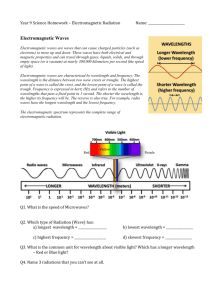
Waves & Particles Worksheet: Frequency, Quantum Theory, EM Spectrum
advertisement

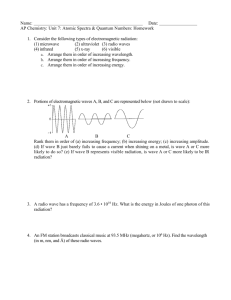
Name Period Date #3 UNIT 4: Waves & Particles (p. 91 – 94 in class MC, 97 – 101 at home in blue MC book) 1. In the diagrams below, which wave has the higher frequency? Explain. In the second diagram we see a higher frequency of radiation: there are more waves in that pass the same given point. We also know that the shorter the wavelength is the higher the frequency of the radiation as well. 2. Briefly describe what Planck and Einstein contributed to the concept of Quantum Theory. Max Planck was studying the emission of light by hot objects. He believed that the hot objects did not emit energy continuously, as would be expected if it were in the form of waves. Instead he suggested that the object emits the energy in small, specific amounts called quanta. A quantum is the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. He proposed the following relationship between a quantum of energy and the frequency of the radiation: E = h. E represents the energy in joules of a quantum of radiation, is the frequency of the radiation emitted, and h is a constant known as Planck’s constant. Albert Einstein introduced the idea that electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave-particle nature. Example: white light exhibits many wavelike particles, it can also be thought of as a stream of particles. Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. He called these particles photons. A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero rest mass and carrying a quantum of energy. 3. One of the lines in the emission spectrum of sodium has a wavelength of 5.90 x 1011 m. What is the frequency of this line? frequency () = speed of light (c)/Wavelength() = (3.00 x 108m/s)/ (5.90 x 1011 m) = 5.08 x 10-4 Hz 4. A radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 91.3 MHz (9.13 107 Hz). What is the wavelength of this EM wave? Wavelength() = speed of light (c)/ frequency () x = (3.00 x 108m/s)/ (9.13 107 Hz) x = 3.29 Hz 5. Calculate the energy of a gamma ray photon with a frequency of 6.0 1022 Hz. Energy (E) = Plank’s constant (h) x frequency () = (6.626 x 10-34 Js) x (6.0 1022 s-1) = 3.98 x 10-11 J 6. Order the following regions of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum from lowest to highest energy: infrared, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible red, visible green, X-rays. Low E microwaves, infrared, visible red, visible green, ultraviolet, X-rays High E Waves & Particles – Ch. 4 C. Johannesson