8.5 Environmental Chemistry
advertisement

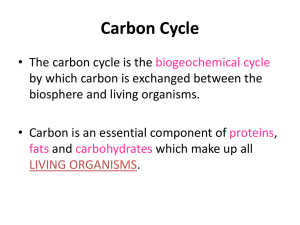
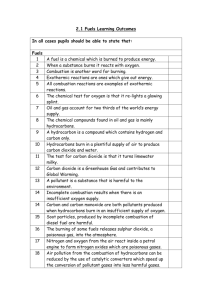
8.5 Environmental Chemistry 8.5.1 Fossil fuels Fossil fuels are formed by the action of heat and pressure on the remains of plants and animals (on land or on the sea bed) over millions of years. The remains were buried in sediments which excluded the air (kept out oxygen) and stopped them decaying. More sediment buried the remains deeper and deeper until pressure and heat eventually turned them into coal, oil and natural gas. Complete combustion of fuels Hydrocarbons are mainly used as fuels. The burning of a substance in air is called combustion. In chemistry, combustion (or burning) means reacting with oxygen. The main products of the combustion of hydrocarbons are carbon dioxide, water and heat. The reaction is exothermic (gives out heat energy). The following experiment can be used to confirm the products of complete combustion of a hydrocarbon. During the combustion of a candle (which contains hydrocarbons) the thermometer increases in temperature showing the reaction is exothermic, Water (which turns blue cobalt chloride paper pink, and white anhydrous copper sulphate blue) condenses in the U-tube, while the limewater turns cloudy indicating the presence of carbon dioxide. In general for complete combustion: hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water TOPIC 8.5 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY 1 We are currently adding over 60 million tonnes of carbon dioxide EVERY DAY to the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is not poisonous, and is naturally present in the atmosphere, however, millions of tonnes of carbon dioxide going constantly into the atmosphere is causing global warming, resulting in climate change all over the planet. Carbon dioxide is called a greenhouse gas. It is causing the global temperature of the Earth to rise. This rise in temperature affects the climate all over the planet in ways which are hard to predict. Some areas may become wetter or dryer, other areas may become hotter. The main (predictable) directions of wind and ocean currents on the planet may slow down, speed up, or change direction. This could have catastrophic consequences for life on planet Earth including rising sea levels because of ice melting at the poles and more extreme weather because of more convection in the hotter wetter atmosphere. Incomplete combustion Incomplete combustion occurs when the supply of air or oxygen is poor. Water is still produced, but carbon monoxide and carbon are produced instead of carbon dioxide. In general for incomplete combustion: hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon monoxide + carbon + water TOPIC 8.5 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY 2 Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas, which is one reason why complete combustion is preferred to incomplete combustion. Gas fires and boilers must be serviced regularly to ensure they do not produce carbon monoxide. The carbon is released as soot. These particles (sometimes called particulates) contain mainly carbon atoms and come from unburnt hydrocarbons. The particles are a pollutant and health hazard which cause breathing problems for people who suffer from asthma. In addition these particles have two effects on the temperature of the environment. High up in the atmosphere they absorb some of the energy from the Sun and prevent it from reaching the Earth's surface. This is called global dimming and has a cooling effect on the climate. Scientists have evidence that particles in the atmosphere have this effect. Big volcanoes erupting in the past have put a lot of particles high up into the atmosphere and have had a global cooling effect. The particles also cause an increase in the rate at which water vapour in the atmosphere condenses to form clouds. Clouds reflect some of the Sun's energy back into space. An increase in the rate of cloud formation also has a cooling effect. The cooling effect from particles in the atmosphere is, however, small compared to the effect of global warming from burning fossil fuels. Petrol and diesel engines also produce poisonous carbon monoxide and release unburnt hydrocarbons. All of this pollution is produced at ground level, mainly in cities where road vehicles gather. The obvious solution is to fit road vehicles with electric motors rather than petrol or diesel engines. One day this will happen. In the meantime, exhausts are fitted with catalytic converters in an attempt to minimise road vehicle pollution. TOPIC 8.5 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY 3 8.5.2 Air Pollution Combustion of fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas) releases the energy which has been stored up in the plant and animal remains for millions of years. Fossil fuels are a finite resource (there are only a certain amount of them). Fossil fuels are a non-renewable energy source. Once used, they are gone. We would