CO measure change in pH (due to gases); measured using pH indicator / pH meter; increase in biomass; dry the plant tissue before finding mass; measured as mass before and after photosynthesis; different batches of plants for each mass determination; colour change of dye / DCPIP (due to transfer of electrons); [8] Question 4 (a) carbohydrates yield monosaccharides / reducing sugars; (do not accept glucose as a substitute for monosaccharides / reducing sugars) proteins yield amino acids; fats yield fatty acids / alkanoic acids and glycerol; [3] 14 5.C 6.A 7.B 8.B 9.C 10.A 11.C 12.C 13.A 14.A 15.A Question 16 (a) name of molecule; function of molecule; [2 max] Fe examples: haemoglobin; transports oxygen (in the blood); myoglobin; store of oxygen in muscle; cytochromes / ferredoxin; electron carrier; (do not accept avoids anaemia) (b) name of molecule; function of molecule; [2 max] P examples: ATP / ADP; energy storage and release; DNA / RNA / nucleotides; genetic (hereditary) material; phospholipid structural component of membrane Question 17 (a) rate of photosynthesis increases (rapidly) / directly proportional; rate of photosynthesis levels off / increases slightly after 10 000 lumen m ; [2] [3 max] (b) maximum photosynthetic rate is highest with highest CO2concentration; at low light levels, higher CO2 slightly increases the photosynthetic rate; at low CO2/ 280 ppm, the photosynthetic rate reaches its maximum at low light levels / constant over most light intensity / at 280 ppm CO concentration limits photosynthesis; at 500 and 1300 ppm CO2 the curve is the same shape but with different maximum rates / each higher light intensity requires a higher CO2 concentration to reach 2 maximum rate; maximum rate of photosynthesis from 280 to 500 ppm / increases 5 to 6 times while 500 to 1300 ppm increases 1.5 times; 15 (c) the rate of photosynthesis will increase (over the rate at 370 ppm); the photosynthetic rate will at least double (but less than 5-6 times); not linear; bigger plants / more growth / more grain / greater yield; [2 max] (d) (accept 13.2 %) 4.3 – 3.8 100 13.16% [1] Question 18 Glucose Property A source of x energy A polysaccarid e A main food store in some seeds Starch x Lipids x x x x b. water Question 19 (a) Q: anaerobic respiration / fermentation; R: aerobic respiration / Kreb’s (citric acid) cycle; [2] (b) A: pyruvate / 3-oxopropanoate; D: carbon dioxide; [2] (c) mitochondrion; [1] Question 20 (a) chlorophyll (a) [1] (b) ATP; NADPH / hydrogen; water; RuBP; Rubisco; [2 max] 16