Effects of the Industrial Revolution
advertisement
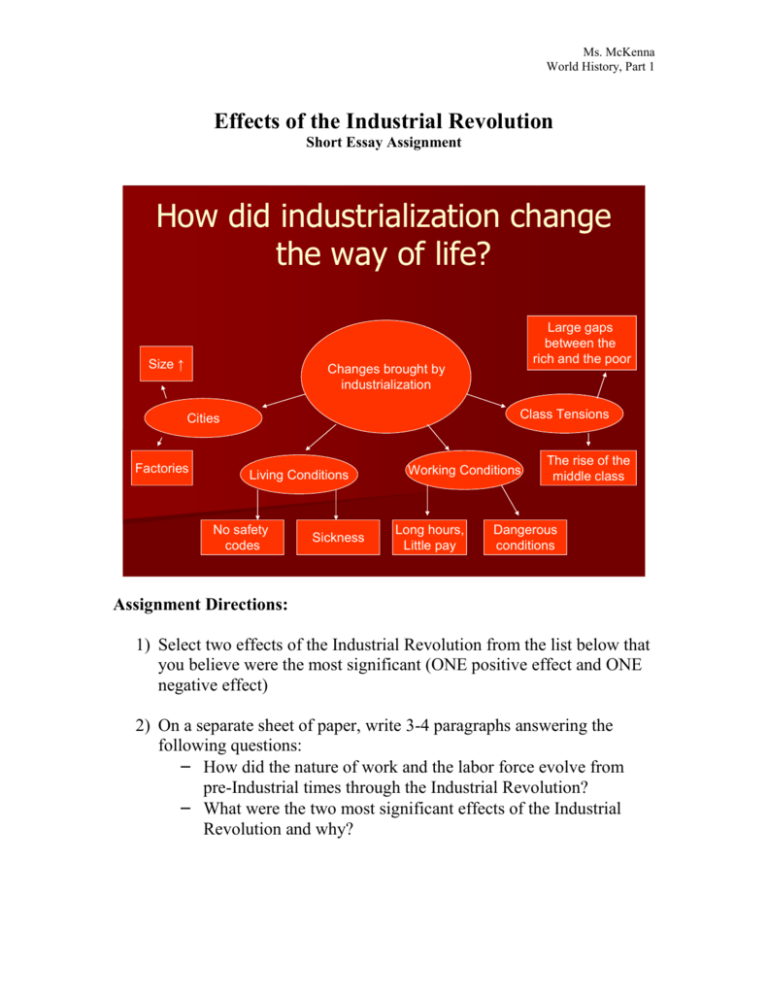
Ms. McKenna World History, Part 1 Effects of the Industrial Revolution Short Essay Assignment How did industrialization change the way of life? Size ↑ Large gaps between the rich and the poor Changes brought by industrialization Class Tensions Cities Factories Living Conditions No safety codes Sickness Working Conditions Long hours, Little pay The rise of the middle class Dangerous conditions Assignment Directions: 1) Select two effects of the Industrial Revolution from the list below that you believe were the most significant (ONE positive effect and ONE negative effect) 2) On a separate sheet of paper, write 3-4 paragraphs answering the following questions: – How did the nature of work and the labor force evolve from pre-Industrial times through the Industrial Revolution? – What were the two most significant effects of the Industrial Revolution and why? Ms. McKenna World History, Part 1 Positive Effects Increased world productivity Growth of railroads (faster and more efficient transportation of goods and people) New entrepreneurs emerged (more money = more technology/inventions) New inventions improved quality of life for many Labor eventually organized (unions) to improve working conditions Laws were enacted to enforce health and safety codes in cities and factories New opportunities for women Rise of the middle class – size, power, and wealth expanded Social structure becomes more flexible Negative Effects Child labor used in factories & mines Miserable (dirty, cramped) and dangerous (fingers, limbs, & lives lost) working conditions Monotonous work with heavy, noisy, repetitive machinery Long working hours – six days a week, with little pay Rigid schedules ruled each day Gas, candle & oil lamps created soot and smoke in factories Diseases such as pneumonia & tuberculosis spread through factories Labor unrest leads to demonstrations (sometimes violent) Strikes take place Women were paid less than men (were actually preferred) Indentured workers Employers had a more impersonal relationship with employees Tenement housing was poorly constructed, crowded, and cold Human and industrial waste contaminated water supplies – typhoid and cholera spread Air pollution increased over cities and industrial areas Technological changes eroded the balance of power in Europe Contributed to the growth of imperialism and communism (Marx’s & Engels’ theories) Produced weaponry that gave Western nations a military advantage over developing nations Not Necessarily Good or Bad The location of work places changed as more goods were produced away from the home environment (towns/factories) Educational systems emphasized more science, technology, and business A global economy began to emerge (growth of worldwide trade)