have to wait for millions of years for nature to replace our coal, oil and natural gas reserves Fossil fuels are burnt on a huge scale to generate electricity. Coal (and to a lesser degree Oil and Natural Gas) contain sulphur impurities. When they are burned in a power station the sulphur oxidises (reacts with oxygen) to form sulphur dioxide gas. sulphur + oxygen sulphur dioxide Sulphur dioxide gas is acidic, poisonous, and smells like burnt matches. Sulphur dioxide can be removed from the burnt waste gases (called flue gases) in the power station chimney by wet scrubbing. If sulphur dioxide gets into the atmosphere it reacts with water and oxygen in the air to form a dilute solution of sulphuric acid. This sulphuric acid is the main pollutant in acid rain. Natural rain is slightly acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide. Natural rain has a pH of about 6, acid rain has a pH of 4 or even less. Acid rain can kill trees and aquatic life. It runs into rivers and gathers in lakes. Eventually, lakes become too acidic, and plants and fish begin to die. Acid rain reacts with limestone and damages limestone buildings. Look at the statue below before and after acid rain damaged it. TOPIC 8.5 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY 4 Powdered limestone or slaked lime can be added to soils or lakes to make them less acidic. It would be better if we could avoid or reduce pollutant gas emissions in the first place. Another important pollutant in acid rain is nitric acid. High temperature combustion (in petrol and diesel engines used in cars and lorries) produces toxic gases in addition to carbon dioxide. At around 1000oC nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen producing oxides of nitrogen. nitrogen + oxygen nitrogen monoxide As well as being poisonous, nitrogen monoxide is a greenhouse gas. It reacts with oxygen in the air to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2). NO and NO2 together are called NOx. It also reacts with water and oxygen in the air to form dilute nitric acid. This acid dissolves in clouds and contributes to acid rain. 8.5.3 Renewable fuels Renewable alternatives to fossil fuels to generate electricity include Bio-Fuel Plantations (bio-ethanol and bio-diesel) Geothermal Power Fuel Cells Hydroelectric Power Solar Cells Wind Turbines Tidal Power. These energy sources are called renewable because they don't run out. They can often produce cheaper electricity than burning fossil fuels, and they are nonpolluting. Not all of these energy sources are suited to all parts of the planet, but in the absence of non-polluting energy yet to be discovered, they are the power sources of the future. TOPIC 8.5 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY 5 TOPIC SUMMARY Fossil fuels are formed from buried plant and animal remains which have been subjected to intense heat and _________ for millions of years. Hydrocarbons are compounds consisting only of the elements __________ and _________. When they are burned in air ( a process called ___________ ) the main products are __________ _________ and water; much ________ is also given off. If the supply of oxygen is limited, ____________ combustion occurs, the products of which are __________ _________ ( a ____________ gas ) and carbon can also be produced. These carbon particles can cause many problems: they are a pollutant which may cause breathing problems for individuals suffering from _________; higher in the atmosphere, they are able to _________ and deflect energy from the sun ( a phenomenon known as global _____________ ) which has the effect of cooling the earth. The particles also speed up the rate of cloud ______________ which also has a cooling effect upon the planet’s surface. Carbon dioxide is a ______________ gas which contributes to the overall increase in the earth’s average temperature ( a phenomenon known as __________ warming ). Fossil fuels ( coal, oil and __________ ______ ) provide us with much of our energy requirements, but they are _____________________ - we are using them faster than they can be created naturally. When coal is burned, sulphur impurities are oxidised to form __________ ___________. This gas reacts with water and oxygen in the atmosphere to form a dilute solution of ______________ acid, the main component of acid rain. TOPIC 8.5 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY 6 High temperature combustion in vehicle engines produces oxides of ___________ , which are another major contributor to acid rain. Alternatives to fossil fuels, such as ______________, __________ ________ and _________ ____________ provide a cleaner, renewable resource which will become ever more crucial as fossil fuels run out. incomplete biofuels carbon asthma heat greenhouse nitrogen natural gas carbon monoxide combustion absorb dimming hydrogen sulphur dioxide global sulphuric non-renewable solar cells pressure formation wind turbines carbon dioxide toxic TOPIC 8.5 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY 7