Light & Atomic Spectra, Planck`s Constant
advertisement
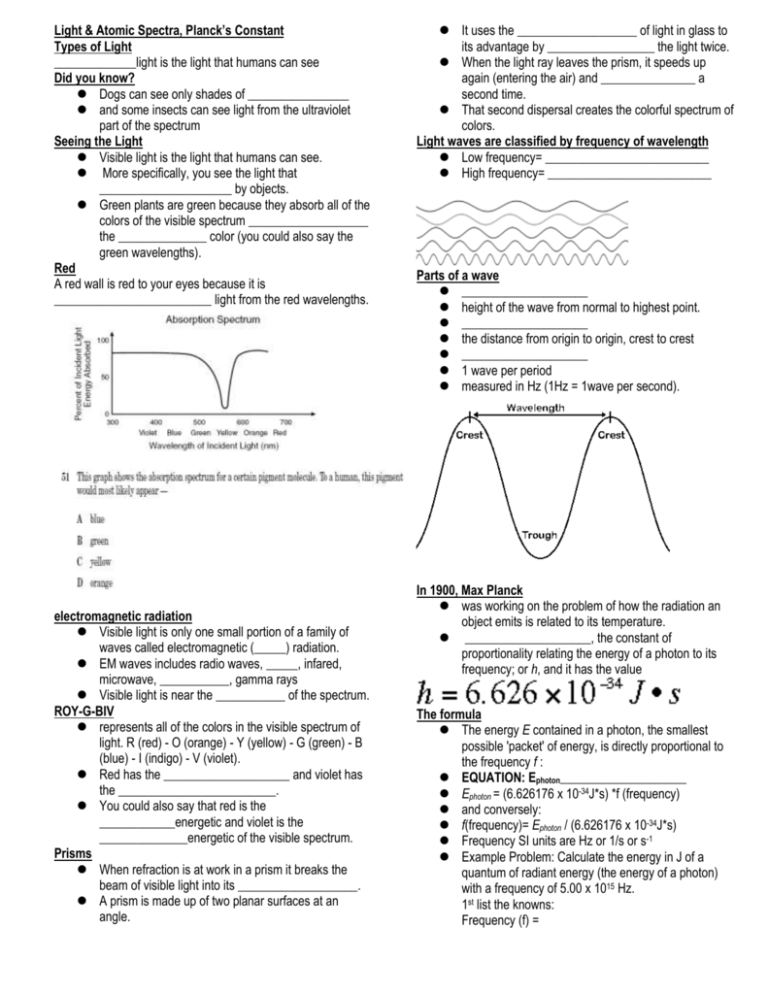
Light & Atomic Spectra, Planck’s Constant Types of Light _____________light is the light that humans can see Did you know? Dogs can see only shades of ________________ and some insects can see light from the ultraviolet part of the spectrum Seeing the Light Visible light is the light that humans can see. More specifically, you see the light that _____________________ by objects. Green plants are green because they absorb all of the colors of the visible spectrum ___________________ the ______________ color (you could also say the green wavelengths). Red A red wall is red to your eyes because it is _________________________ light from the red wavelengths. electromagnetic radiation Visible light is only one small portion of a family of waves called electromagnetic (_____) radiation. EM waves includes radio waves, _____, infared, microwave, ___________, gamma rays Visible light is near the ___________ of the spectrum. ROY-G-BIV represents all of the colors in the visible spectrum of light. R (red) - O (orange) - Y (yellow) - G (green) - B (blue) - I (indigo) - V (violet). Red has the ____________________ and violet has the _________________________. You could also say that red is the ____________energetic and violet is the ______________energetic of the visible spectrum. Prisms When refraction is at work in a prism it breaks the beam of visible light into its ___________________. A prism is made up of two planar surfaces at an angle. It uses the ___________________ of light in glass to its advantage by _________________ the light twice. When the light ray leaves the prism, it speeds up again (entering the air) and _______________ a second time. That second dispersal creates the colorful spectrum of colors. Light waves are classified by frequency of wavelength Low frequency= __________________________ High frequency= __________________________ Parts of a wave ____________________ height of the wave from normal to highest point. ____________________ the distance from origin to origin, crest to crest ____________________ 1 wave per period measured in Hz (1Hz = 1wave per second). In 1900, Max Planck was working on the problem of how the radiation an object emits is related to its temperature. ____________________, the constant of proportionality relating the energy of a photon to its frequency; or h, and it has the value The formula The energy E contained in a photon, the smallest possible 'packet' of energy, is directly proportional to the frequency f : EQUATION: Ephoton____________________ Ephoton = (6.626176 x 10-34J*s) *f (frequency) and conversely: f(frequency)= Ephoton / (6.626176 x 10-34J*s) Frequency SI units are Hz or 1/s or s-1 Example Problem: Calculate the energy in J of a quantum of radiant energy (the energy of a photon) with a frequency of 5.00 x 1015 Hz. 1st list the knowns: Frequency (f) = h= 6.626 x 10-34 J*s (Planck’s constant) Unknown: E Solve for the unknown: E= h x f E= E= What is the energy of a photon of microwave radiation with a frequency of 3.20 x 10-11 Hz? What is the energy of a photon of green light with a frequency of 5.80 x 1014 Hz? Einstein Based on Planck's work, Einstein proposed that light also delivers its energy in chunks; light would then consist of little particles, or quanta, called ____________________, each with an energy of Planck's constant times its frequency. c=λf c=speed of light = 3.0 x 108 m/s λ= wavelength (make sure it is in meters (m) so the units will match) f=frequency in Hz Calculate the wavelength of the yellow light emitted by a sodium lamp if the frequency of the radiation is 5.10 x 1014 Hz List the knowns: Frequency (f) = c=speed of light = Unknown: λ in m λ=c/f λ= = What is the wavelength of radiation with a frequency of 1.50 x 1013 Hz What frequency is radiation with a wavelength of 5.00 x 10-6 cm? It's all Energy The quantum theory says light consists of very small bundles of energy/particles called ____________________. ____________________ determines: energy & type of EM radiation ____________________: states how much radiation is present Photons determine how bright the light is…. Lots of photons give a ____________________, more intense type of light. Fewer photons give a ____________________and less intense light. Think of a dimmer switch When you use the dimmer switch on the wall, you are decreasing the number of photons sent from the light bulb. The type of light is the same while the amount has changed. Flame Test Lab Flame tests are used to identify the presence of a relatively small number of ____________________in a compound. Flame colors are produced from the movement of the ____________________ in the metal ions present in the compounds. So in the flame, electrons get ____________________and pushed to ____________________levels When they fall back down, they give off ____________________ of light of different ____________________, based upon how far they fall. For example, a sodium (na) ion in an unexcited state has the structure 1s22s22p6. When heated: electrons gain energy and jump into any of the empty orbitals at higher levels – for example, into the 7s or 6p or 4d, depending on how much energy is ____________________ from the flame. Because the electrons are now at a higher and more energetically ____________________, they tend to fall back down to where they were before It might fall straight back or jump through many levels… Each of these jumps involves a specific amount of energy being released as light energy, and each corresponds to a particular ____________________. Whatever color is produced, tells you what ____________________. This is a great way to determine an unknown substance…