Section 6.6
advertisement

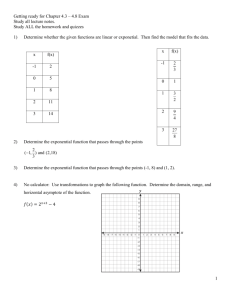
MATH 1100 SECTION 6.6 Notes Applications of Exponential & Logarithmic Functions Text Pages 419-430 Interest Formulas: If a principal P is invested at a rate r for a period of t years, then the amount A of the investment is given by: Simple Interest: A P1 rt Compounded n Times per Year: r At P1 n nt Compounded Continuously: At Pe rt Annual Percentage Yield: (APY) If an investment earns compound interest, then the annual percentage yield is the simple interest rate that yields the same amount at the end of one year. Exponential Growth and Decay: If no is an initial value experiencing exponential growth or decay, then the value at time t is modeled by the function, Growth: Decay: Half-Life: nt no e rt nt no e rt Physicists express the rate of decay in terms of the half-life = h, the time required for half the mass to decay. In terms of half-life, the rate of decay is, r ln 2 h Newton’s Law of Cooling: If Do is the initial temperature difference between an object and its surroundings, and if its surrounding have temperature TS, then the temperature of the object at time t is modeled by the function T t TS DO e kt where k is a positive constant that depends on the type of object. The pH Scale: pH log H where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions measured in moles per liter. The Richter Scale: The magnitude M of an earthquake is modeled by the function M log I S where I is the intensity of the earthquake (measured by the amplitude of a seismograph reading taken 100 km from the epicenter of the earthquake) and S is the intensity of a “standard” earthquake. The Decibel Scale: The intensity level of a sound, measured in decibels (dB), is modeled by the function I 10 log IO where I o is the reference intensity at a frequency of 1000 hertz, I O 10 12 W/m 2 Example 1: Finding the Term for an Investment to Double A sum of $5000 is invested at an interest rate of 9% per year. Find the time required for the money to double if the interest is compounded semiannually and continuously. Example 2: Calculating the Annual Percentage Yield Find the annual percentage yield for an investment that earns interest at a rate of 6% per year, compounded daily. Example 3: World Population Projections The population of the world in 2000 was 6.1 billion, and the estimated relative growth rate was 1.4% per year. If the population continues to grow at this rate, when will it reach 122 billion? Example 4: Number of Bacteria in a Culture A culture starts with 10,000 bacteria, and the number doubles every 40 minutes. a.) Find a function that models the number of bacteria at time t. b.) Find the number of bacteria after one hour. c.) After how many minutes will there be 50,000 bacteria? Example 5: Radioactive Decay Polonium-210 has a half-life of 140 days. substance has a mass of 300 mg. Suppose a sample of this a.) Find a function that models the amount of the sample remaining at time t. b.) Find the mass remaining after one year. c.) How long will it take the sample to decay to a mass of 200 mg? Example 6: Newton’s Law of Cooling A cup of coffee has a temperature of 200F and is placed in a room that has a temperature of 70F. After 10 min the temperature of the coffee is 150F. a.) Find a function that models the temperature of the coffee at time t. b.) Find the temperature of the coffee after 15 min. c.) When will the coffee have cooled to 100F? Example 7: PH Scale and Hydrogen Ion Cooling The most acidic rainfall ever measured occurred in Scotland in 1974; its pH was 2.4. Find the hydrogen ion concentration. Example 8: Sound Intensity of a Jet Takeoff Find the decibel intensity level of a jet engine during takeoff if the intensity was measured at 100 W/m2. Example 9: Magnitude of Earthquakes The 1906 earthquake in San Francisco had an estimated magnitude of 8.3 on the Richter scale. In the same year the strongest earthquake ever recorded occurred on the Columbia-Ecuador border and was four times as intense. What was the magnitude of the Columbia-Ecuador earthquake on the Richter scale? Example 10: Intensity of Earthquakes The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake that shook San Francisco had a magnitude of 7.1 on the Richter scale. How many times more intense was the 1906 San Francisco earthquake than the 1989 event?