Solid and Hazardous Waste
advertisement
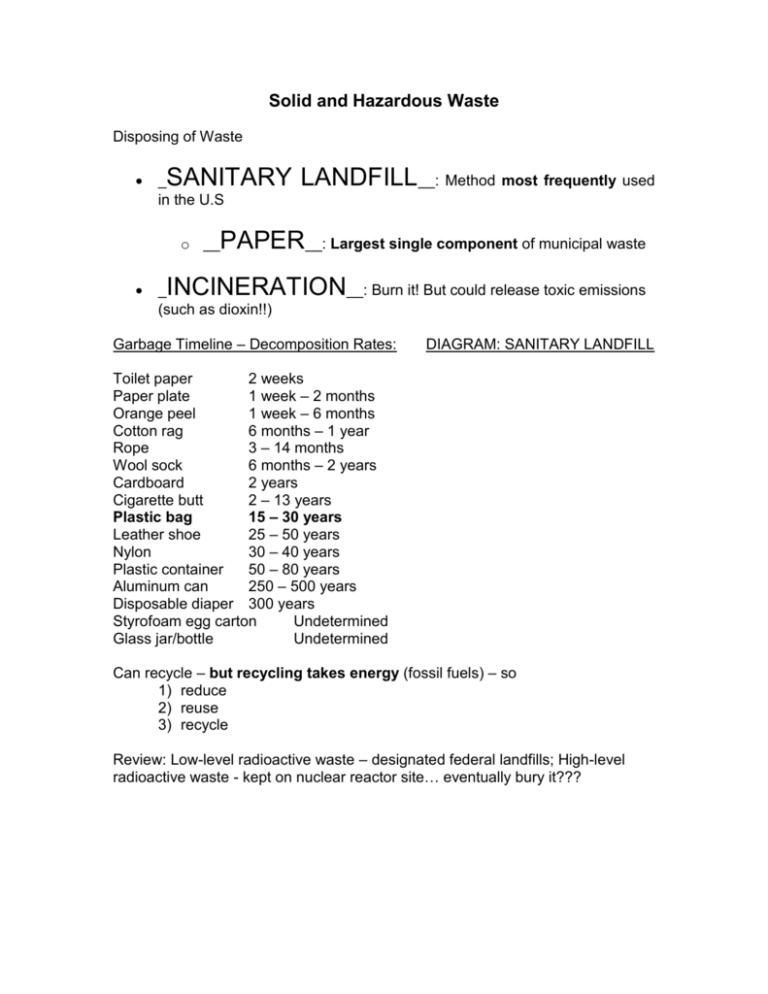
Solid and Hazardous Waste Disposing of Waste SANITARY LANDFILL__: Method most frequently used _ in the U.S o __ PAPER__: Largest single component of municipal waste INCINERATION__: Burn it! But could release toxic emissions _ (such as dioxin!!) Garbage Timeline – Decomposition Rates: DIAGRAM: SANITARY LANDFILL Toilet paper 2 weeks Paper plate 1 week – 2 months Orange peel 1 week – 6 months Cotton rag 6 months – 1 year Rope 3 – 14 months Wool sock 6 months – 2 years Cardboard 2 years Cigarette butt 2 – 13 years Plastic bag 15 – 30 years Leather shoe 25 – 50 years Nylon 30 – 40 years Plastic container 50 – 80 years Aluminum can 250 – 500 years Disposable diaper 300 years Styrofoam egg carton Undetermined Glass jar/bottle Undetermined Can recycle – but recycling takes energy (fossil fuels) – so 1) reduce 2) reuse 3) recycle Review: Low-level radioactive waste – designated federal landfills; High-level radioactive waste - kept on nuclear reactor site… eventually bury it??? Hazardous Waste (toxic and/or ignitable) Case Study: LOVE CANAL: Hazardous chemicals sealed in steel drums dumped into canal near Niagra NY (1942 – 1953) – canal covered with clay and topsoil and sold to Niagra school board for $1 – the area was developed – (1970’s) drums leaked toxic chemicals into area, people were getting SICK – was declared a Federal Disaster Area (Jimmy Carter) – became first declared Superfund Site (1983) – clean up cost: $400 million!! Case Study: BHOPAL INDIA: 1984 – World’s worst industrial accident – pesticide plant explosion – chemicals used to make carbamates released into atmosphere – up to 23,000 deaths, and up to 150,000 suffering from chronic illnesses can explode or release toxic fumes developed countries produce the most *by CHEMICAL and PETROLEUM industries, and by MINING and METAL industries. regulated by RCRA: (only regulates 5% of hazardous wastes because you have to produce/use/throw away 100 kg/month) RESOURCE CONSERVATION AND RECOVERY ACT * “Cradle to Grave” – monitors hazardous materials from their production to their disposal (Most) regulations fall under CERCLA: COMPREHENSIVE ENVIRONMENTAL RESPONSE, COMPENSATION, AND LIABILITY ACT * SUPERFUND!! * identify abandoned hazardous waste sites * protect and/or clean up groundwater and the site * put worst sites on NPL: _NATIONAL PRIORITIES LIST_ * $$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$ * parties responsible pay??????? or * government pays for clean up *2004: EPA identified approx. 11,300 sites, including 1,250 that were put on the NPL. *BROWNFIELD: A brownfield is a property, the expansion, redevelopment, or reuse of which may be complicated by the presence or potential presence of a hazardous substance, pollutant, or contaminant. It is estimated that there are more than 450,000 brownfields in the U.S. * Five WORST states: (MOST superfund sites) 1. New Jersey 2. California 3. Pennsylvania 4. New York 5. Michigan http://www.epa.gov/superfund/sites/ PREVENTION CHEAPER THAN CLEAN-UP!!!!!!!!! Remove or Detoxify Hazardous Waste: PHYSICAL TREATMENT___= * __ Filtering out solids Distilling liquids CHEMICAL TREATMENT__= *__ Precipitating chemicals out of solution Neutralize acids/bases BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT * __ _= Microorganisms breakdown waste/hazardous waste/ oil and other organic compounds BIOREMEDIATION Bacteria and enzymes help destroy or convert toxic compounds. PHYTOREMEDIATION Natural/genetically engineered plants absorb/filter/remove contaminants from soil and water. Ex: inserted Hg detoxifying gene of E. coli into genome of common soil bacteria = extracts Hg+ PLASMA TORCH_= *__ High temps decompose hazardous organic material, convert into simple molecules – can then be cleaned up easily